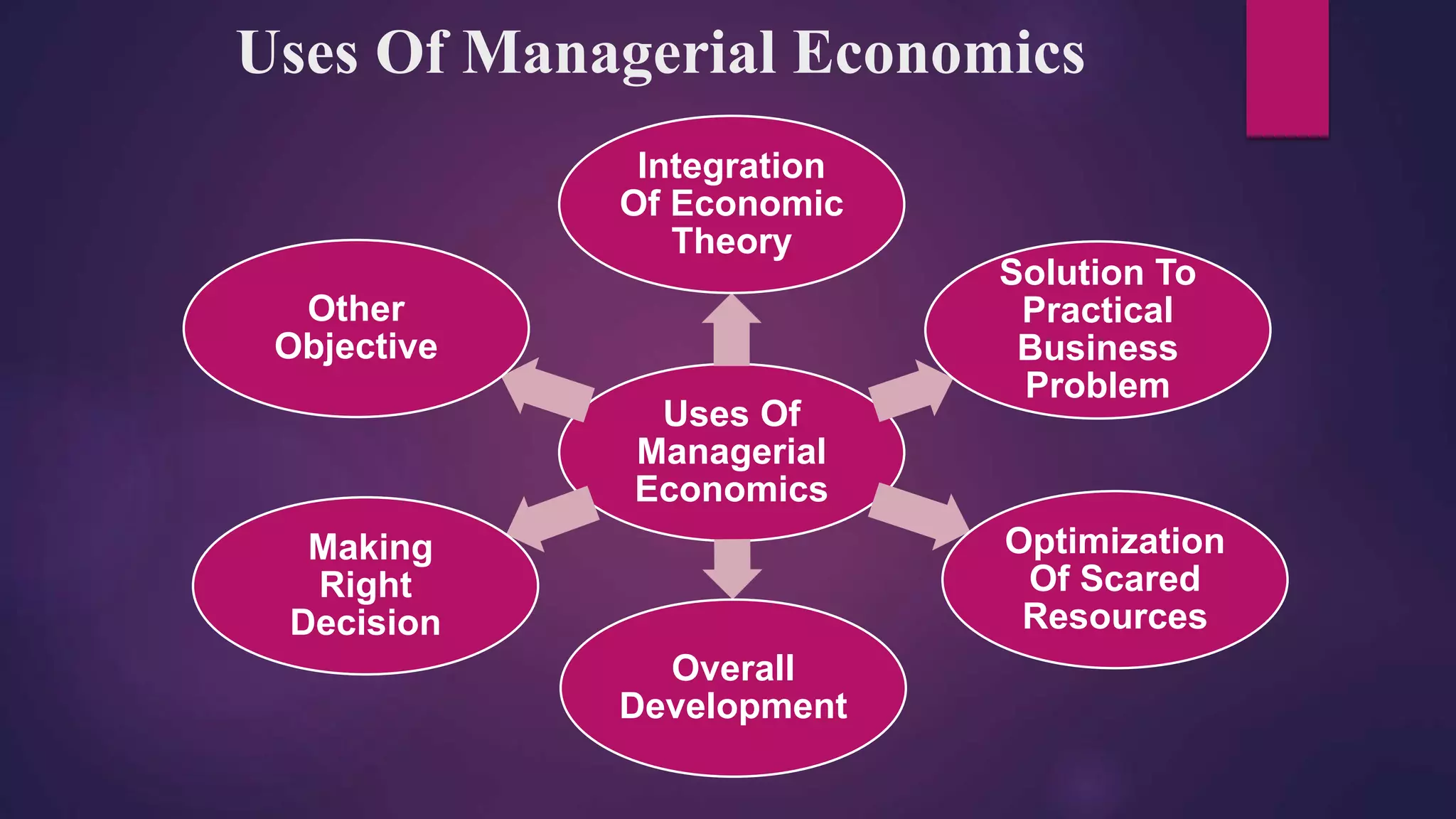
This document provides an introduction to the topic of managerial economics. It defines managerial economics as the study of how scarce resources are efficiently directed to achieve managerial goals. The document outlines the nature, scope, and significance of managerial economics. It also discusses the roles and responsibilities of managerial economists in providing analysis to help with production, cost, marketing, investment and other business decisions.