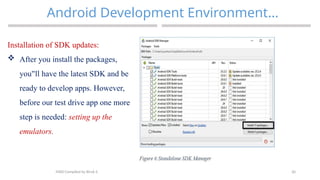
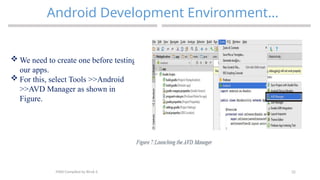
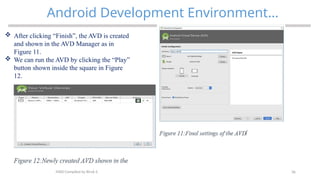
The document provides an overview of mobile application development, focusing on the key operating systems iOS and Android, their respective development tools, and trends in app development such as augmented reality, artificial intelligence, and blockchain. It also outlines key drivers for mobile app adoption, including consumer behavior and personalized content delivery, and reviews the requirements for setting up an Android development environment. Additionally, the document describes the installation process for Android Studio and the creation of Android Virtual Devices for testing applications.