Embed presentation
Download to read offline

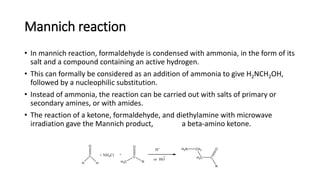
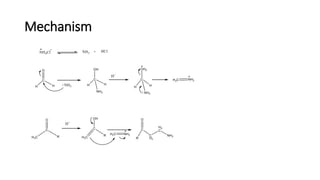
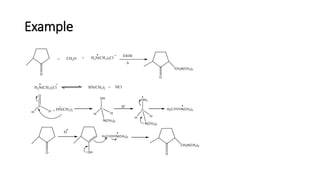
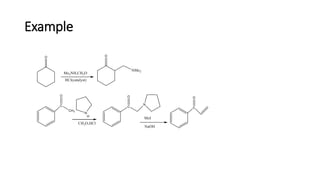

The Mannich reaction involves the condensation of formaldehyde with ammonia (or its salts) and a compound containing active hydrogen, leading to the formation of beta-amino ketones. This reaction can also utilize salts of primary or secondary amines or amides instead of ammonia. A specific example is provided where a ketone, formaldehyde, and diethylamine react under microwave irradiation to produce the Mannich product.





