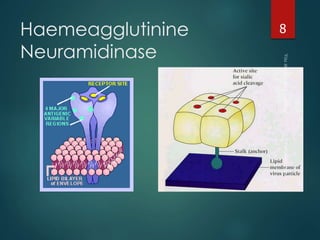
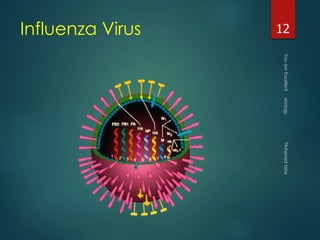
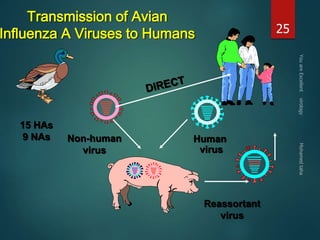
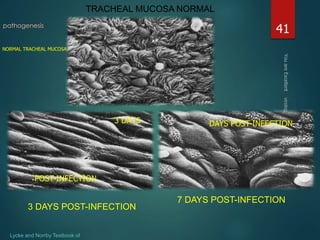
This document discusses influenza viruses and pandemics. It covers the taxonomy and anatomy of influenza viruses, noting there are three types (A, B, C) that can infect humans. Type A is of most concern as it can undergo antigenic shift, resulting in new subtypes that have caused past pandemics like the 1918 Spanish flu. The document outlines the influenza virus life cycle and how it is transmitted. It also discusses diagnosis of both human and avian influenza, noting some strains of avian H5N1 can cause severe disease in humans.