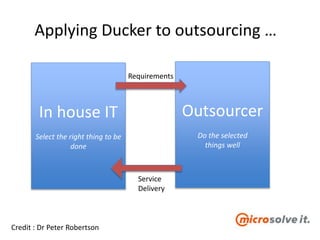
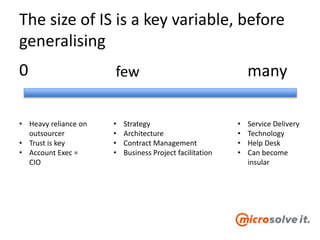
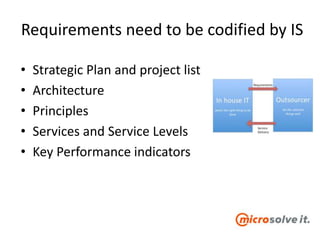
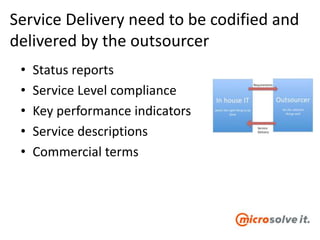
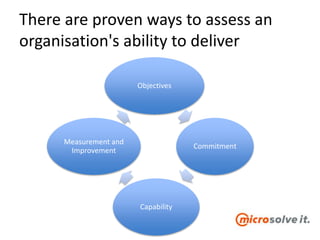
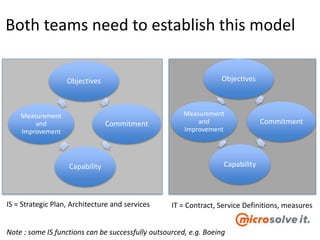
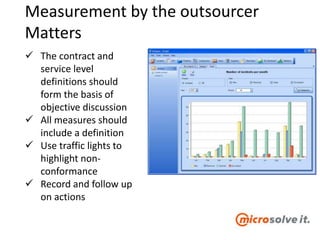
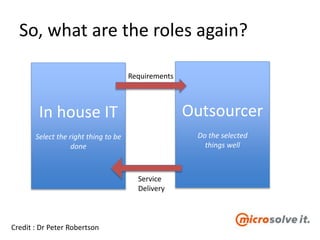
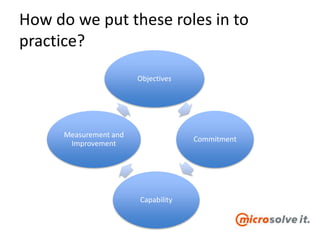
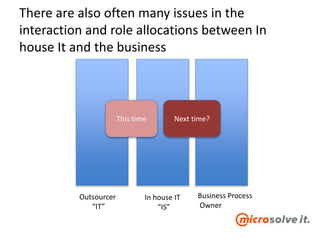
The document discusses the roles and responsibilities of in-house IT and outsourcers in a technology and IT conference presentation, emphasizing the importance of trust and clear objectives. It highlights the need for service delivery metrics, customer satisfaction, and regular communication to improve collaboration. Furthermore, it suggests tools like RACI and service charters to facilitate effective partnership between the parties involved.