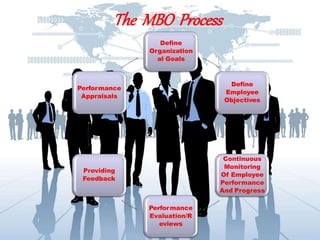
Peter Drucker invented the concept of Management by Objectives (MBO) which involves employees setting goals with their managers, periodically reviewing progress, and rewarding achievement. The key aspects of MBO are collaborative goal setting within a specific time period, regular performance evaluations focused on results, and linking rewards to goal completion. While MBO can improve planning, communication, and employee commitment, it also requires significant effort and may not integrate well with other management systems.