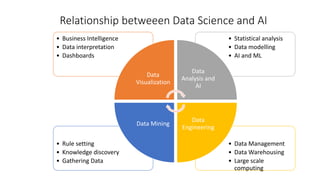
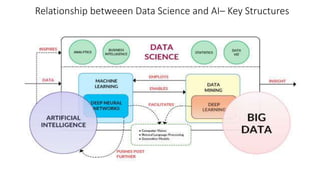
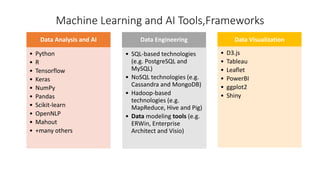
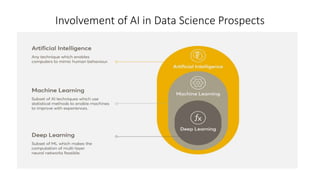
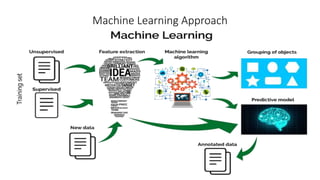
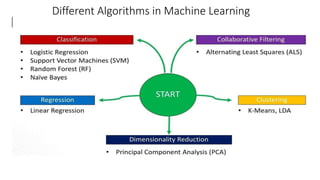
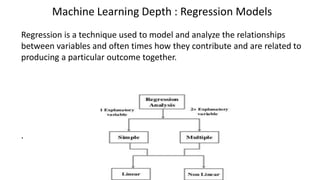
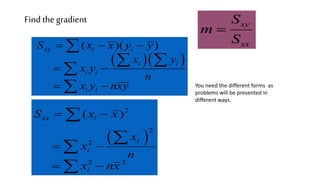
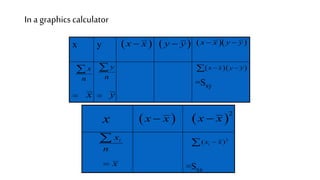
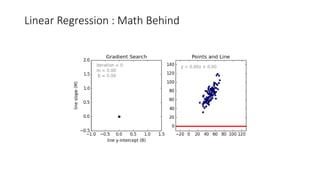
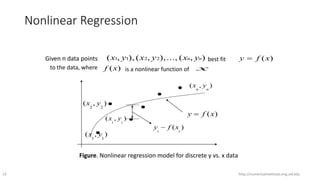
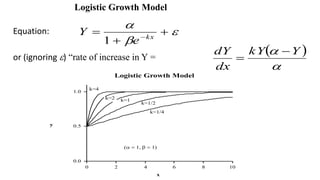
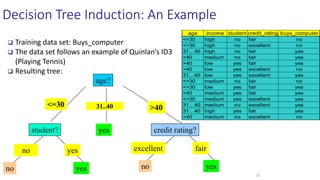
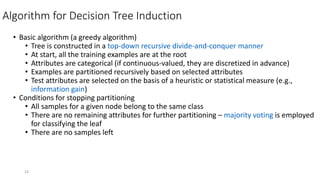
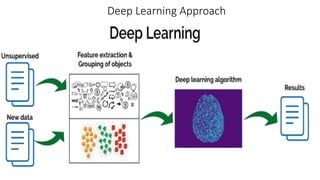
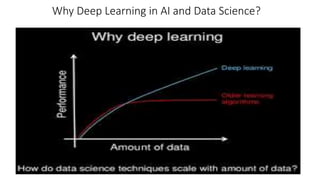
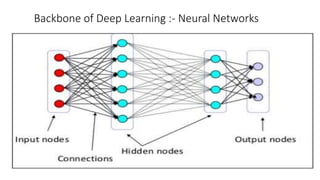
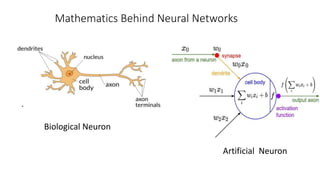
The document discusses the importance of machine learning and AI, their applications, and the relationship between data science and AI, along with various tools and frameworks used in these fields. It provides in-depth explanations of machine learning concepts, including regression models and decision trees, as well as a brief overview of deep learning methods and their mathematical foundations. Additionally, it highlights the growing opportunities for data analytics professionals in light of increasing data generation and business awareness.