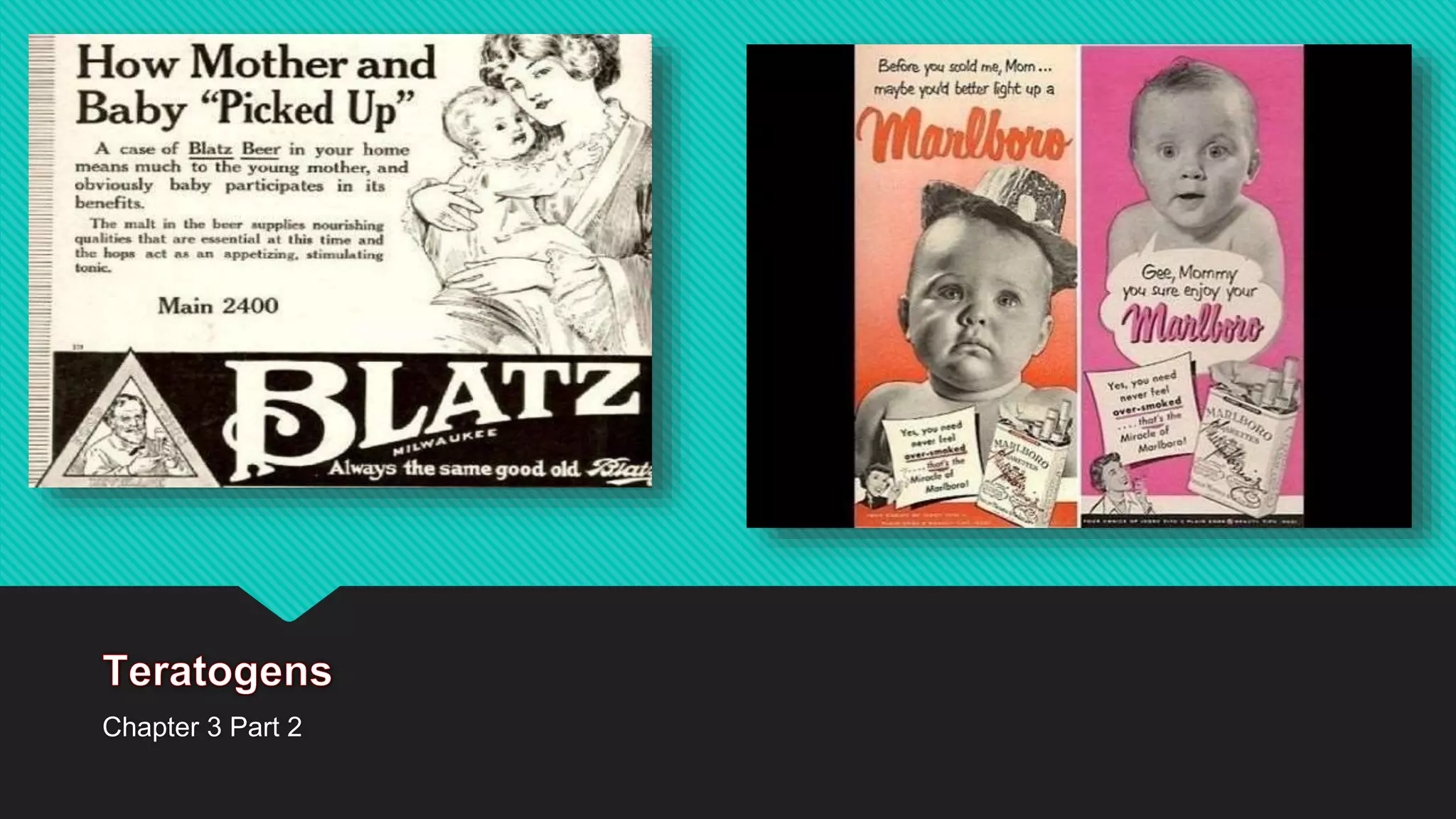
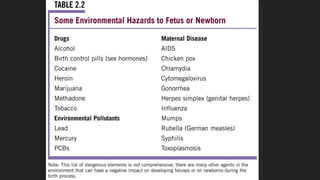
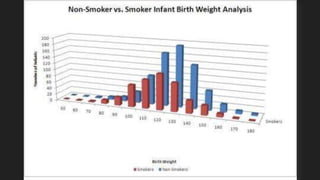
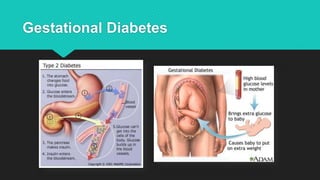
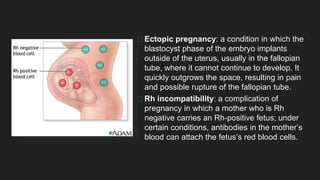
Maternal behaviors and environmental factors can negatively impact fetal development. Alcohol is a leading cause of fetal abnormalities and fetal alcohol syndrome, which causes distinctive facial features and intellectual disabilities. Smoking during pregnancy doubles the risk of complications like placenta previa and placental abruption. Illicit drugs and certain medications also pose risks to the developing fetus. Untreated maternal diseases, stress, and nutritional deficiencies increase health risks as well. Proper prenatal care is important for monitoring risks and promoting healthy pregnancies.