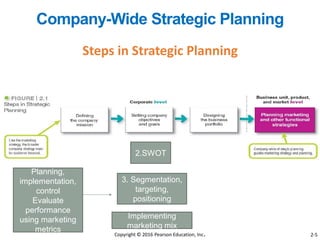
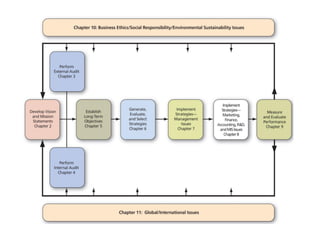
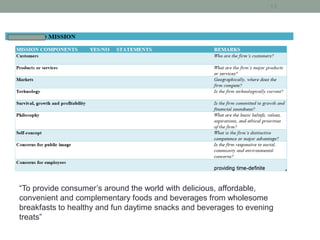
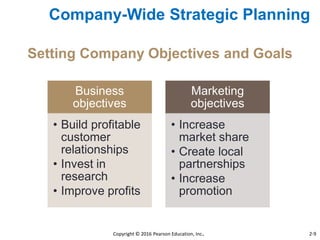
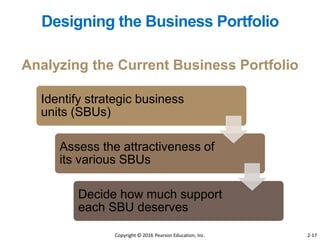
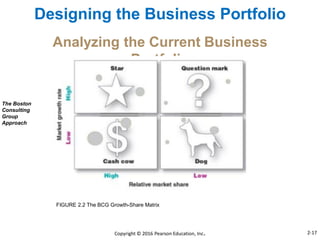
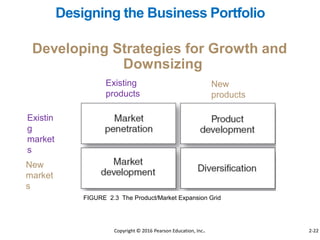
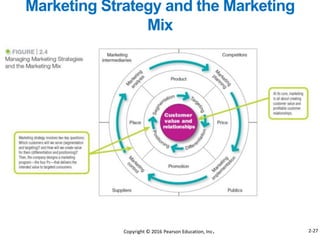
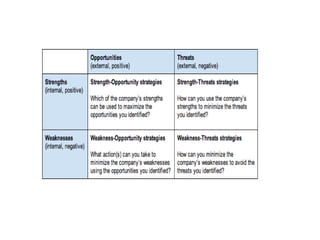
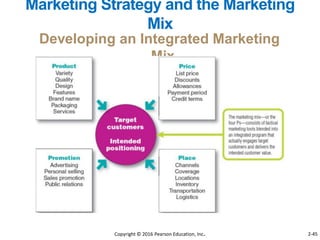
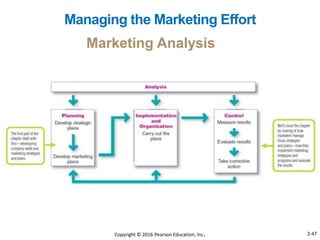
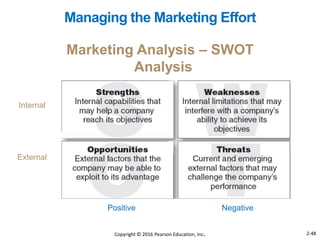
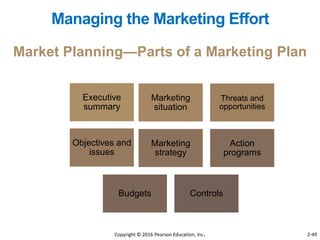
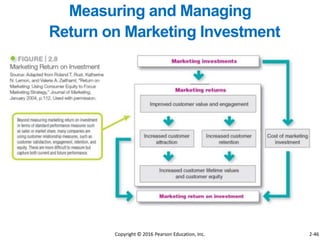
This document provides an overview of key concepts from Chapter 2 of the textbook "Strategic Marketing Management" including company-wide strategic planning, designing business portfolios, developing growth strategies, partnering with other departments, developing a customer value-driven marketing strategy, and using tools like SWOT analysis, segmentation, targeting, and positioning. The learning objectives, steps in strategic planning, components of a mission statement, and analyzing business portfolios are described over several pages.