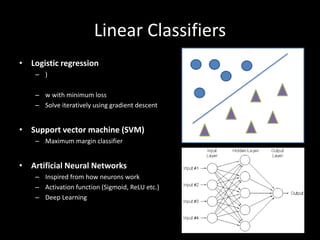
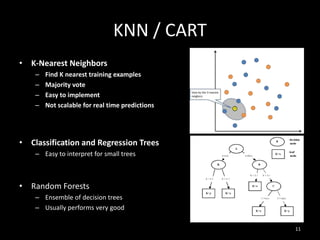
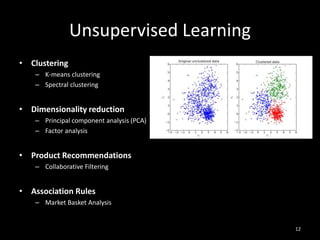
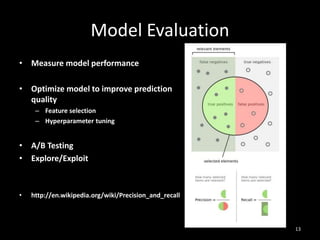
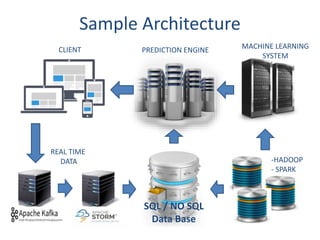
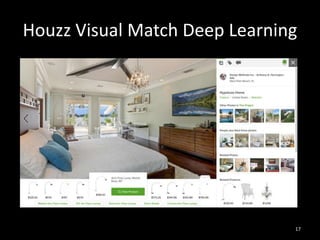
This document provides an overview of machine learning:
1. Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence that uses data to help computers learn without being explicitly programmed. It can recognize patterns in large amounts of data.
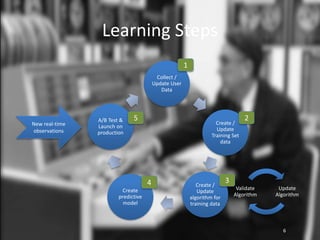
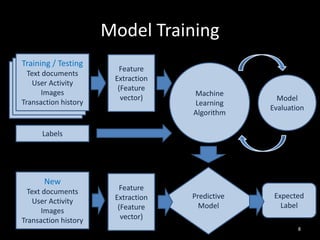
2. Machine learning involves collecting large datasets, creating algorithms to detect patterns in the data, and using those patterns to make predictions on new data.
3. Machine learning has many applications like improving health, making utilities more efficient, and simplifying the future through technologies like personalized assistants, optimized transportation, and computer vision.