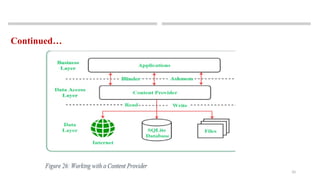
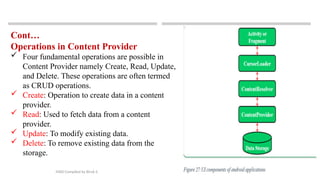
The document outlines various data storage options available in Android, including shared preferences, internal and external storage, SQLite databases, and network connections. It emphasizes the importance of data synchronization for maintaining data integrity and introduces content providers as a means for applications to securely access and modify stored data. Additionally, it covers basic CRUD operations that can be performed on data within a content provider.