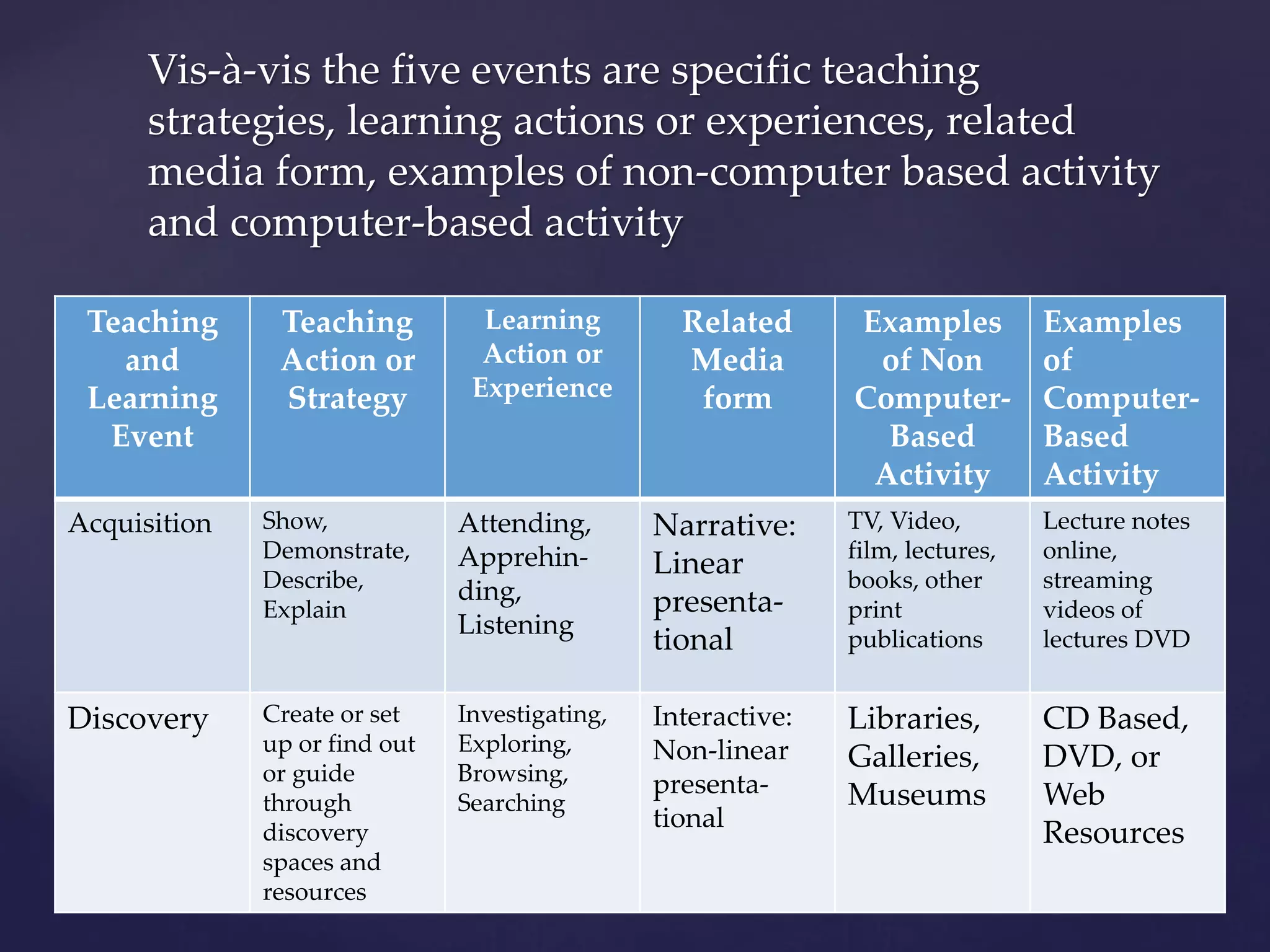
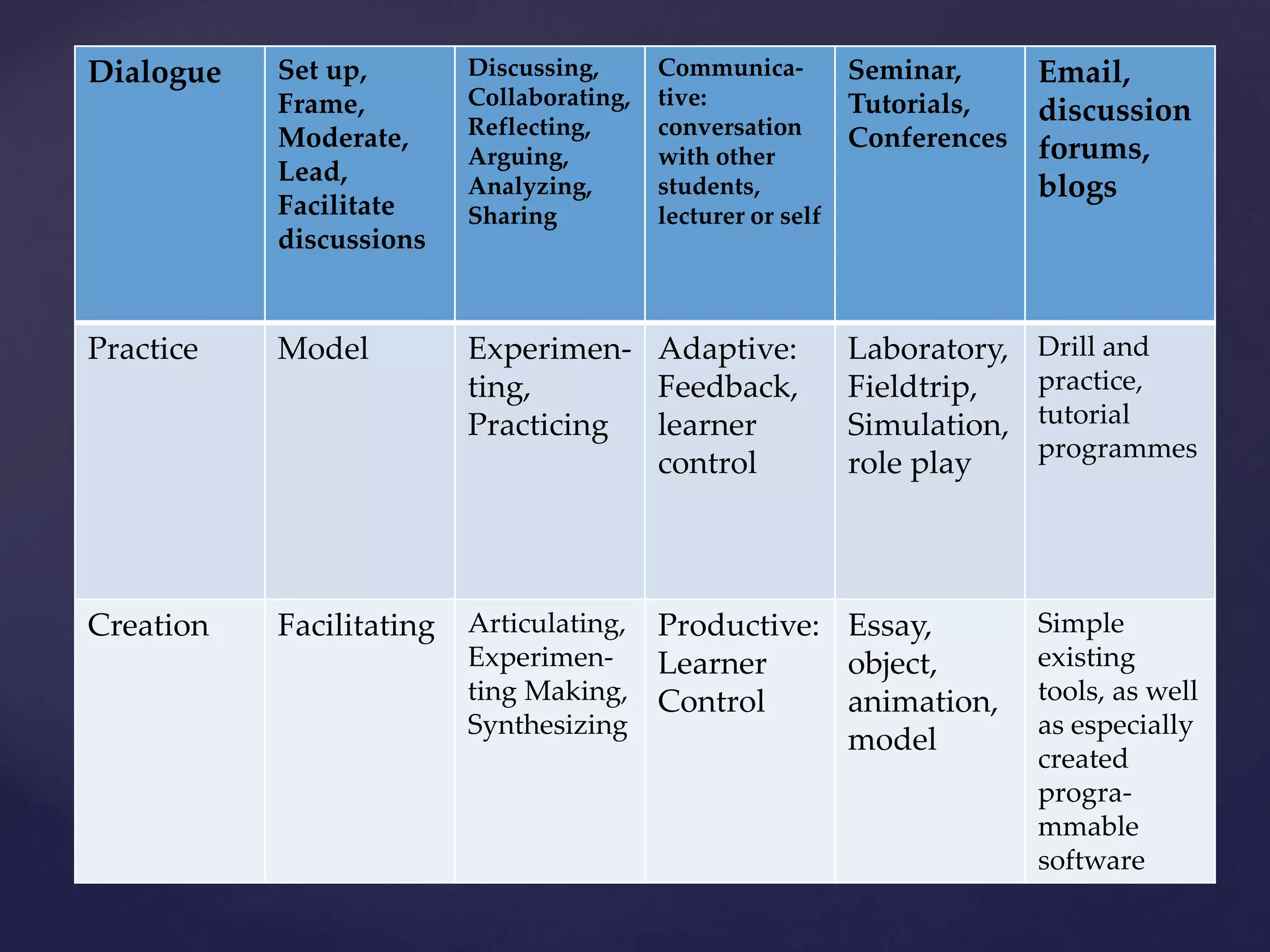
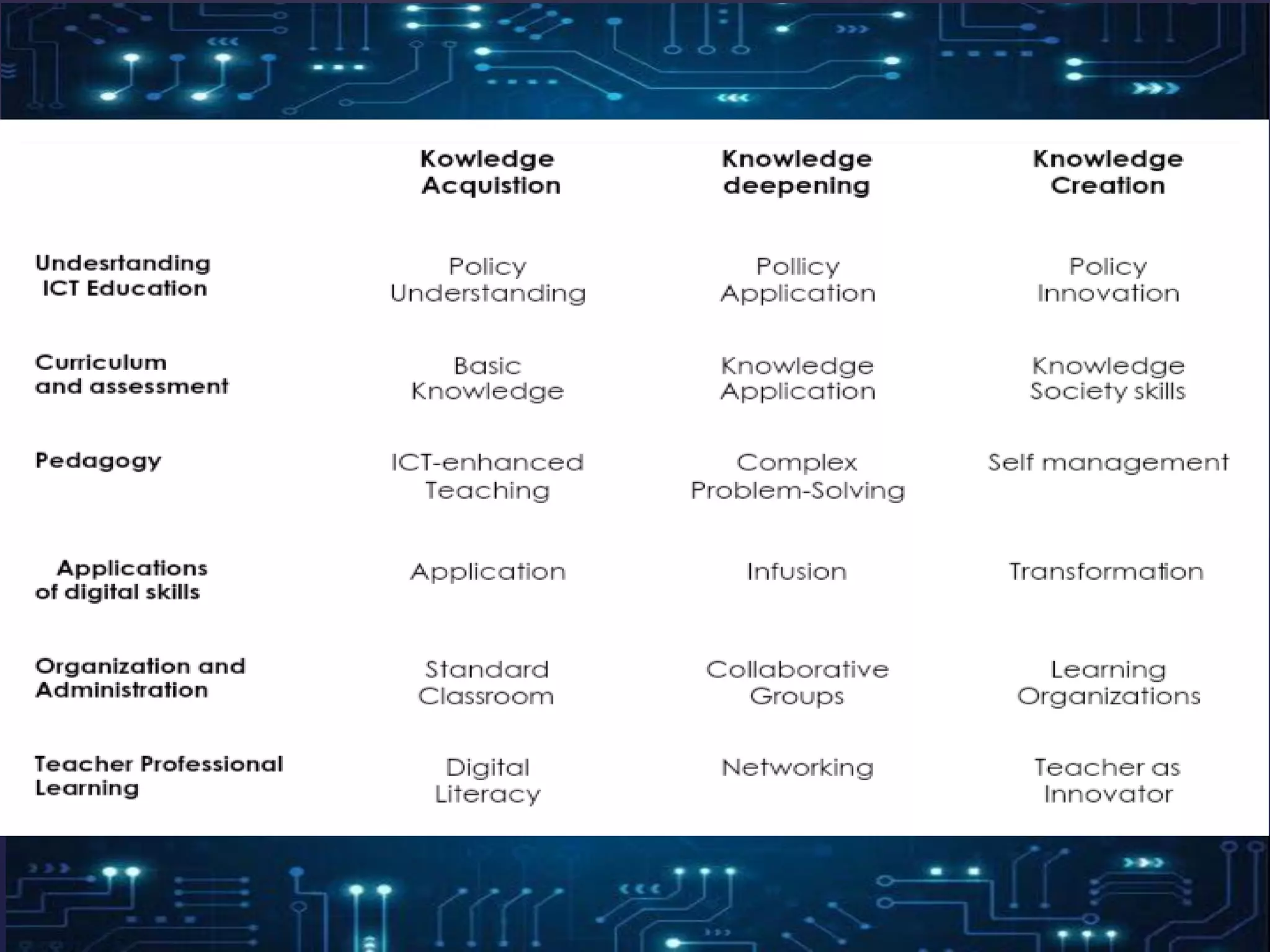
The document discusses the integration of information and communication technology (ICT) in language learning plans, emphasizing the need for teachers to engage educational technologies to enhance teaching and learning processes. It outlines learning outcomes related to ICT integration, key principles from various educators, and frameworks for implementing ICT in instruction, highlighting the importance of pedagogy, social interaction, and technology. Furthermore, it references UNESCO's ICT competency framework for teachers aimed at educational reform and sustainable development.