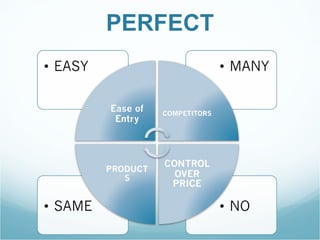
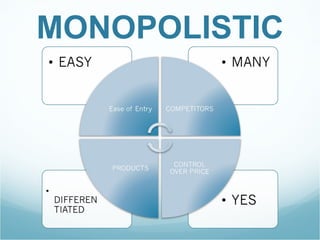
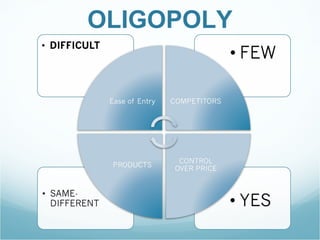
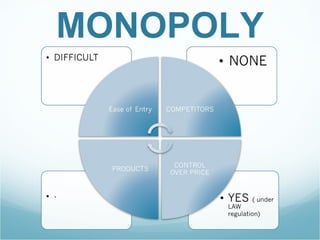
The document discusses the market structures of competition, specifically focusing on Wal-Mart as a case study. It categorizes Wal-Mart primarily as a monopolistic competitor, yet suggests it also exhibits characteristics of an oligopoly due to its dominance in the general merchandise retailing industry. The document highlights how Wal-Mart's pricing strategies and supplier dynamics affect demand and supply within the market.