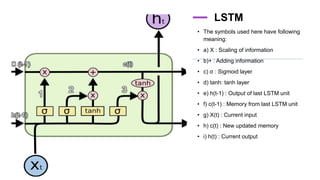
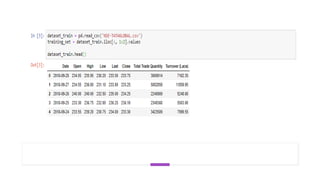
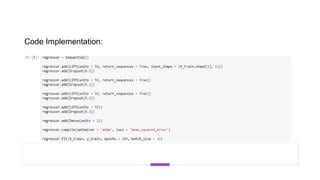
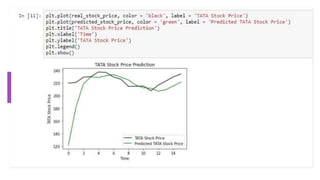
The document provides information about implementing LSTM for stock market analysis. It discusses LSTM architecture, applications of LSTM including time series prediction and speech recognition, advantages such as dealing with vanishing gradients, and disadvantages including longer training time. It also discusses applications of LSTM in areas like robot control, rhythm learning, and handwriting recognition.