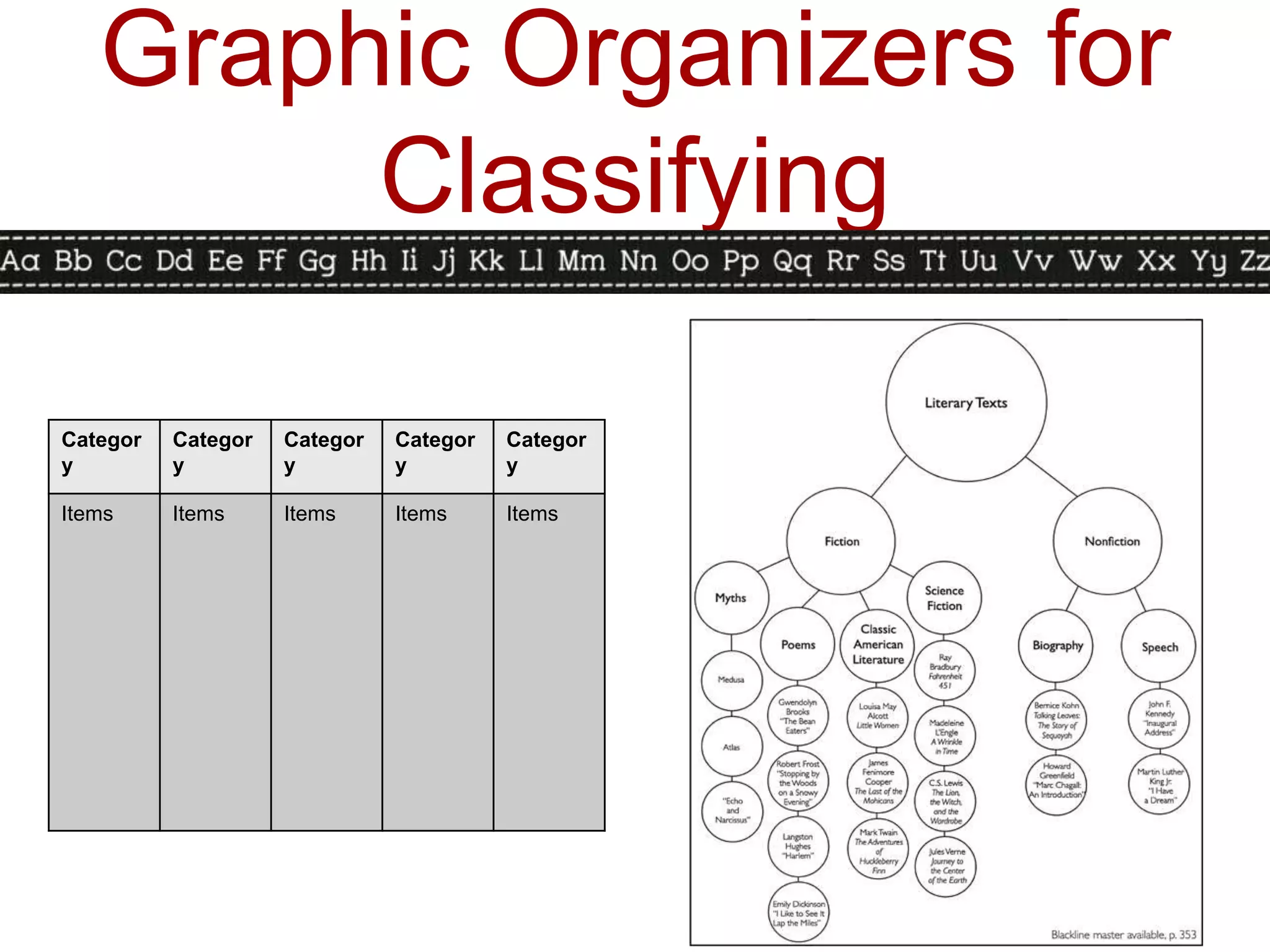
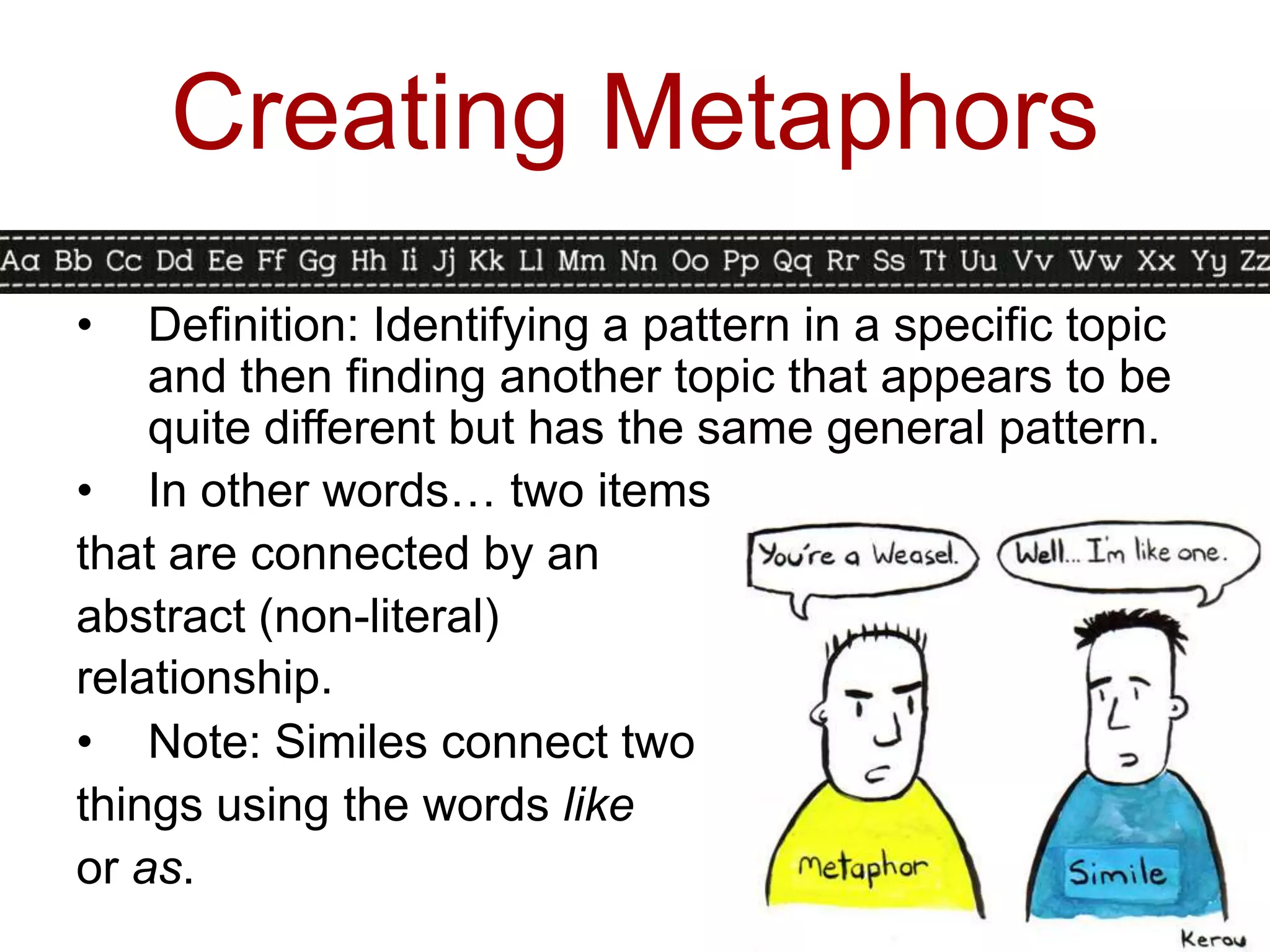
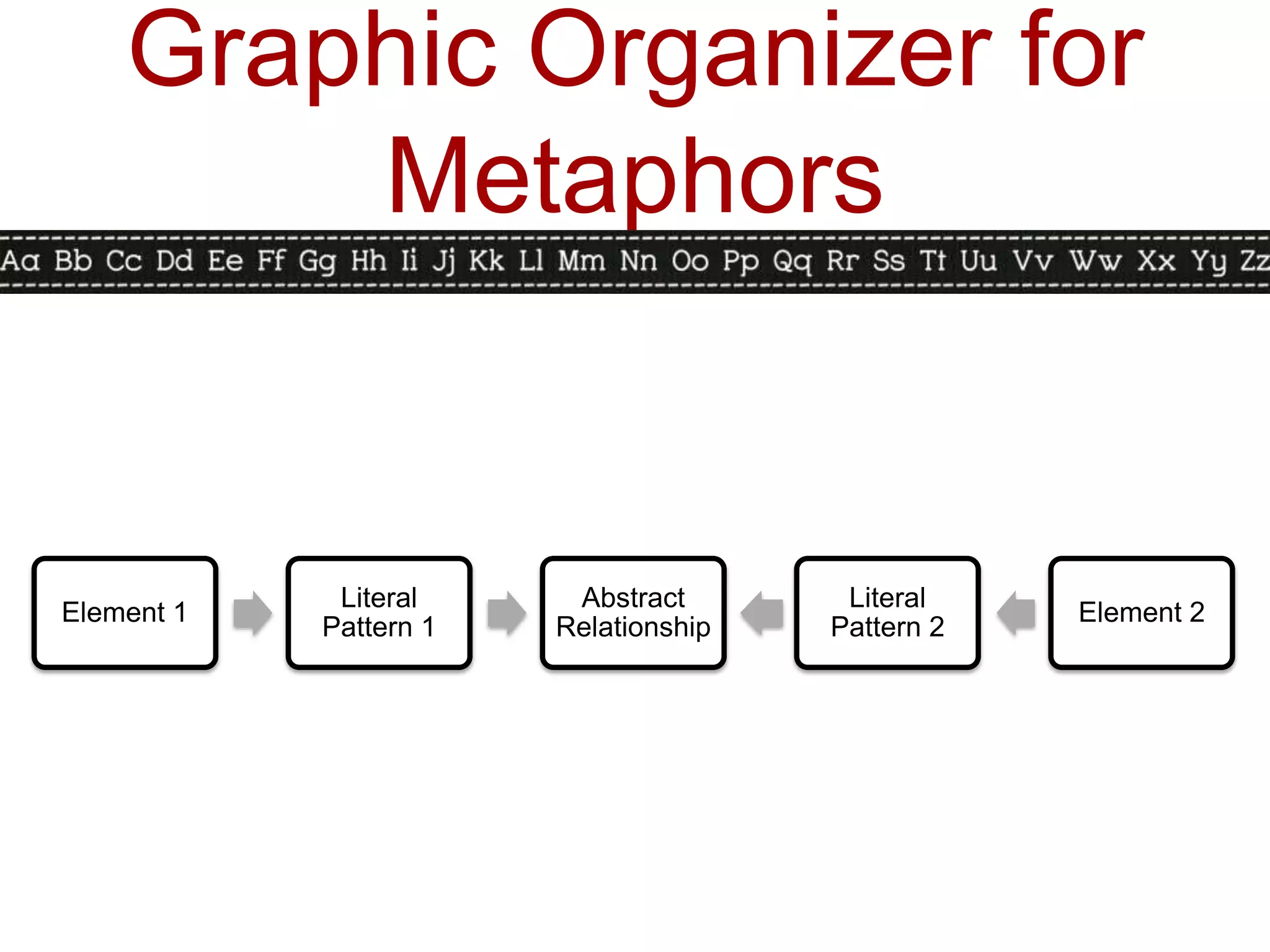
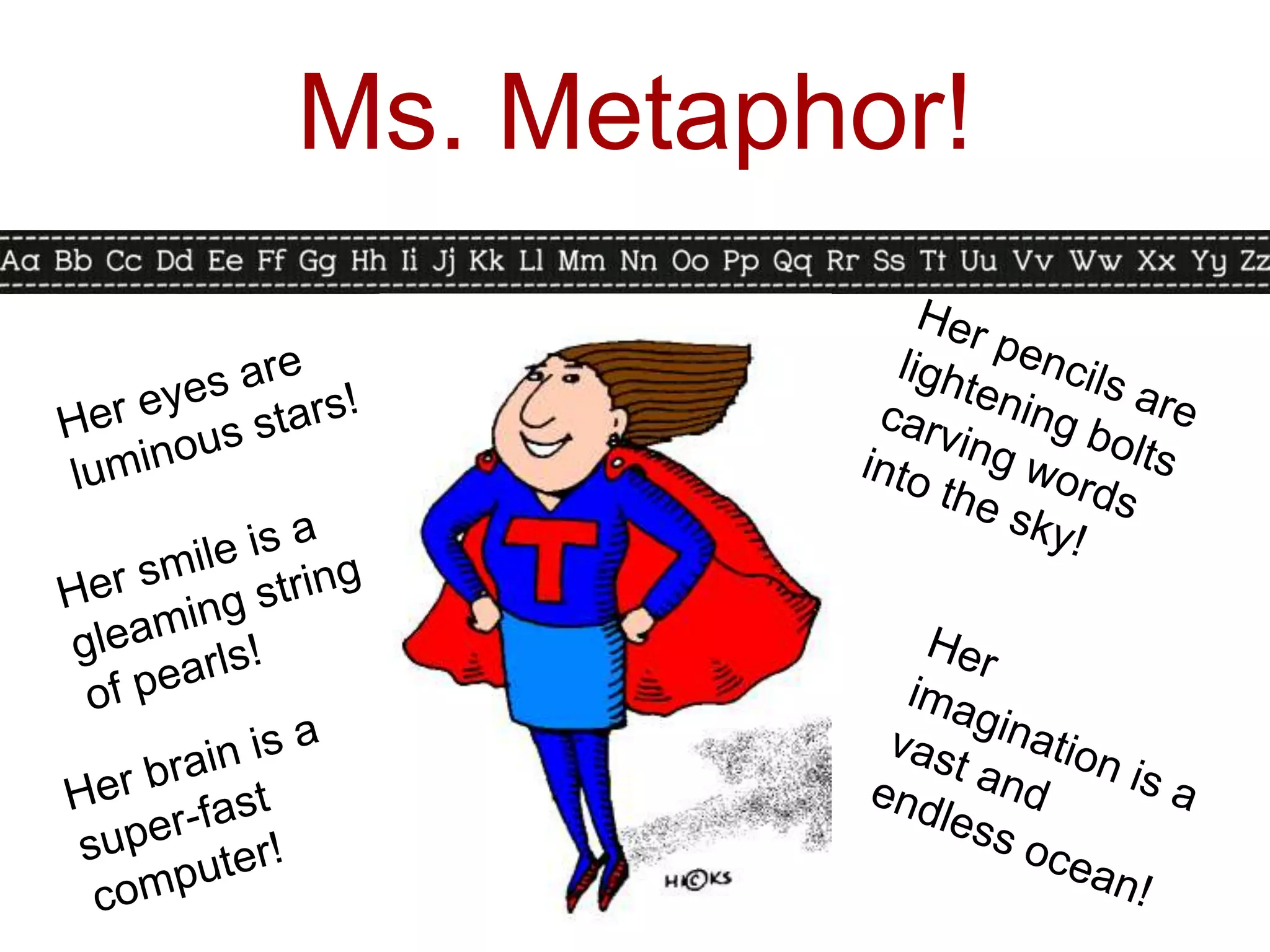
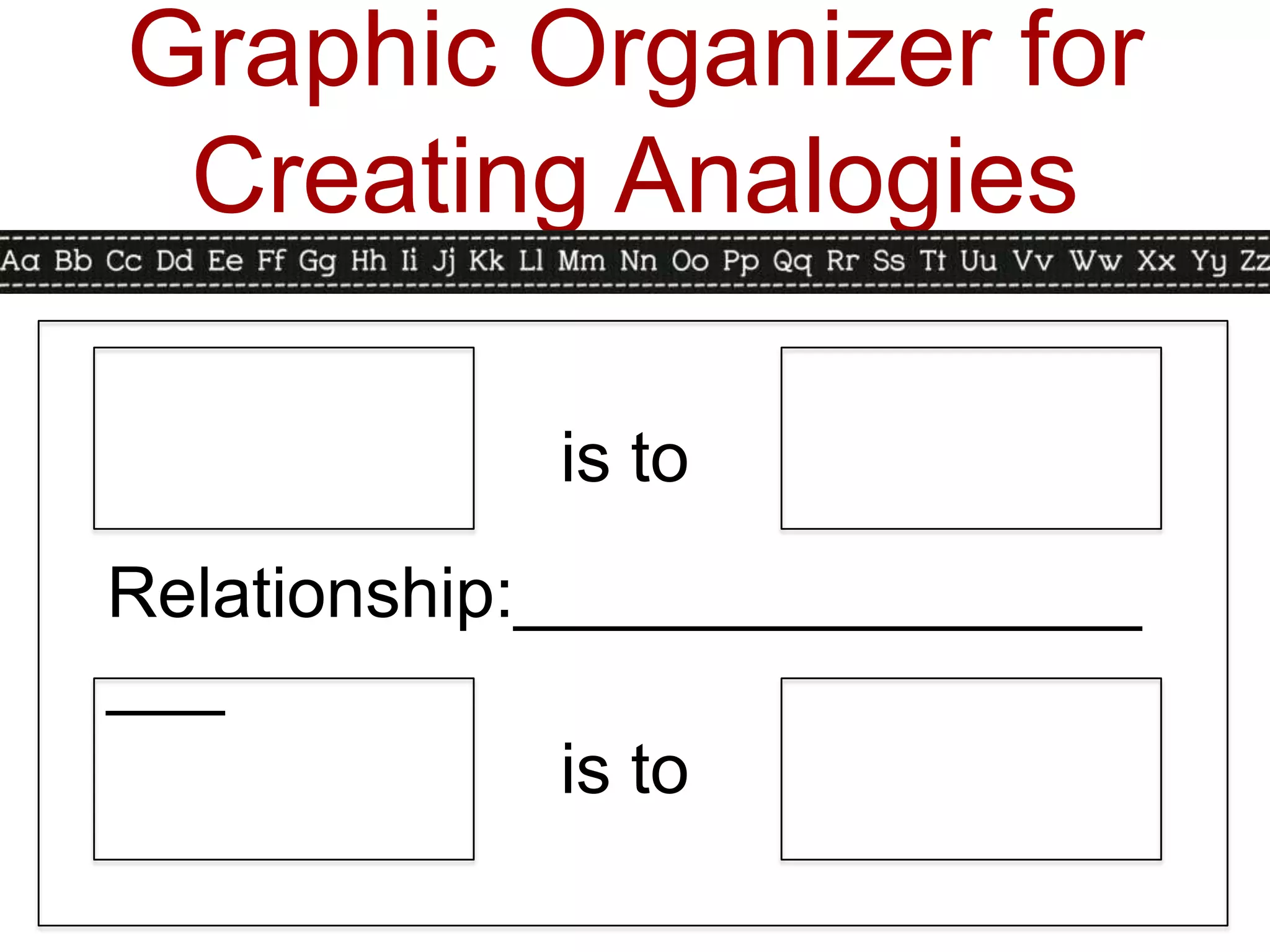
This document discusses identifying similarities and differences, which is a higher-order thinking skill. It explores comparing, classifying, creating metaphors, and creating analogies. Specific steps and graphic organizers are provided for each technique to help students identify patterns and make connections between concepts. Examples and activities are included to demonstrate how to teach these skills in a structured way beginning with teacher-directed instruction and progressing to more student-directed approaches.