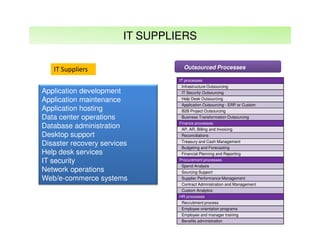
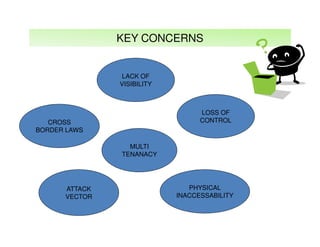
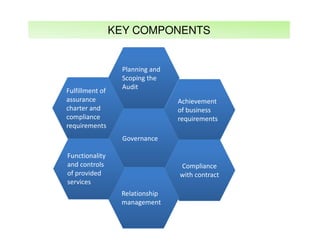
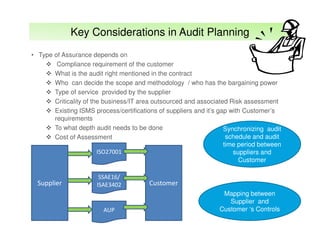
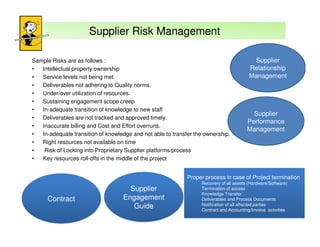
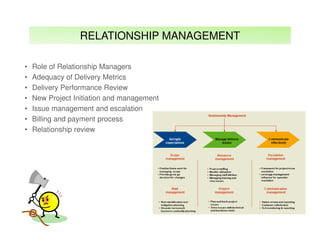
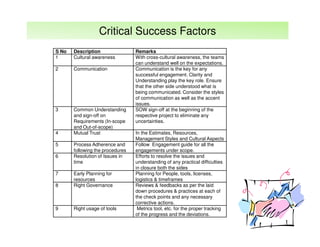
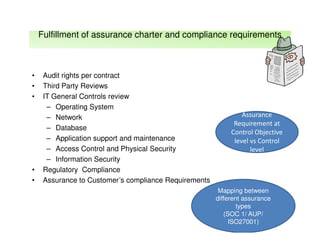
The document outlines best practices and considerations for auditing IT suppliers, emphasizing the growing dependency on such suppliers due to technological advancements and changing business models. Key topics include governance, audit planning, supplier performance management, and relationship management, with a focus on compliance and risk assessment. The ISACA guidelines serve as a framework for ensuring effective auditing in outsourced environments.