1) The document discusses different market structures including perfect competition and monopoly.
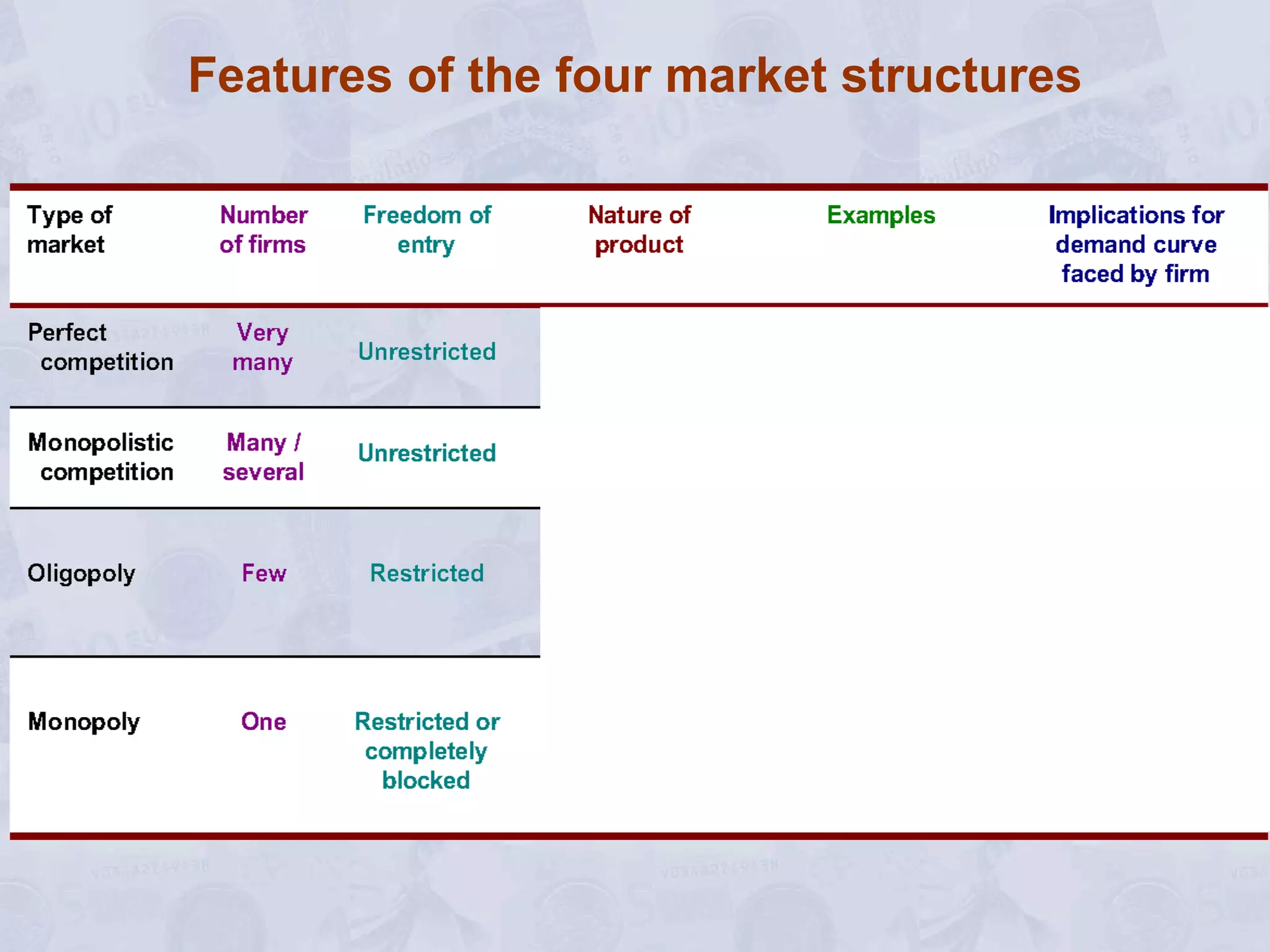
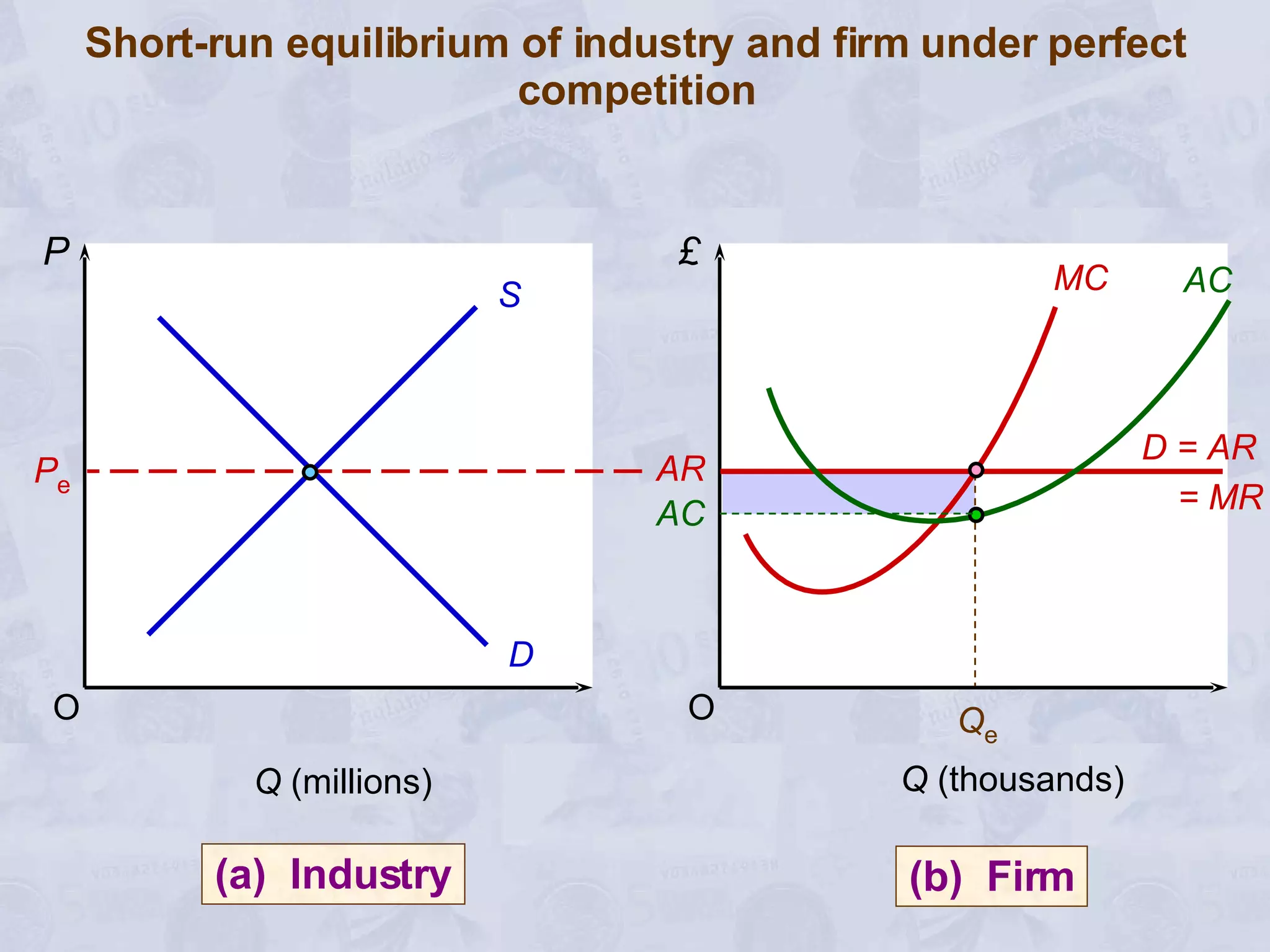
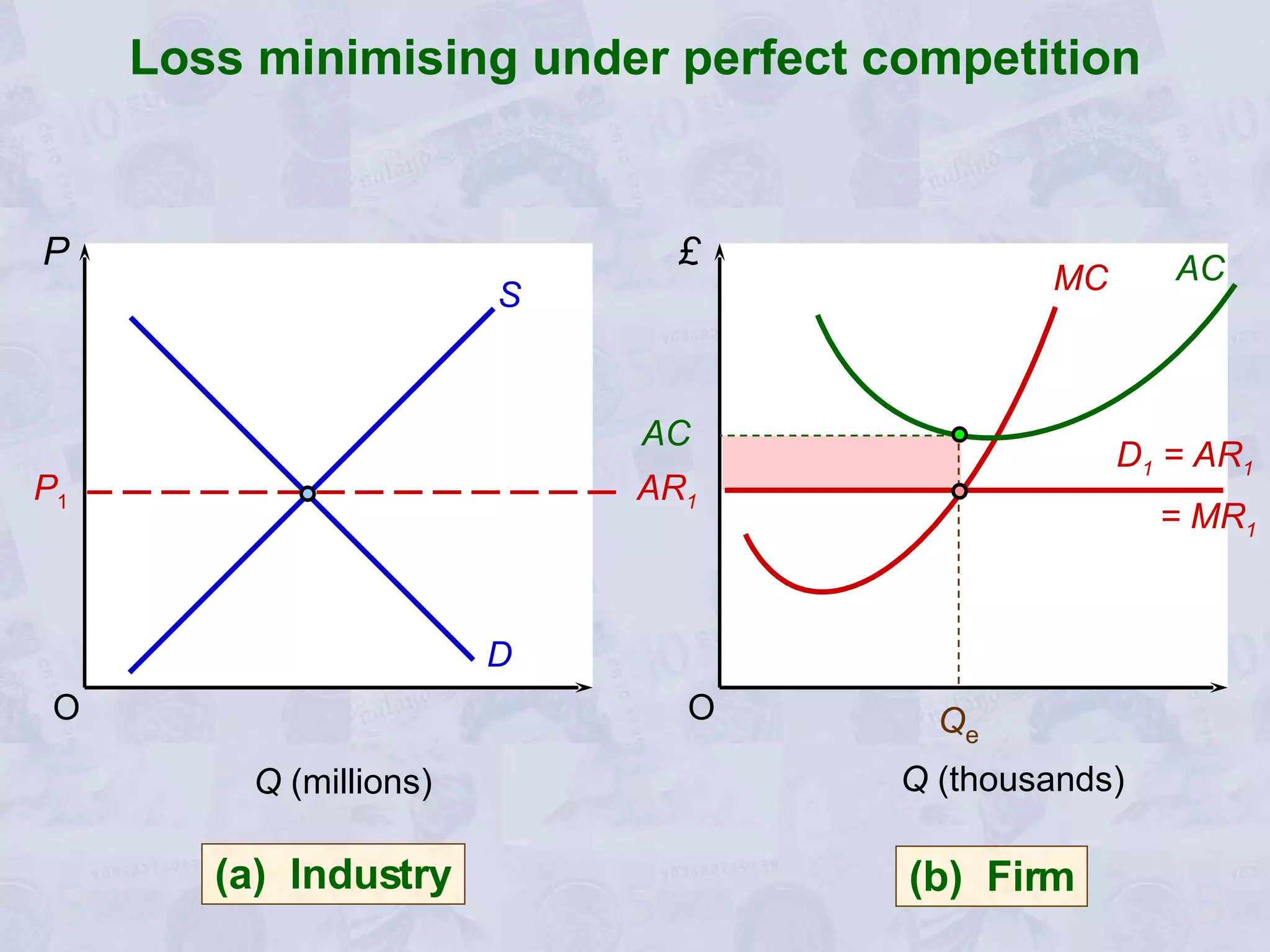
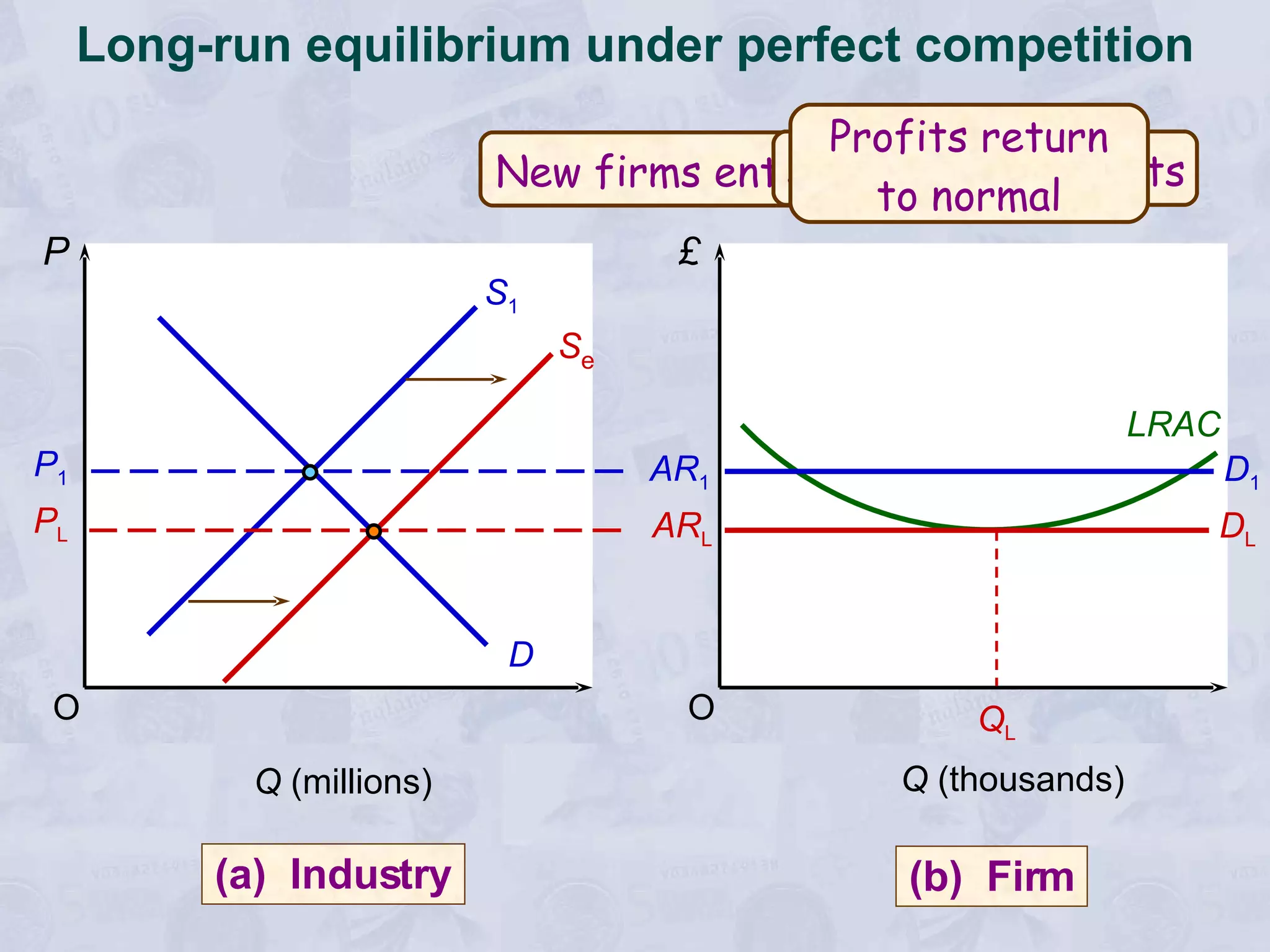
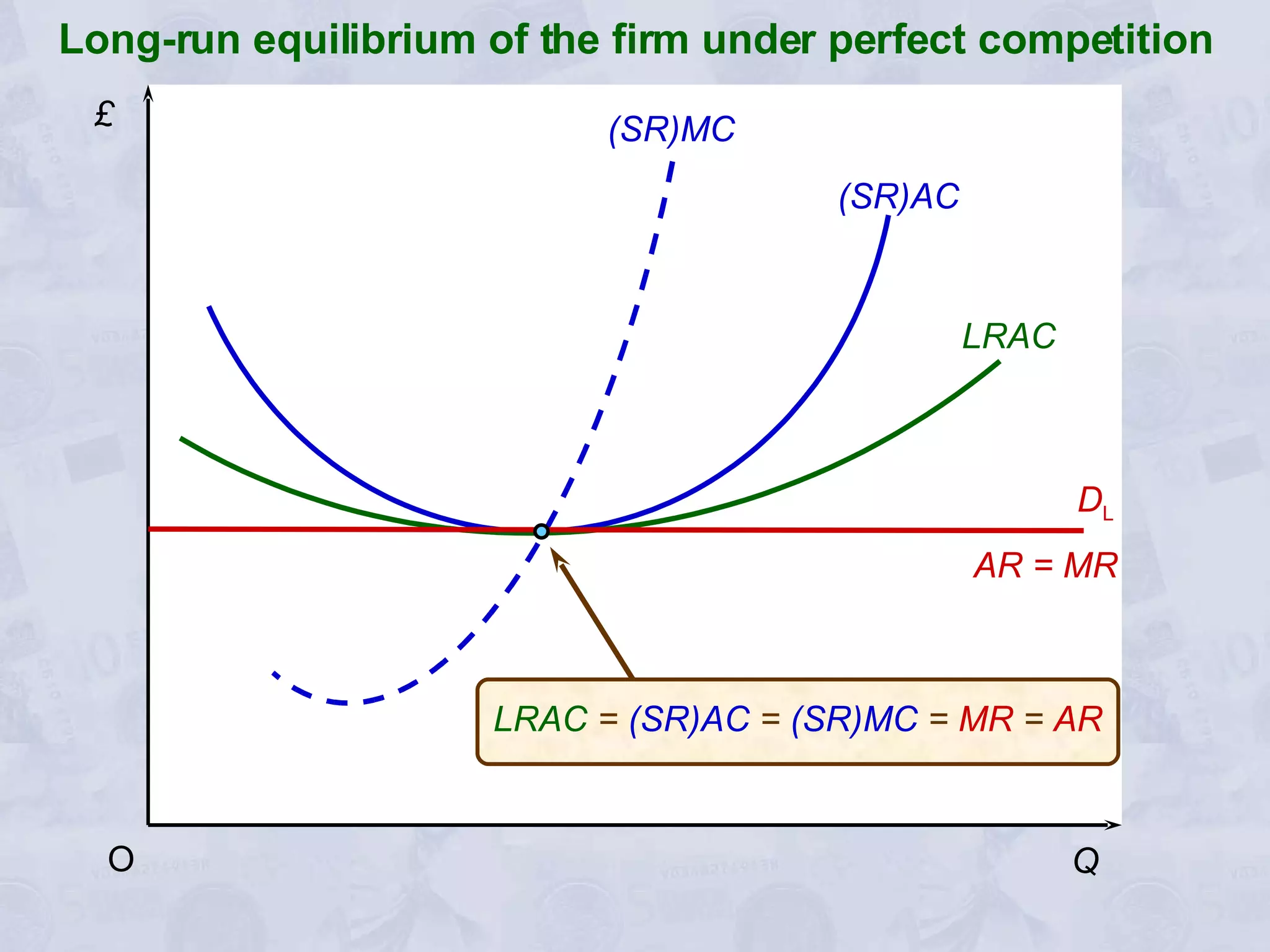
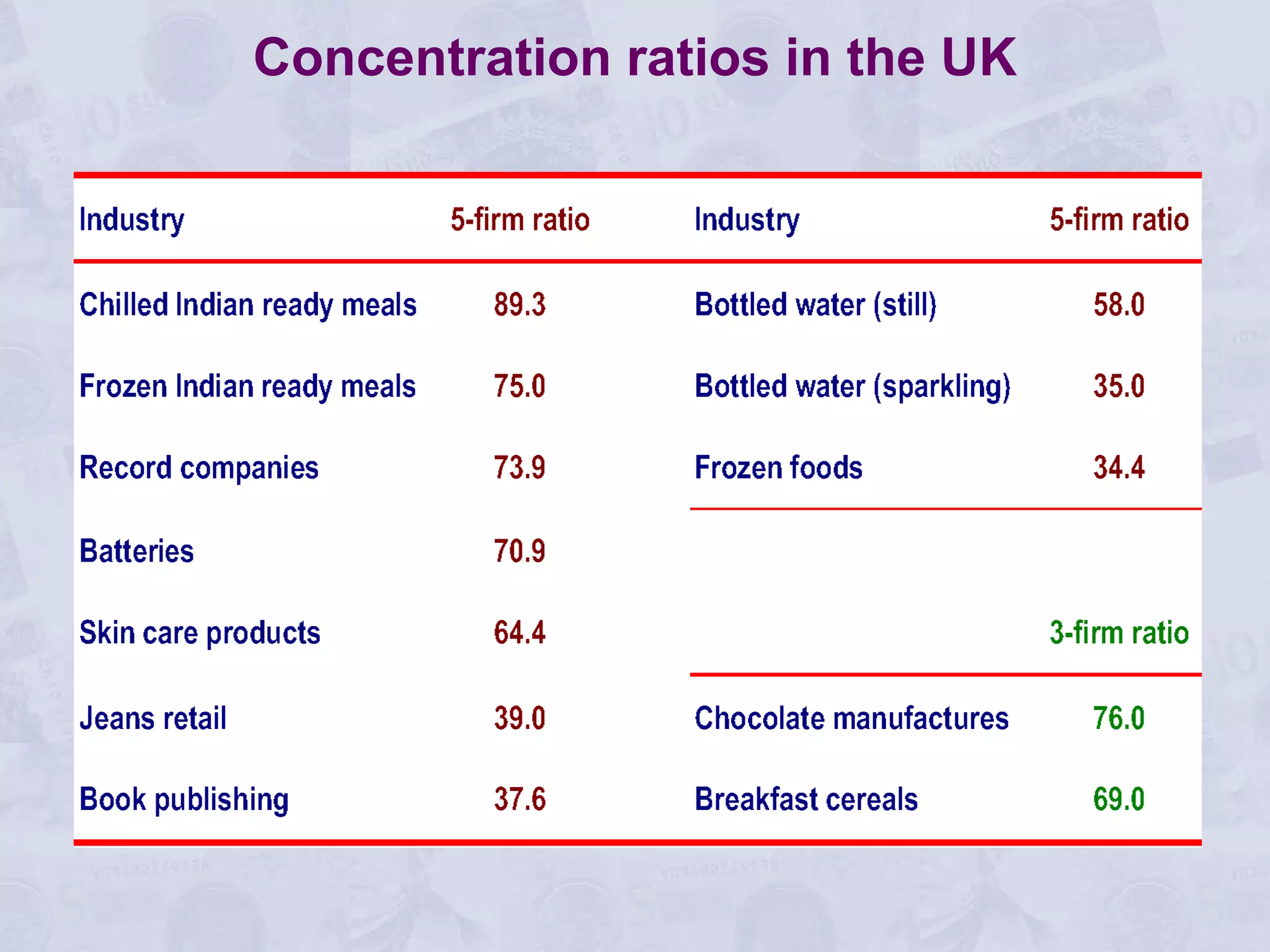
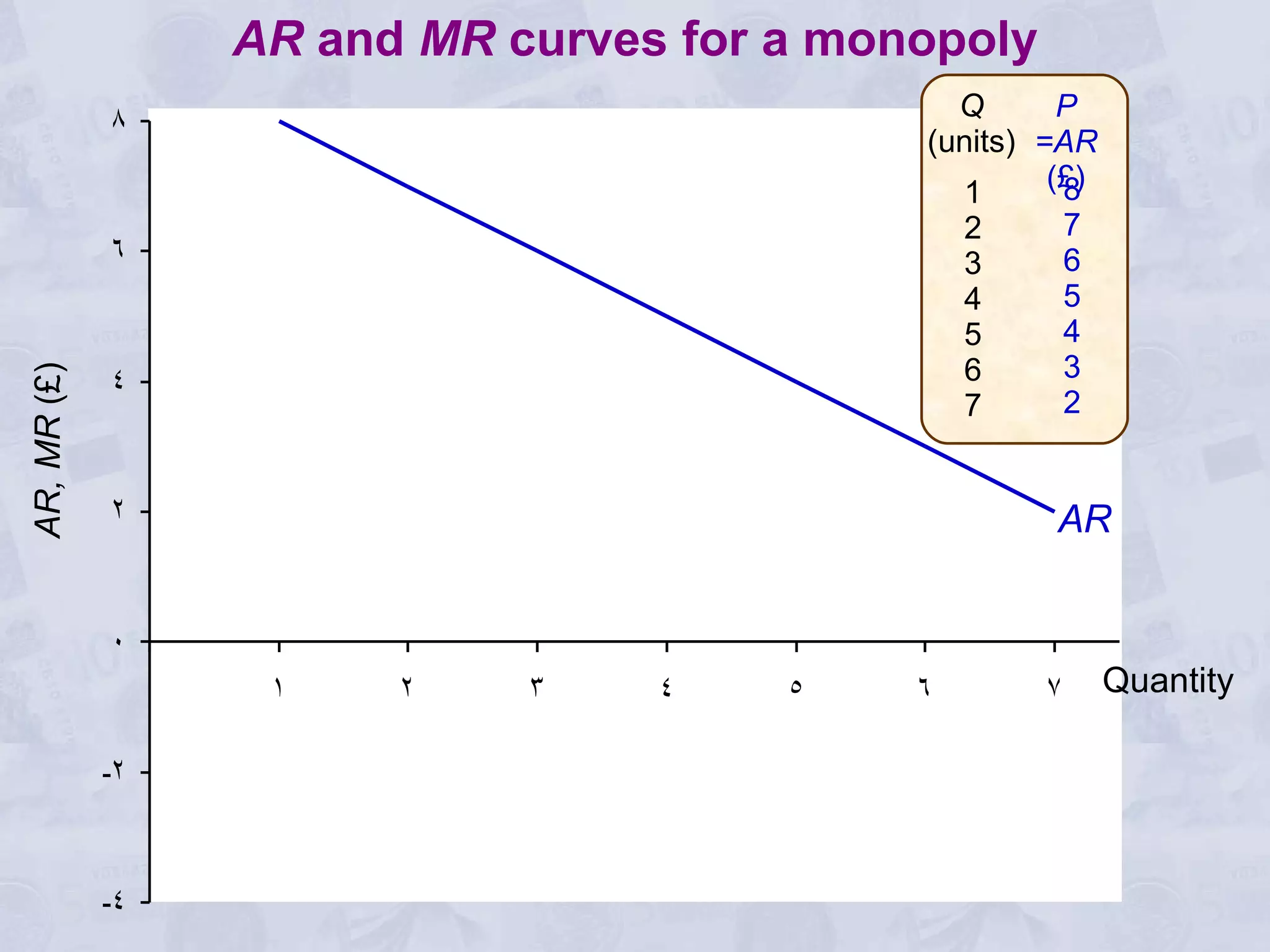
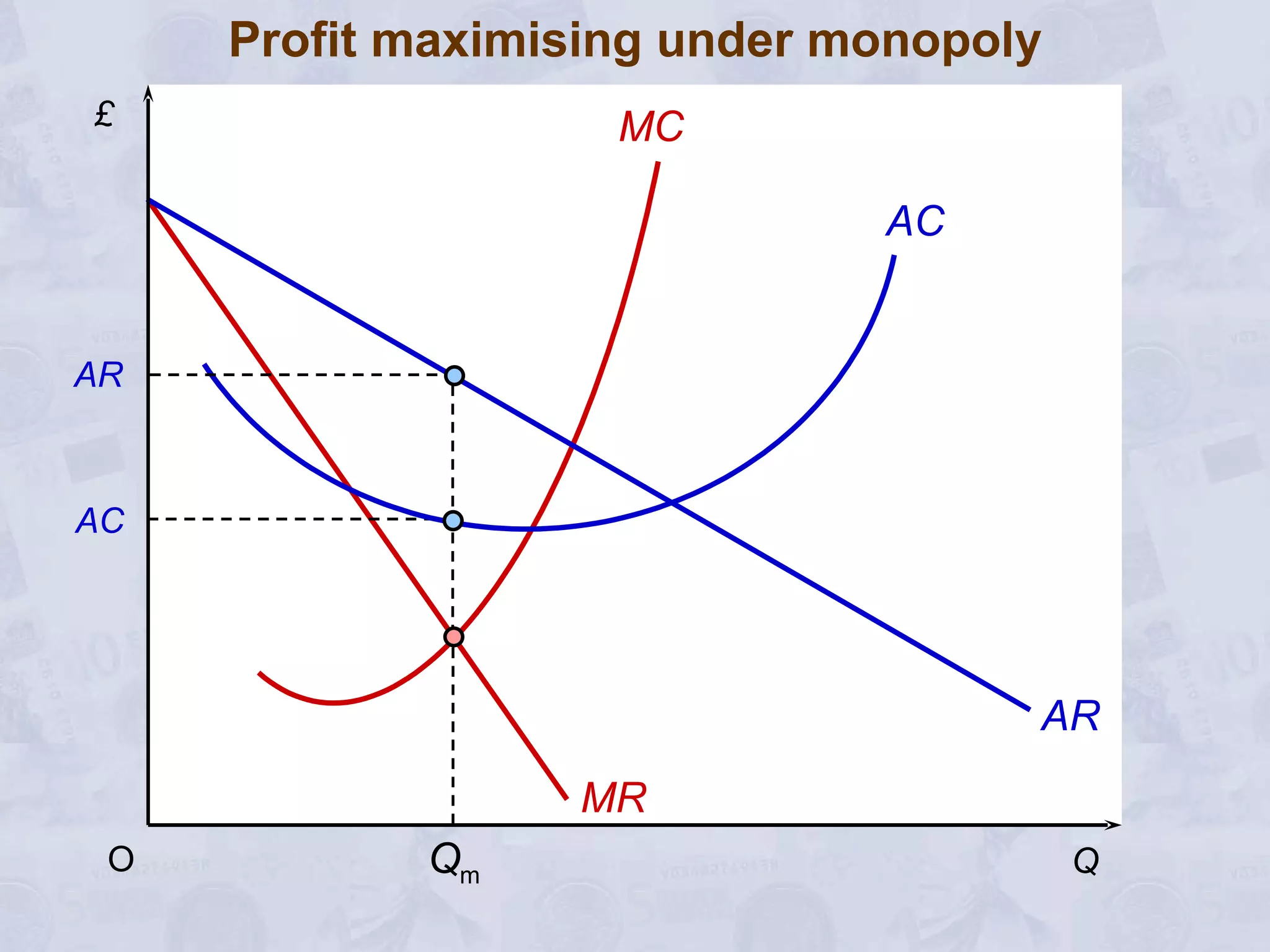
2) Under perfect competition, firms are price takers and can only earn normal profits in the long run. A monopoly has market power to set prices and can earn supernormal profits.
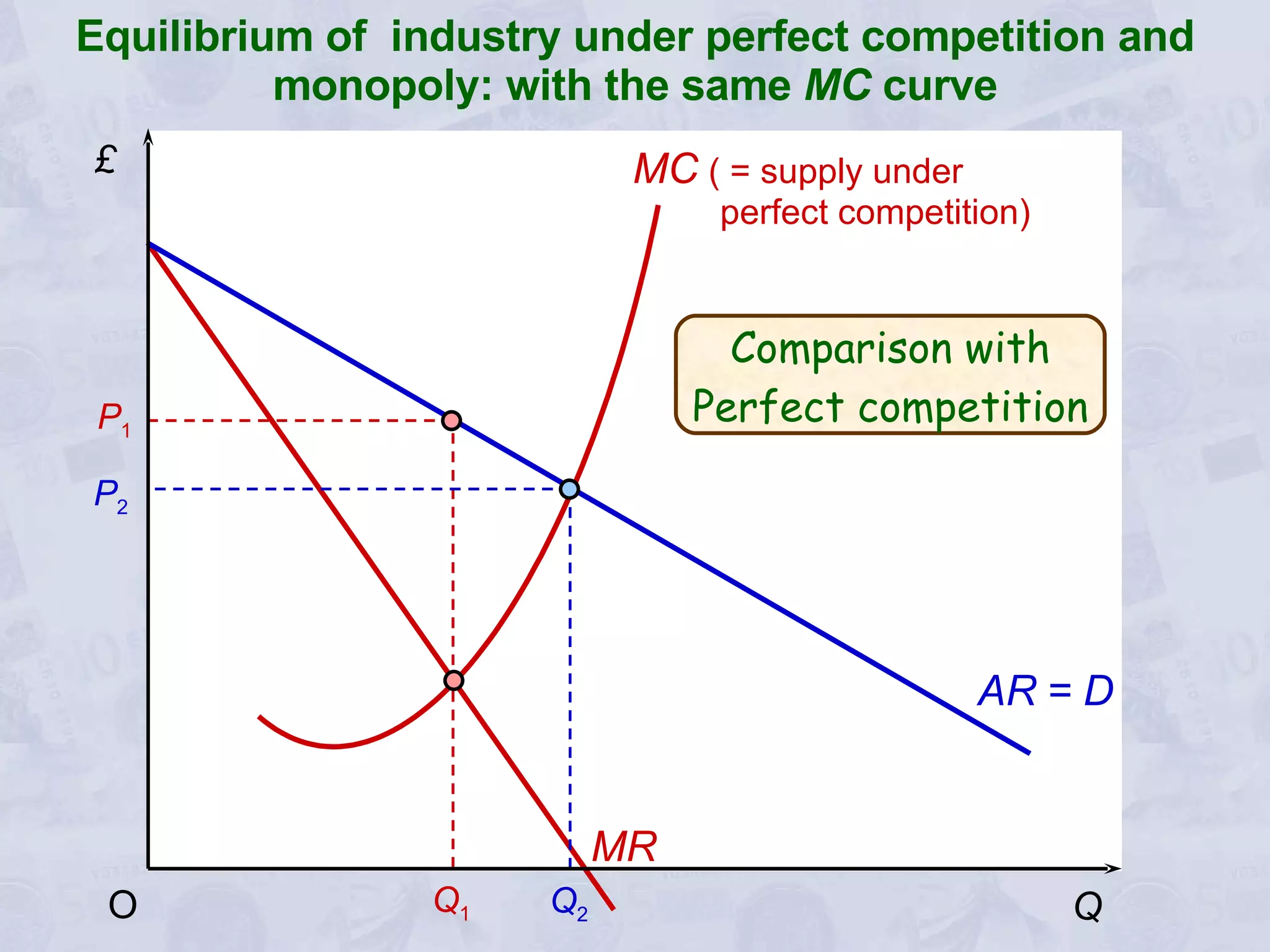
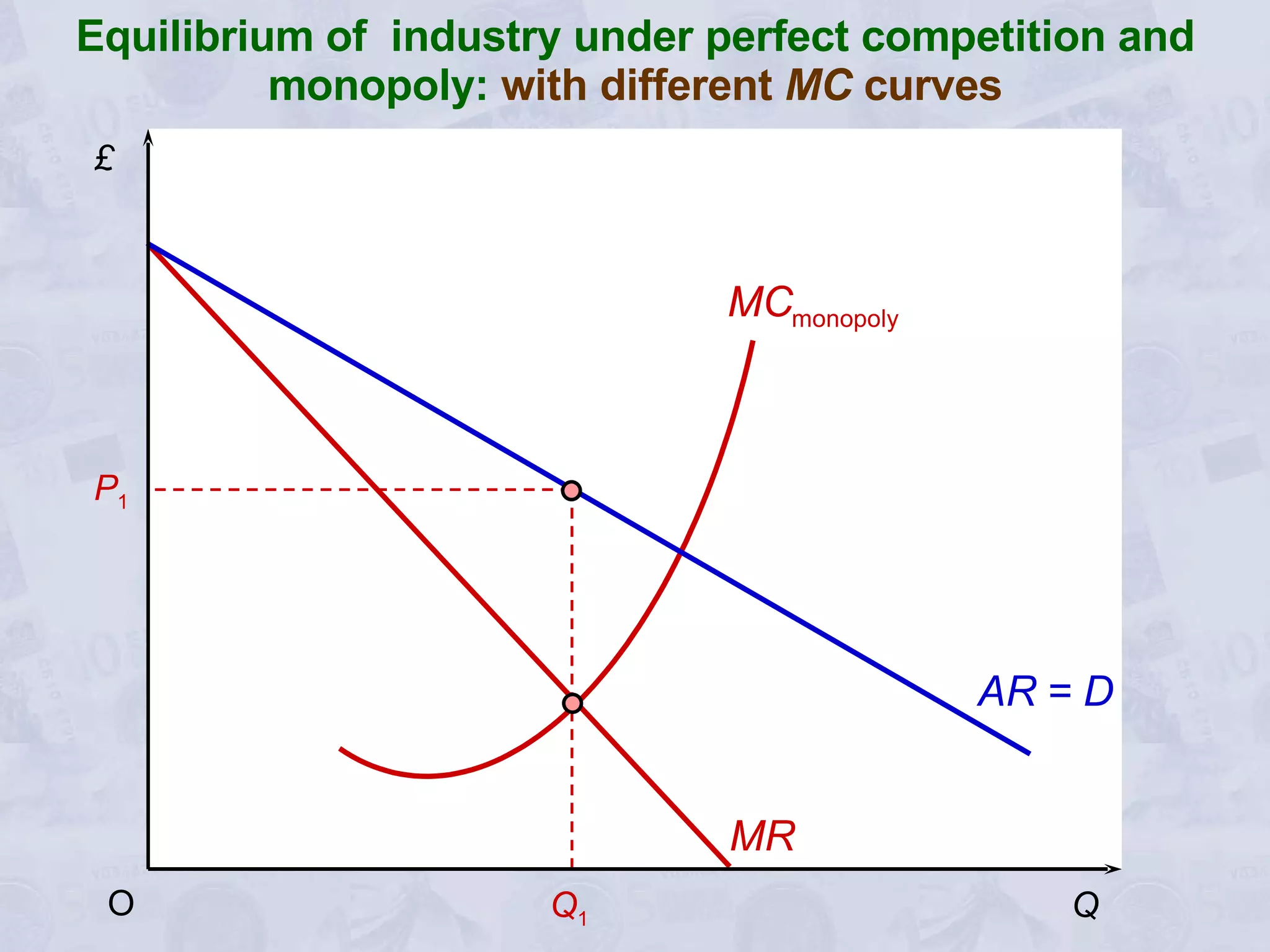
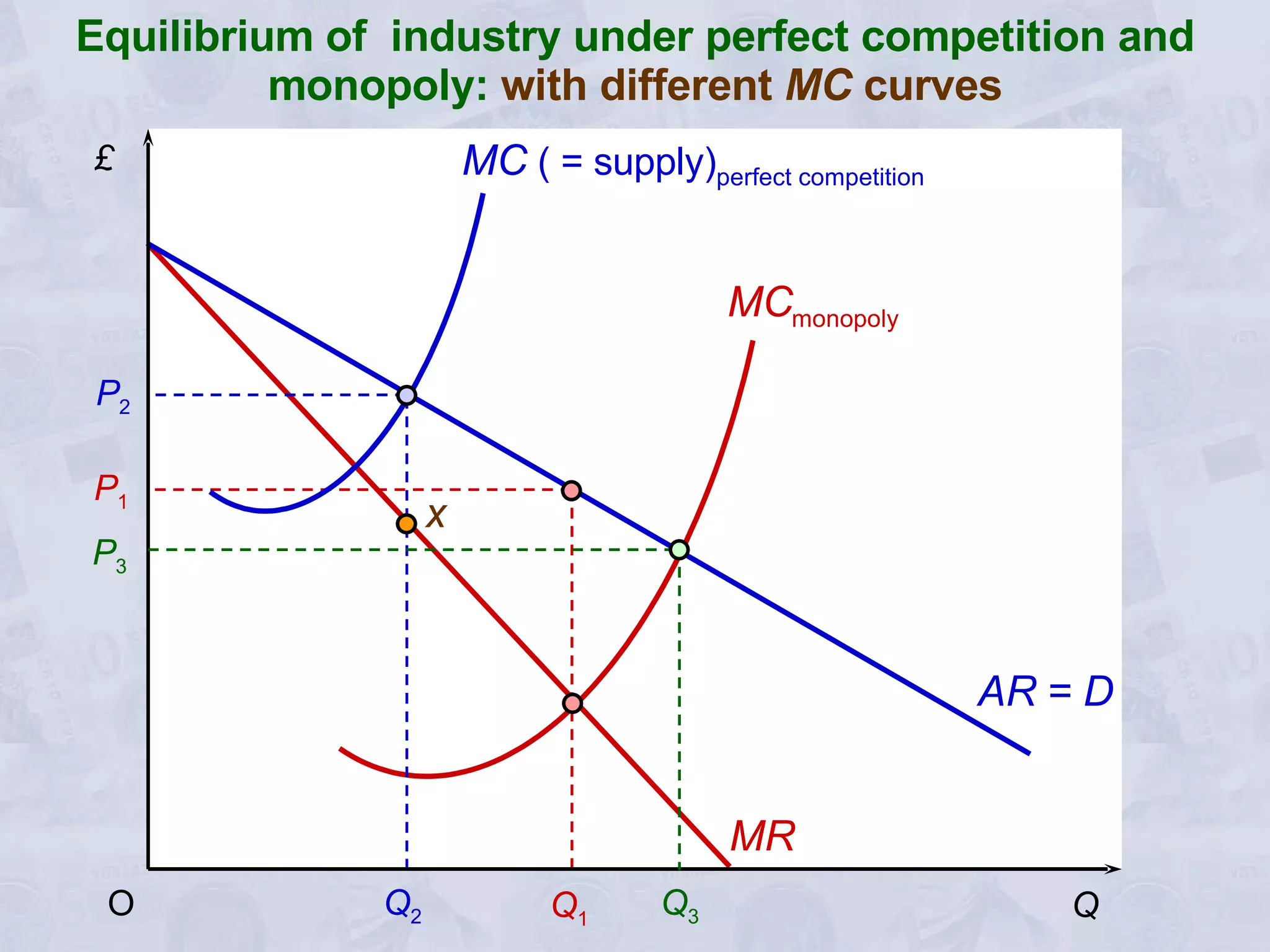
3) A monopoly will choose to produce a lower quantity at a higher price than under perfect competition, resulting in lower output but higher profits for the monopoly.