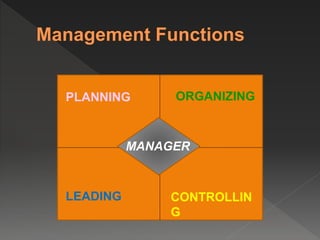
The document describes five functional areas of an organization: research and development, marketing, finance, production, and human resources. It then provides details on what each functional area involves, including new product design for R&D, financial planning for finance, and human capital management for HR. The document also discusses different levels of management, including first-line managers who oversee front-line employees, middle managers who manage first-line managers, and top managers who make organization-wide decisions. Effective management involves coordinating work through planning, organizing, leading, and controlling to achieve goals efficiently and effectively.