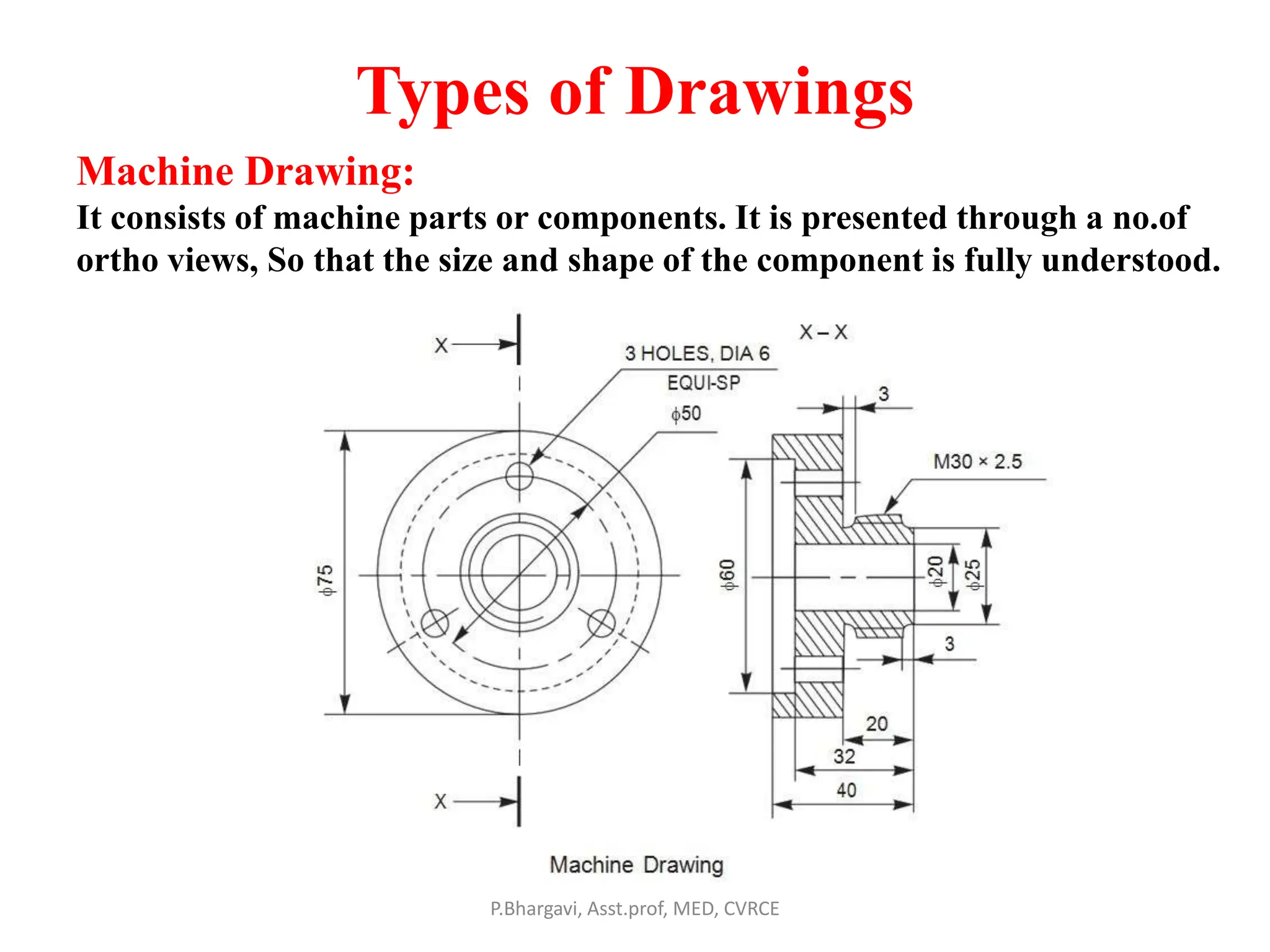
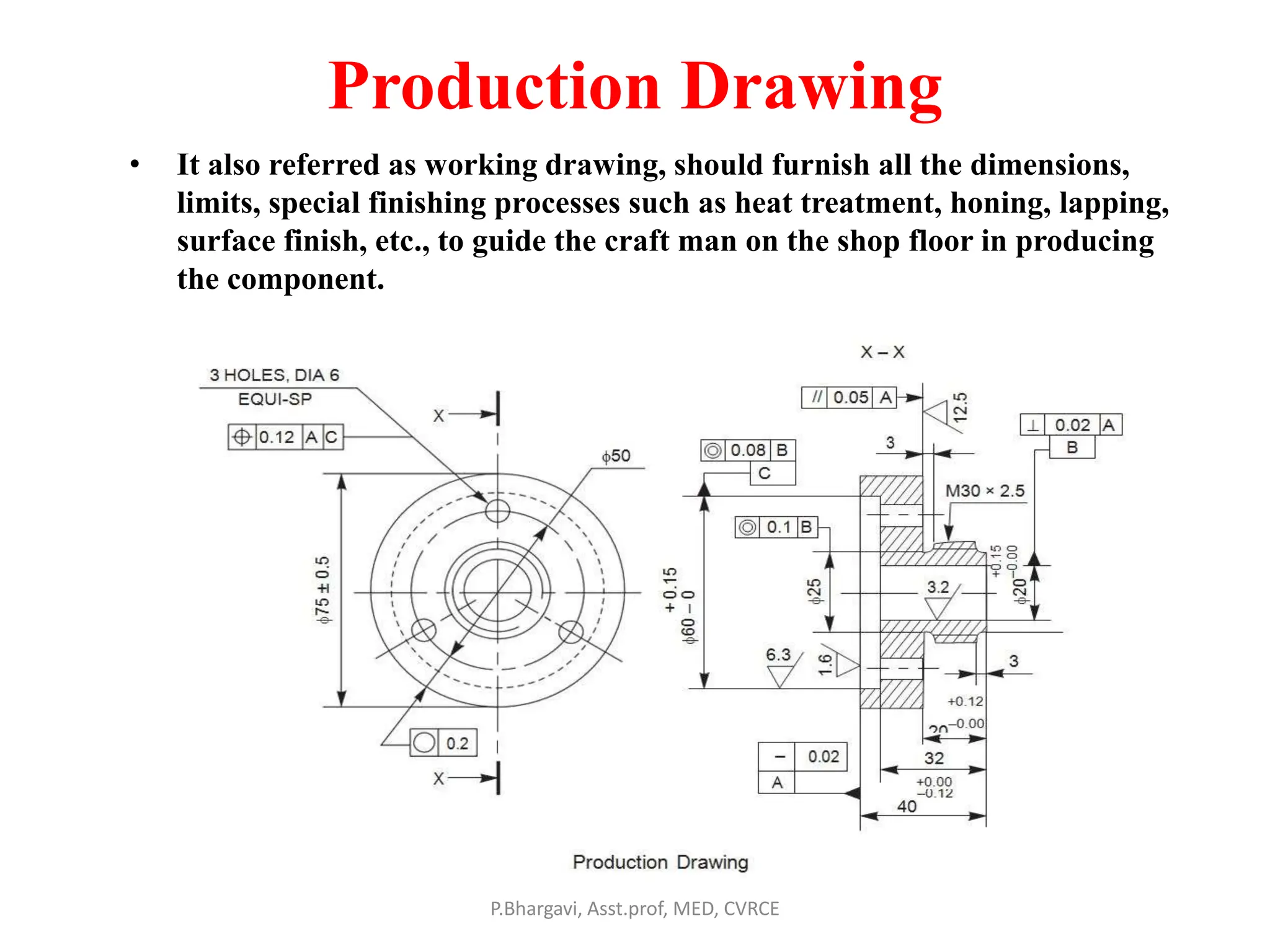
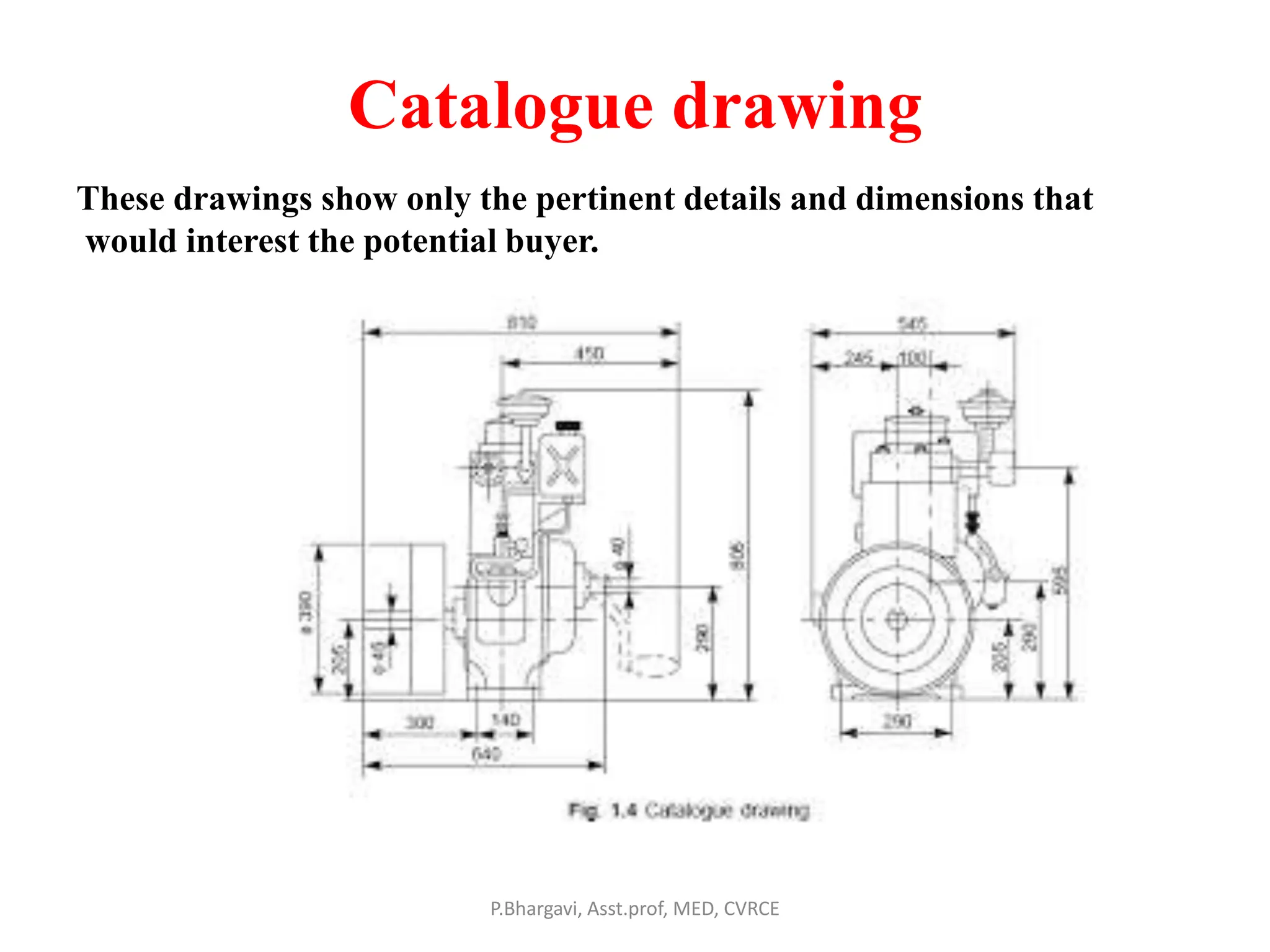
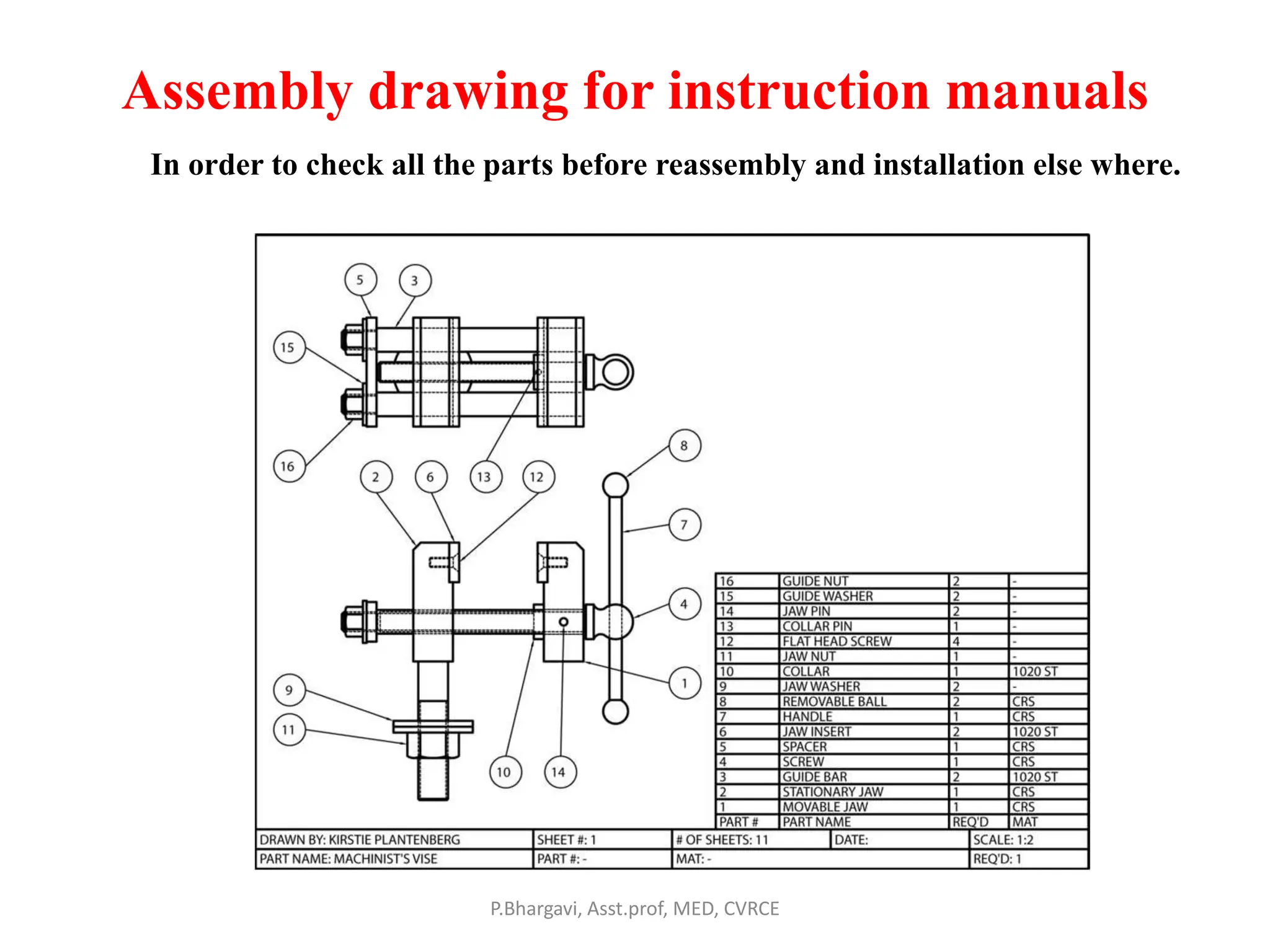
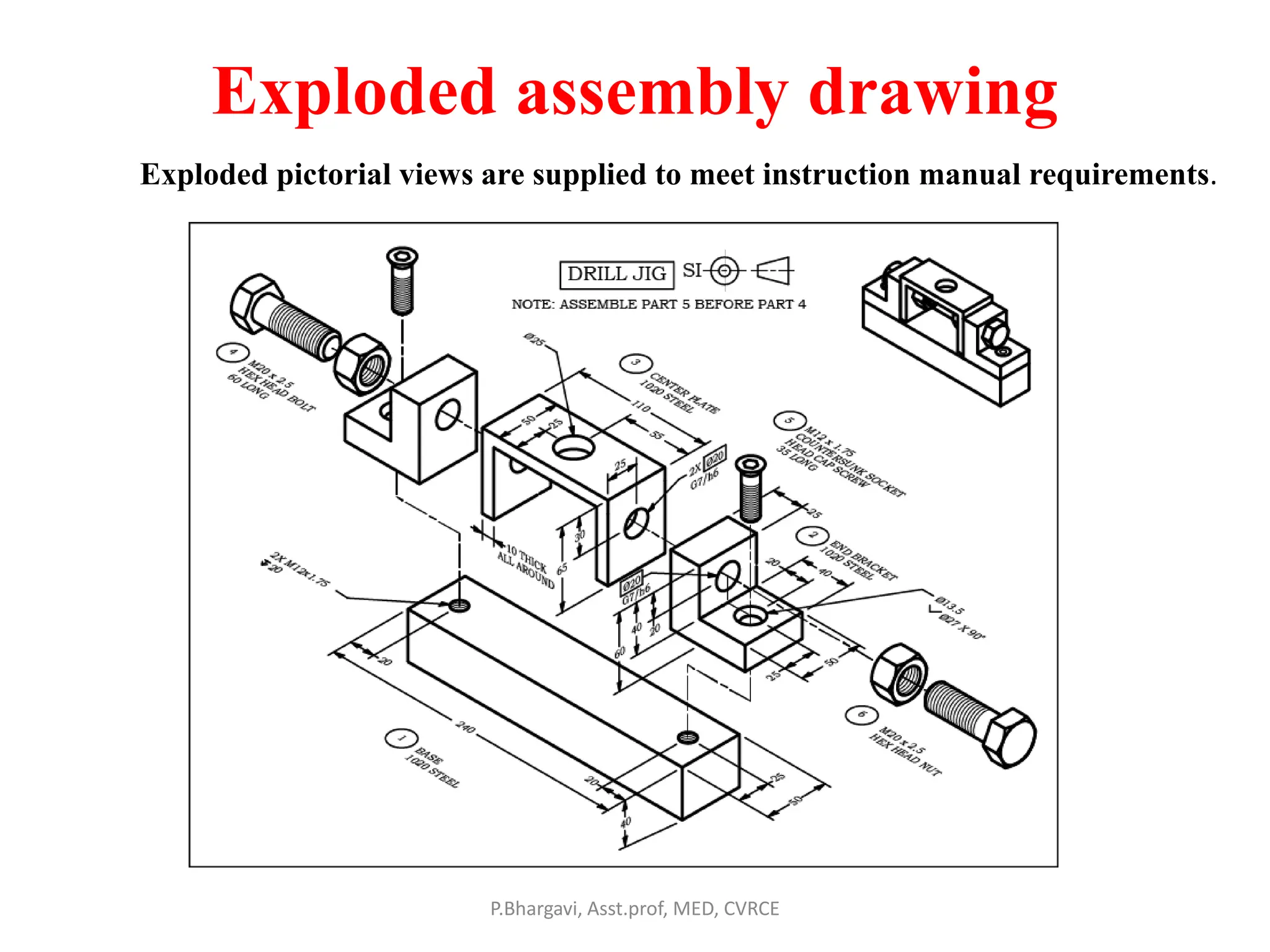
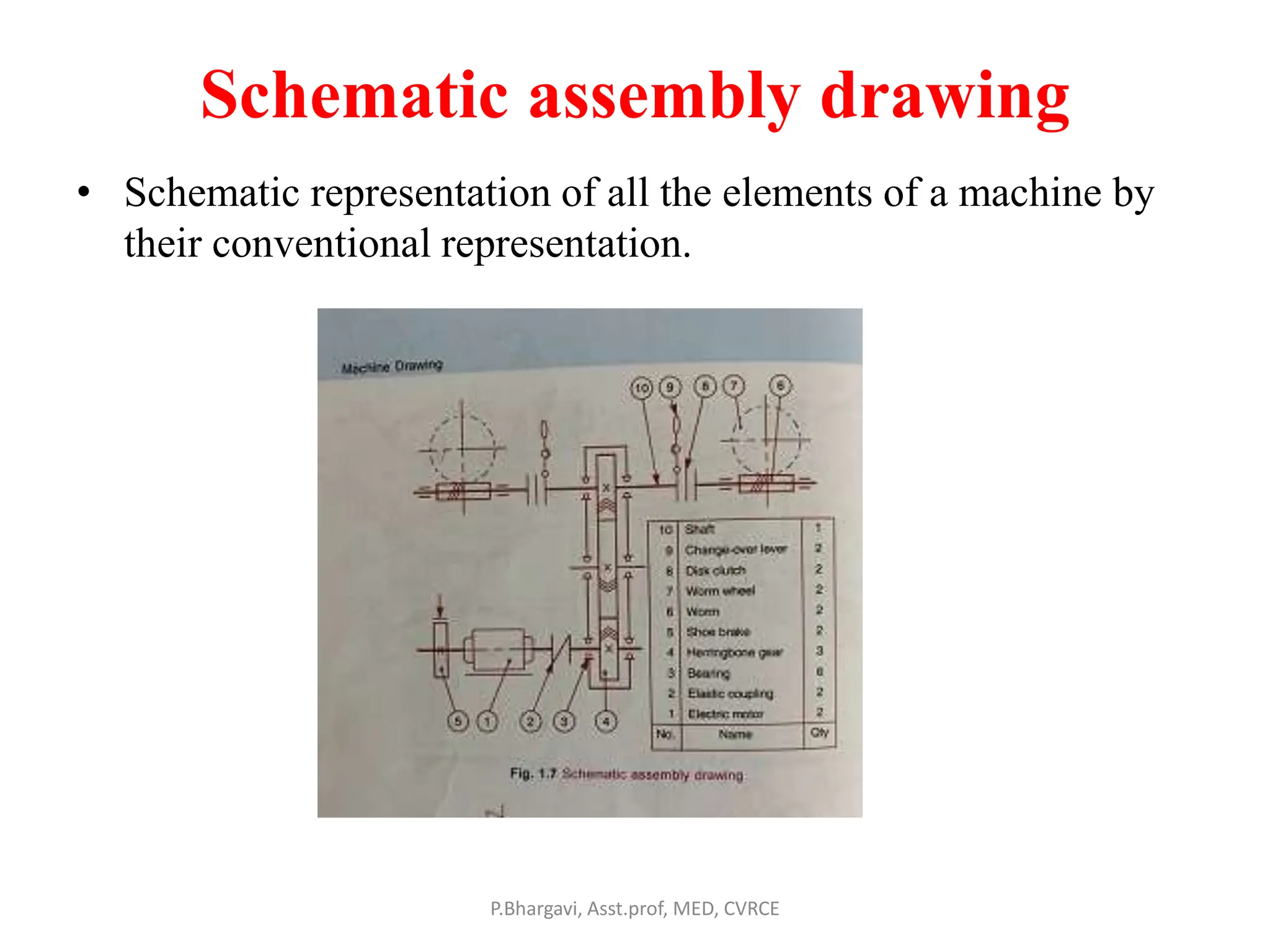
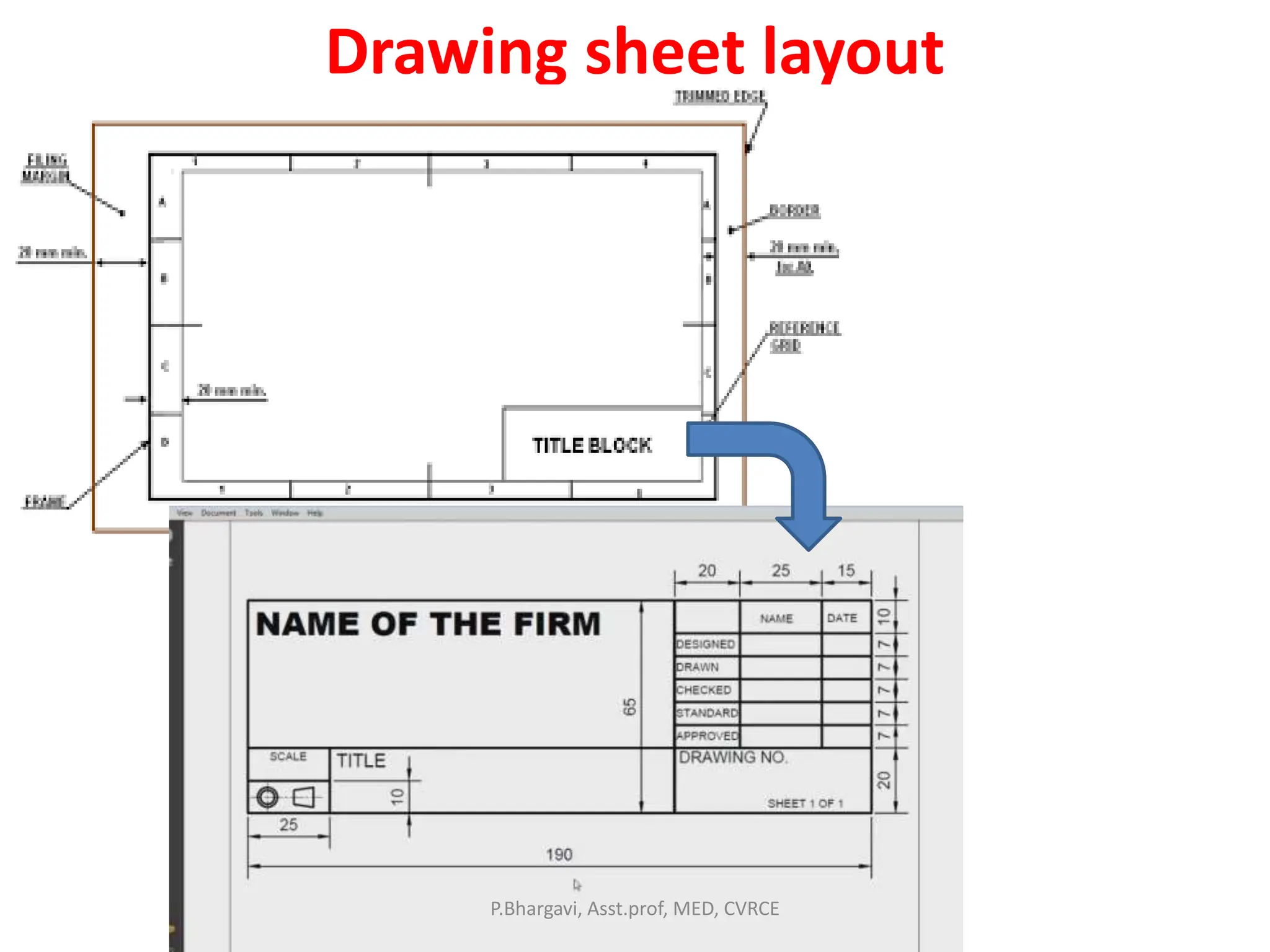
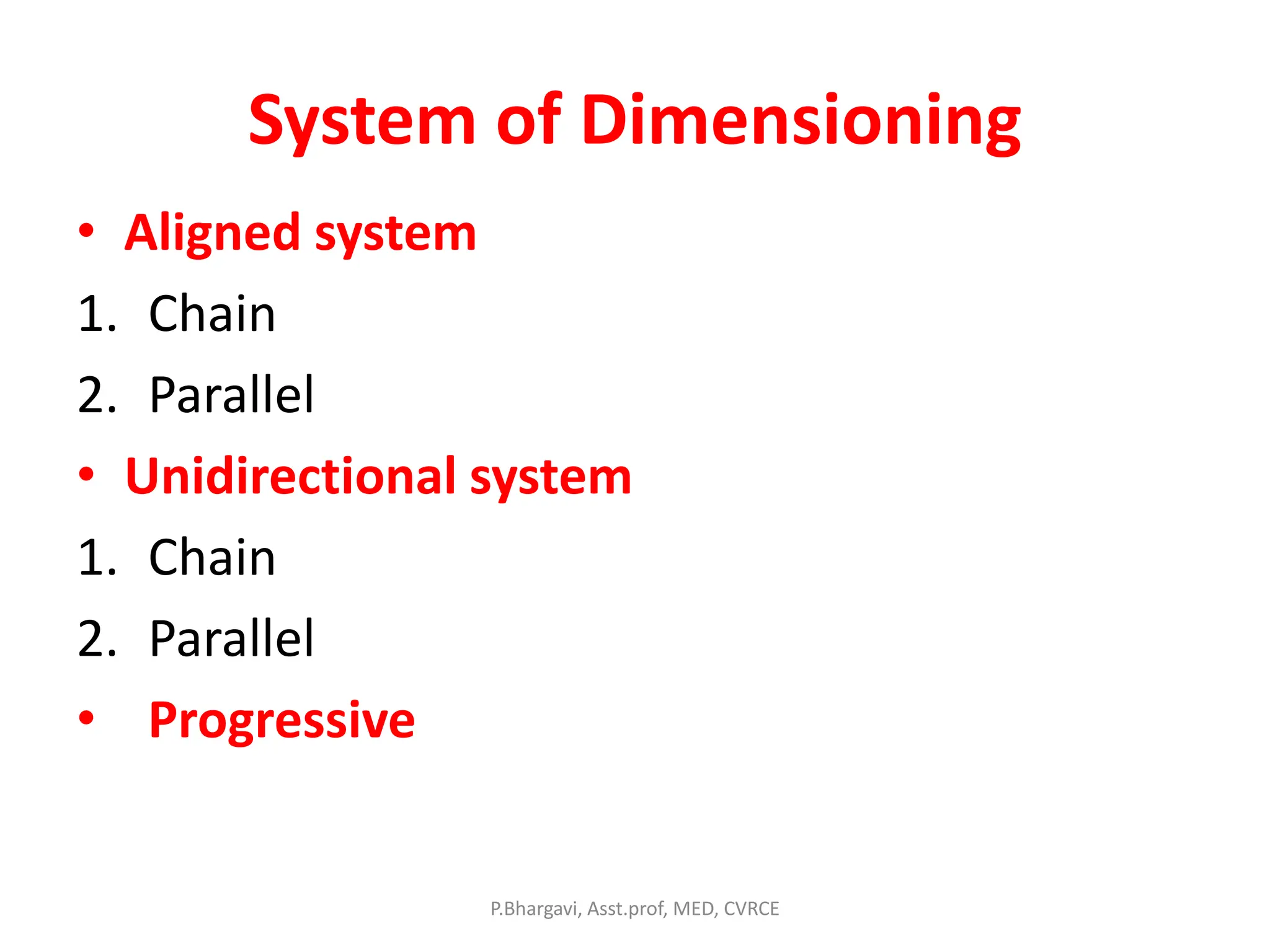
The document discusses machine drawing conventions and guidelines for creating drawings using AutoCAD. It covers topics like drawing views, dimensions, sections, materials representation, and machine elements. The list of experiments involves drawing various machine parts and elements like screws, bolts, keys, gears, bearings, valves etc using appropriate drawing conventions and views. Dimensioning, sectioning, title blocks and other guidelines are also discussed for creating production and working drawings of machine components.