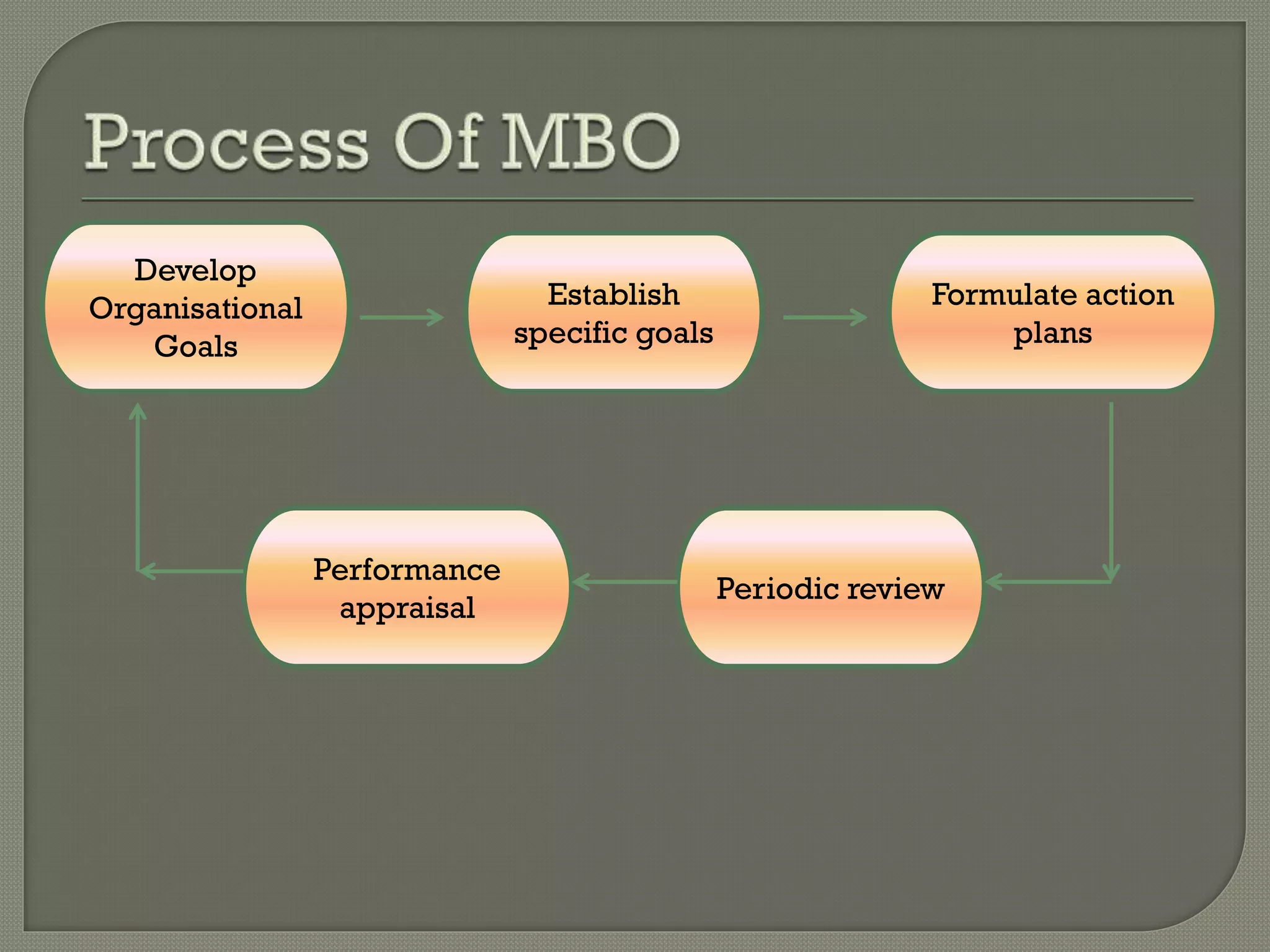
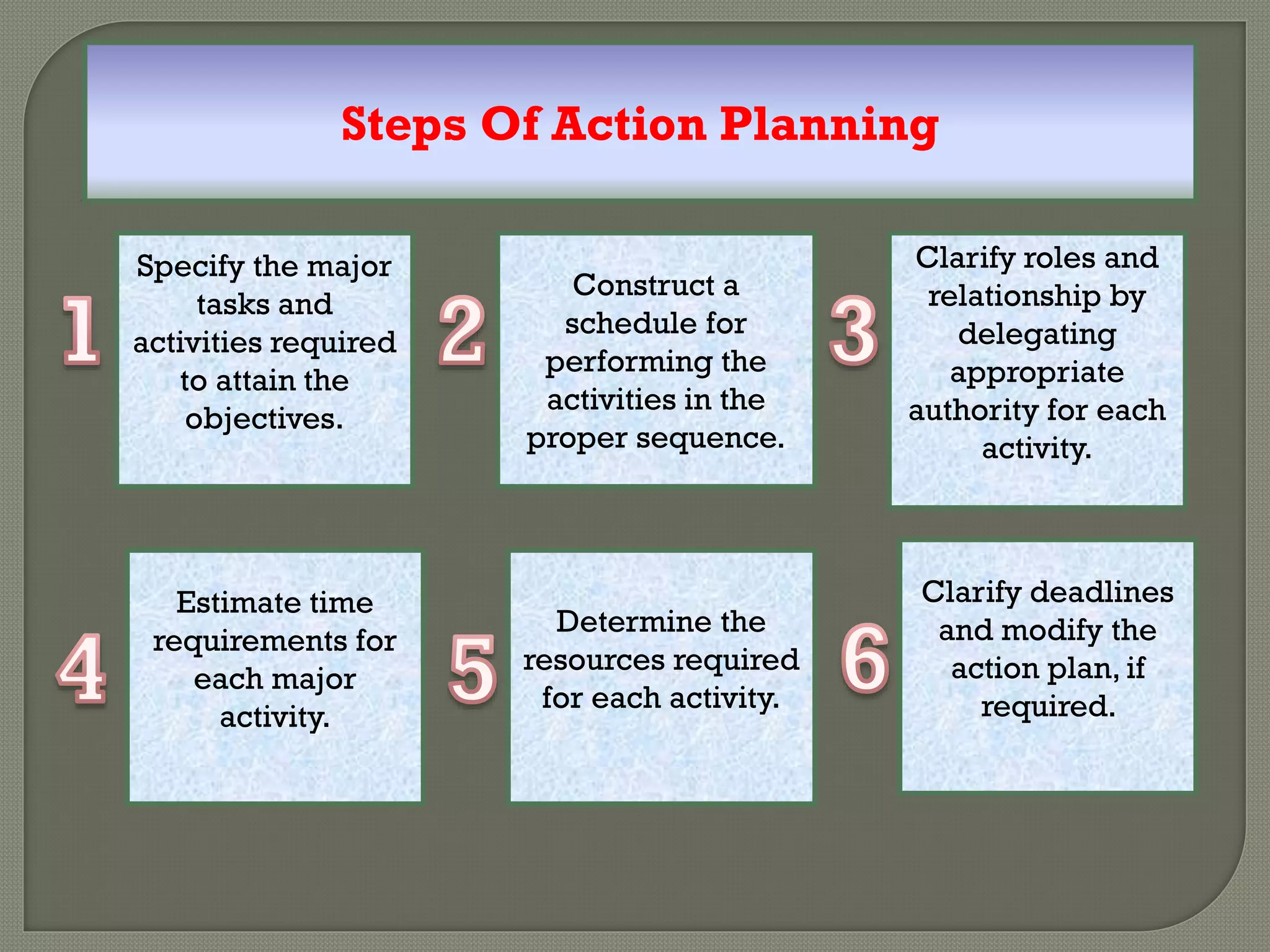
Management by objectives (MBO) is a process where managers and employees jointly set objectives for employees' work and assess their performance against these objectives. It involves participative goal setting, choosing actions, and periodic performance reviews. MBO aims to align individual employee goals with organizational goals to improve planning, motivation, and performance management. However, some weaknesses include that goal setting can be time consuming and difficult, participation may be challenging, and it risks becoming too inflexible or pressure-oriented.