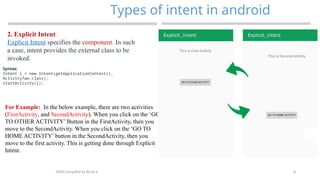
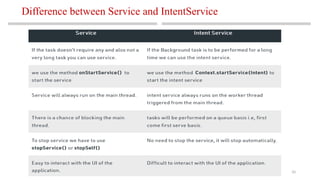
The document outlines the use of services and intents in Android development, explaining how they enable background operations and facilitate communication between different components of applications. It distinguishes between foreground, background, and bound services, as well as between implicit and explicit intents. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of a systematic approach to mobile application development, detailing steps for creating successful mobile apps.