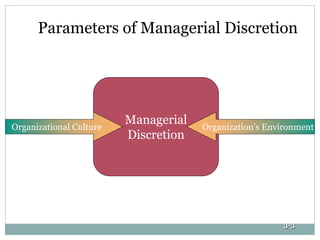
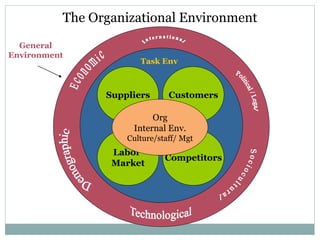
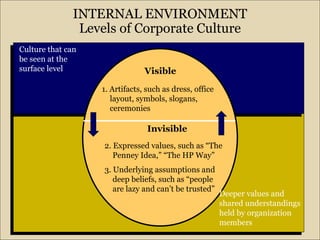
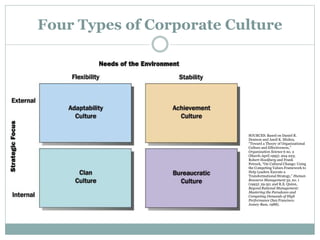
The document discusses the organizational environment and corporate culture. It defines the organizational environment as all external elements that can potentially affect the organization. The external environment has two layers - the task environment (customers, suppliers, competitors, labor) and the general environment (technological, socio-cultural, economic, legal-political). The internal environment includes organizational culture, staff, and management. Corporate culture has visible and invisible levels, and can take different forms like clan, adhocracy, market, or hierarchy culture. Cultural leadership influences culture by articulating a vision and reinforcing cultural values through daily activities.