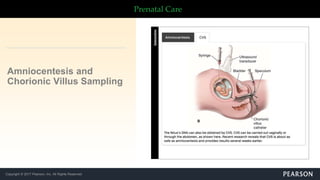
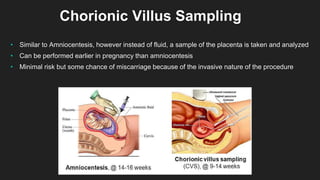
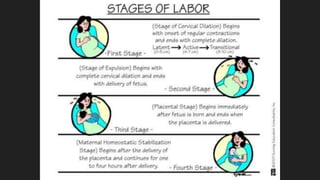
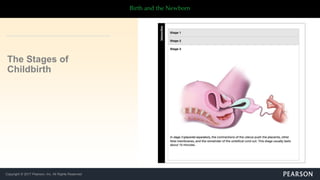
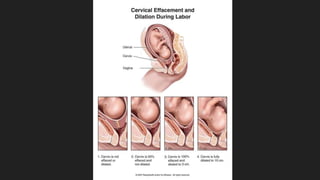
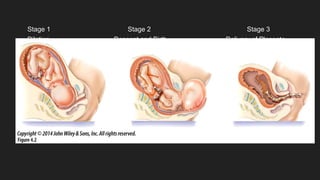
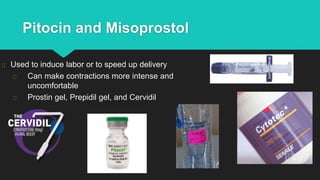
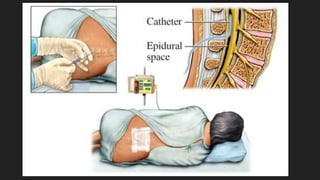
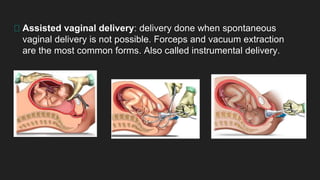
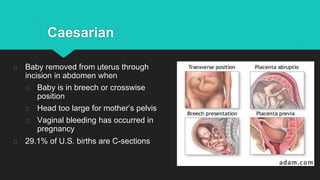
Ultrasound uses sound waves to view the baby in the uterus and has been used safely for over 40 years. Two prenatal tests are amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling, which carry small risks of miscarriage. Birth preparation classes educate expectant mothers, while a birth plan outlines wishes. Labor has three stages: dilation of the cervix in stage 1, descent and birth in stage 2, and delivery of the placenta in stage 3. Pain management options include analgesics, anesthetics like epidurals, and assisted delivery or C-section for complicated births.