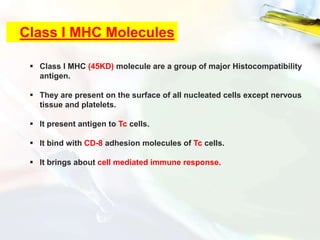
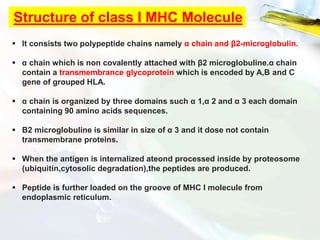
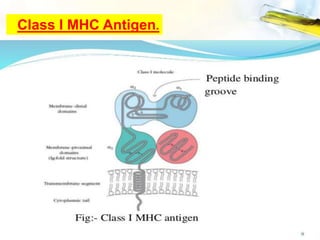
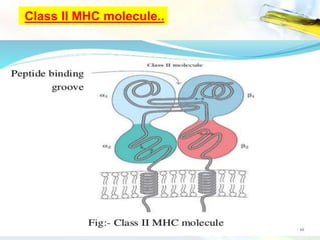
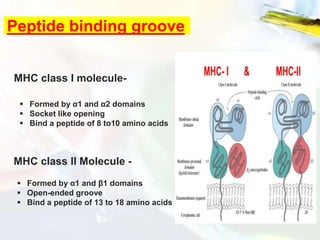
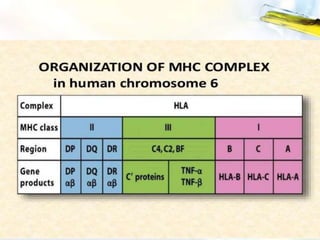
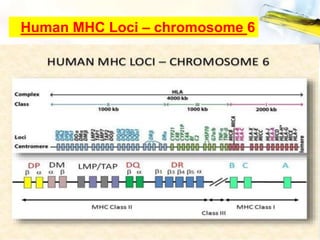
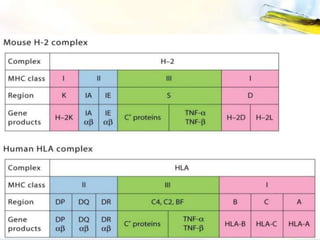
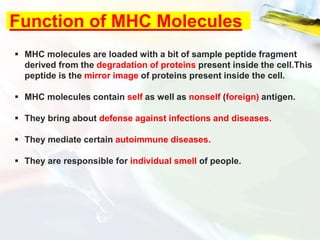
The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) is a set of surface proteins located on nucleated cells that present antigens and play an important role in the immune system. There are four classes of MHC molecules - Class I molecules present intracellular antigens to cytotoxic T cells, Class II present extracellular antigens to helper T cells, and Classes III and IV have other immune functions. MHC molecules are encoded by genes on chromosome 6 in humans and chromosome 17 in mice, and are important for self/non-self recognition, immune responses, and tissue compatibility.