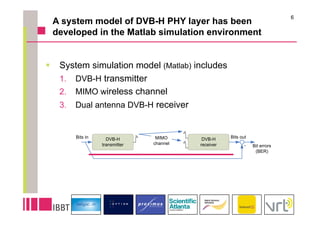
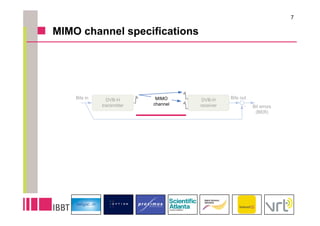
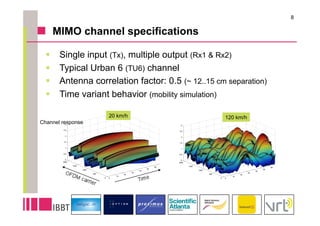
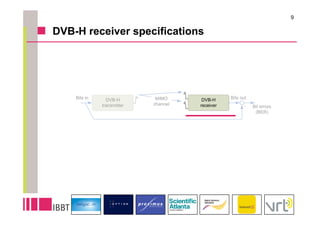
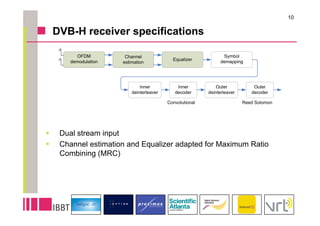
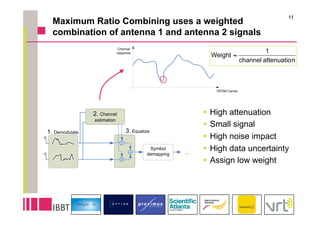
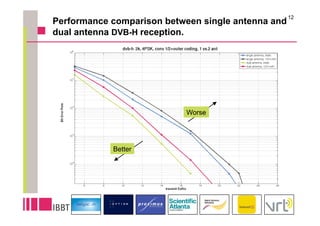
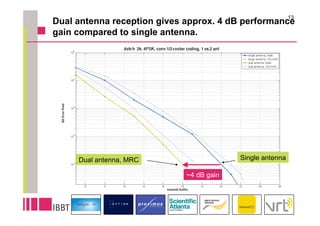
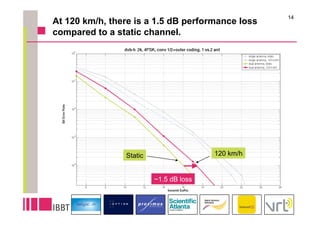
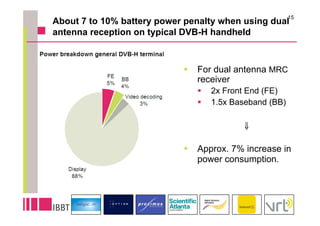
This document summarizes research on the impact of using a dual-antenna receiver for DVB-H reception. It outlines that a system model was developed in Matlab to simulate a standard compliant DVB-H system with a dual antenna receiver using maximum ratio combining. The simulation found the dual antenna receiver provided approximately 4dB better reception performance than a single antenna receiver, though with a 7-10% increase in power consumption for the additional antenna circuitry. Mobility up to 120km/h resulted in a 1.5dB loss in performance compared to a static channel.