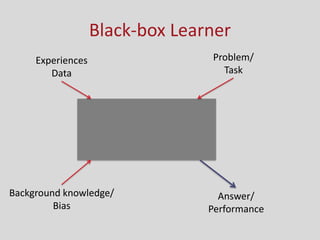
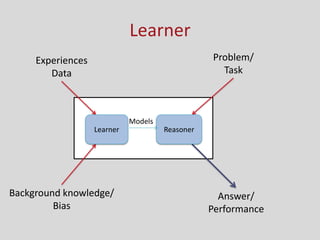
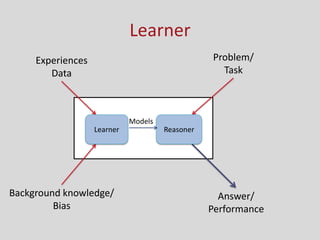
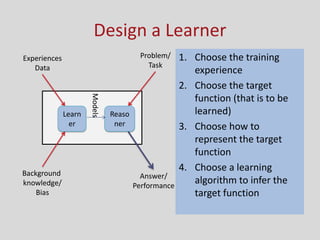
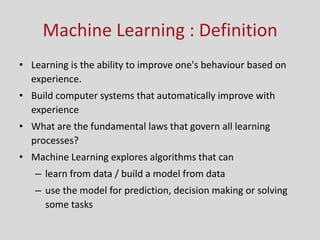
This document provides an introduction to machine learning. It discusses the history of machine learning, including early work in neural networks and decision trees. It defines machine learning as the ability to improve performance on tasks based on experience. The key components of a learning problem are identified as the task, data used for learning, and a performance measure. Linear regression, decision trees, instance-based learning, Bayesian learning, support vector machines, neural networks, and clustering are listed as machine learning algorithms. Designing a learning system involves choosing training experiences, a target function, representation of that function, and a learning algorithm.





![Machine Learning : Definition
• A computer program is said to learn from
experience E with respect to some class of
tasks T and performance measure P, if its
performance at tasks in T, as measured by P,
improves with experience E.
[Mitchell]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1a-introduction-230221055532-3d6c4a73/85/Introduction-to-Machine-Learning-9-320.jpg)