Embed presentation
Download to read offline




The document discusses the process of lexical analysis in compiler design. It explains that a lexical analyzer takes source code as input and outputs tokens. It uses two pointers - a begin pointer that points to the start of each token, and a forward pointer that moves through the input string character by character. The document then describes two approaches for buffering input - a single buffer scheme that has issues if a token spans the buffer, and a two buffer scheme that avoids this issue by using two buffers and switching between them.
An introductory slide presenting the speaker, Rushikesh Kadam, and the topic related to System Software.
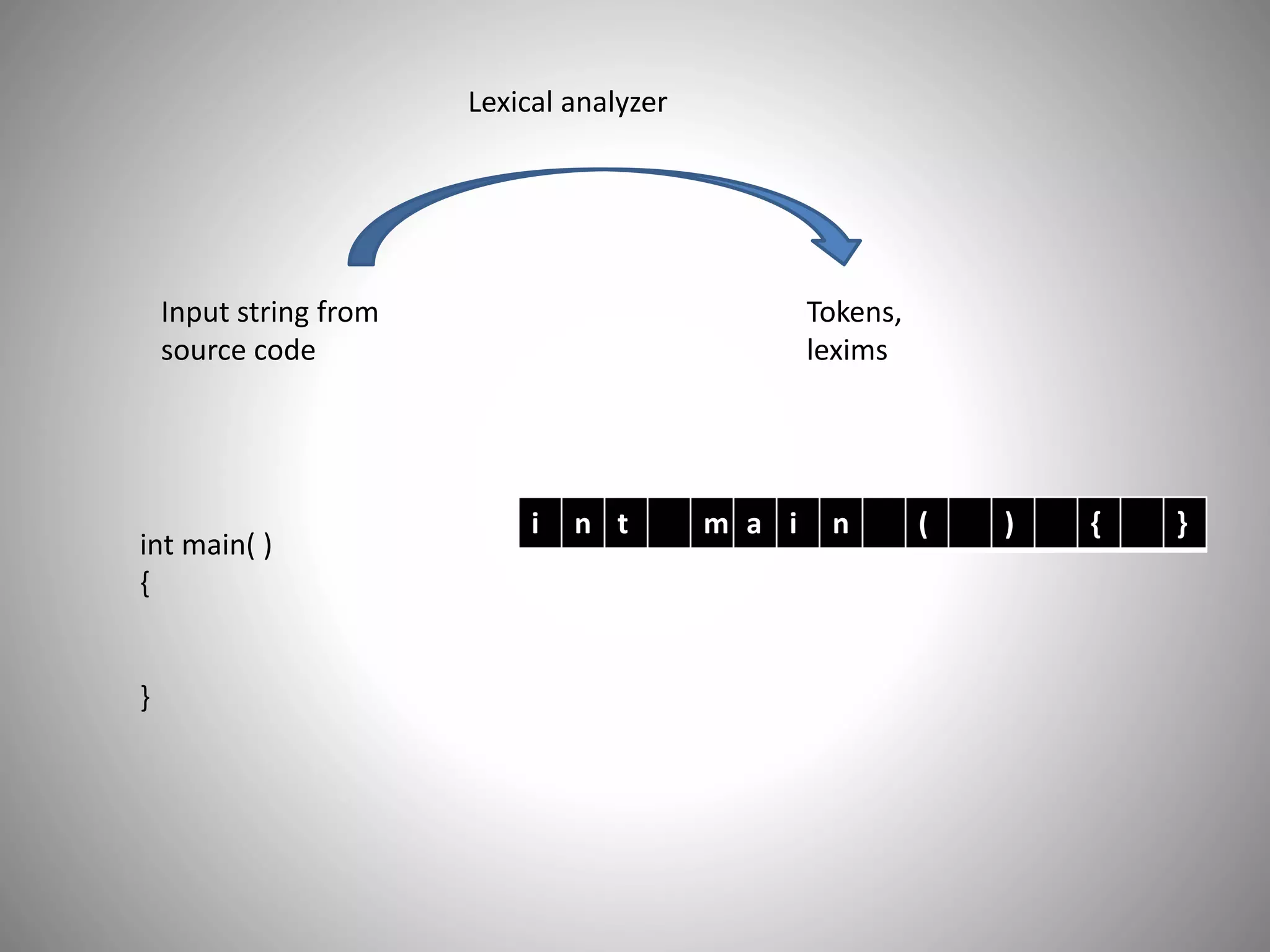
Introduction to the lexical analyzer with input from source code producing tokens and lexis using an example 'int main() {}'.
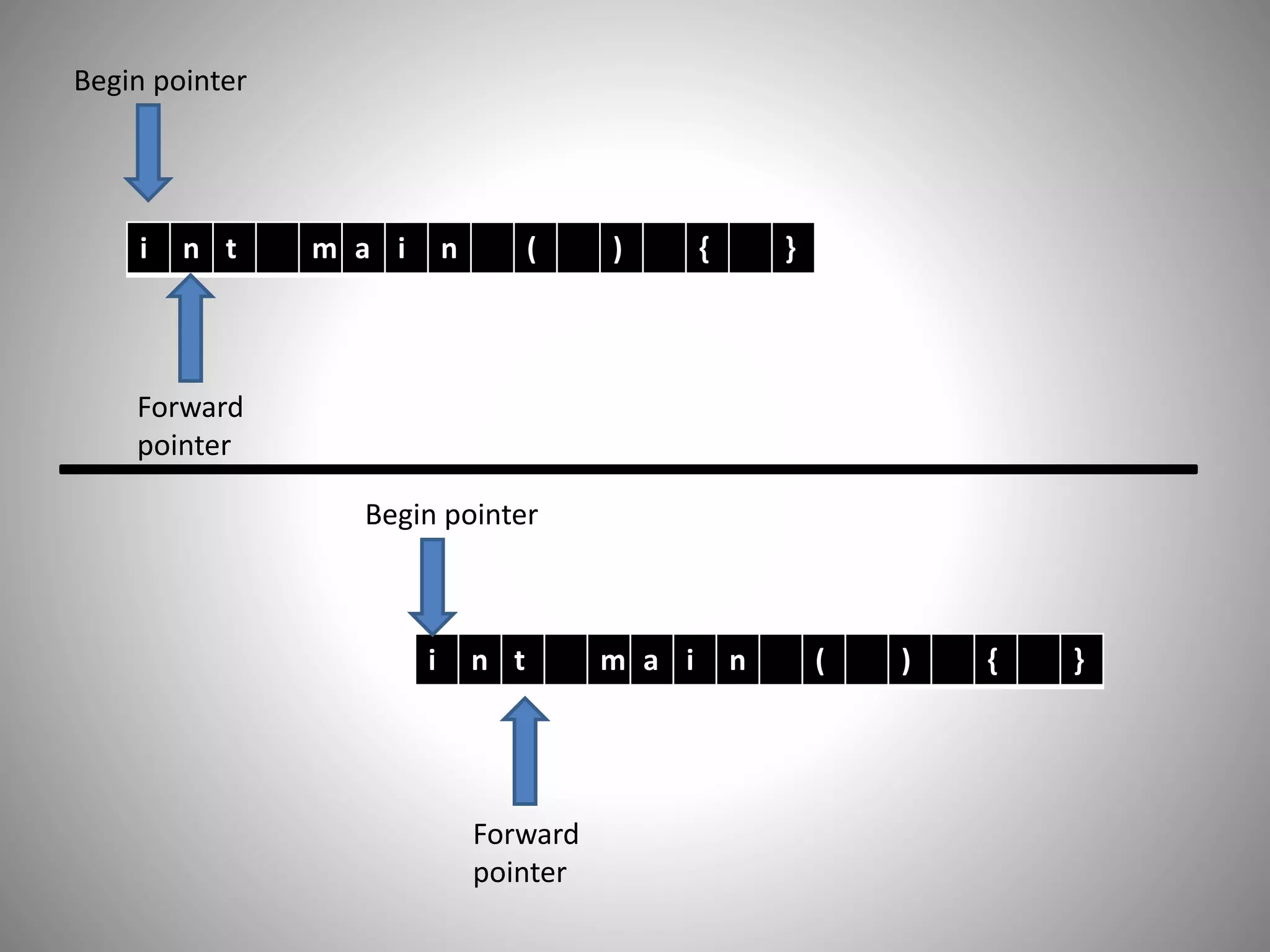
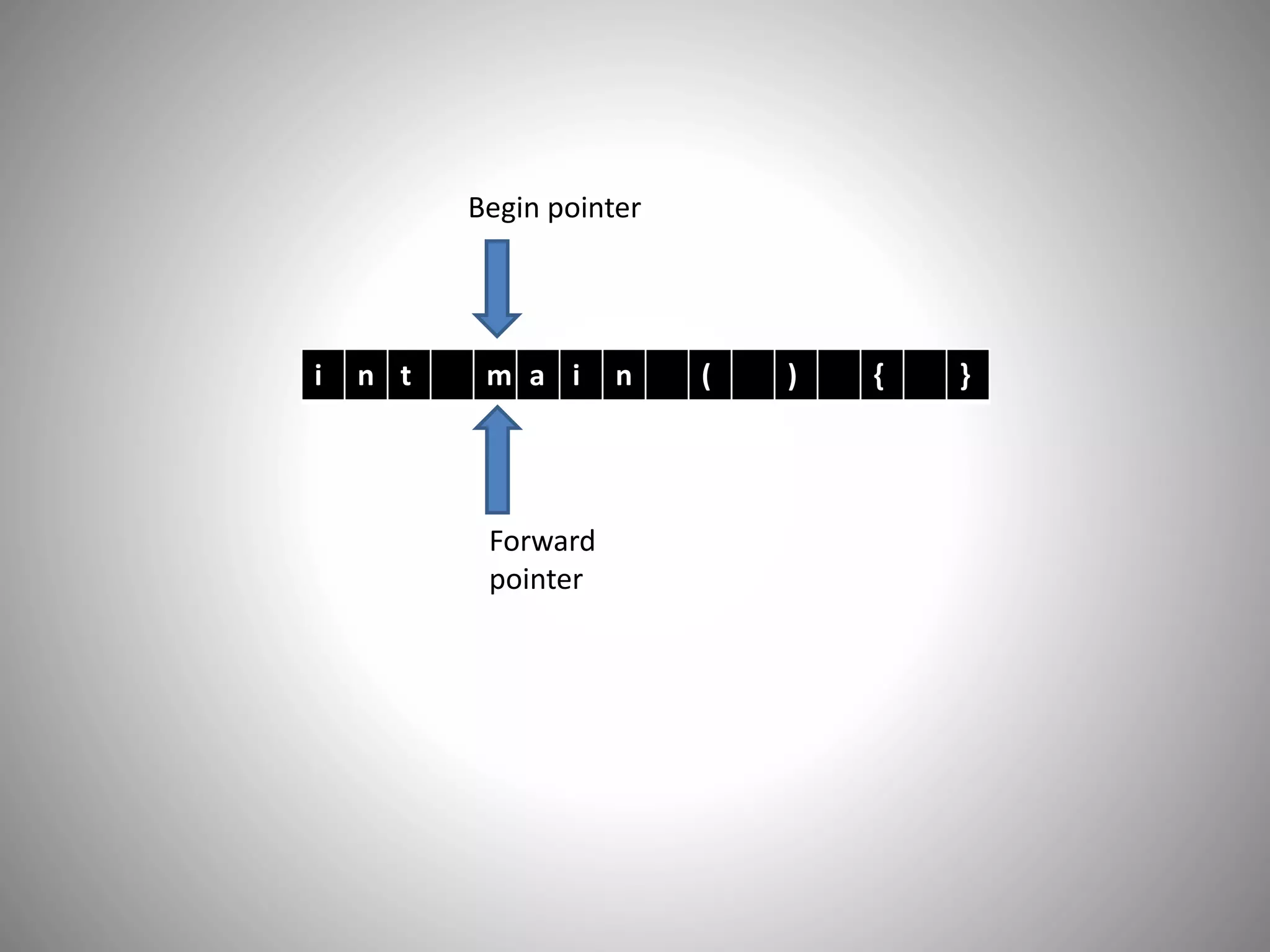
Explanation of pointers in lexical analysis: Begin pointer (marks token start) and Forward pointer (points to next character).
Further visualization of the Begin and Forward pointers using the example 'int main() {}' to illustrate functionality.
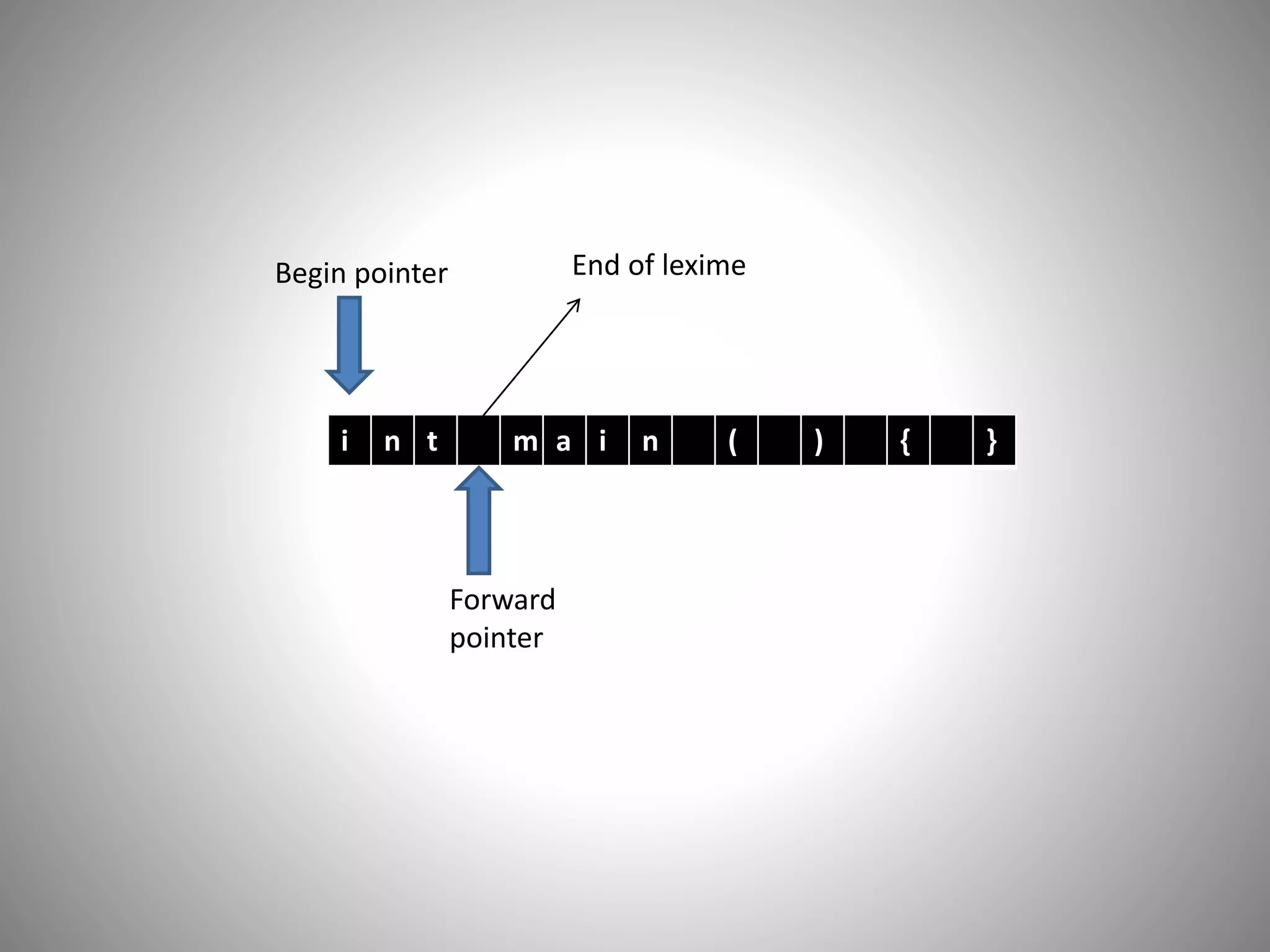
Continuing with the visualization focusing on the mechanics of determining the end of a lexeme.
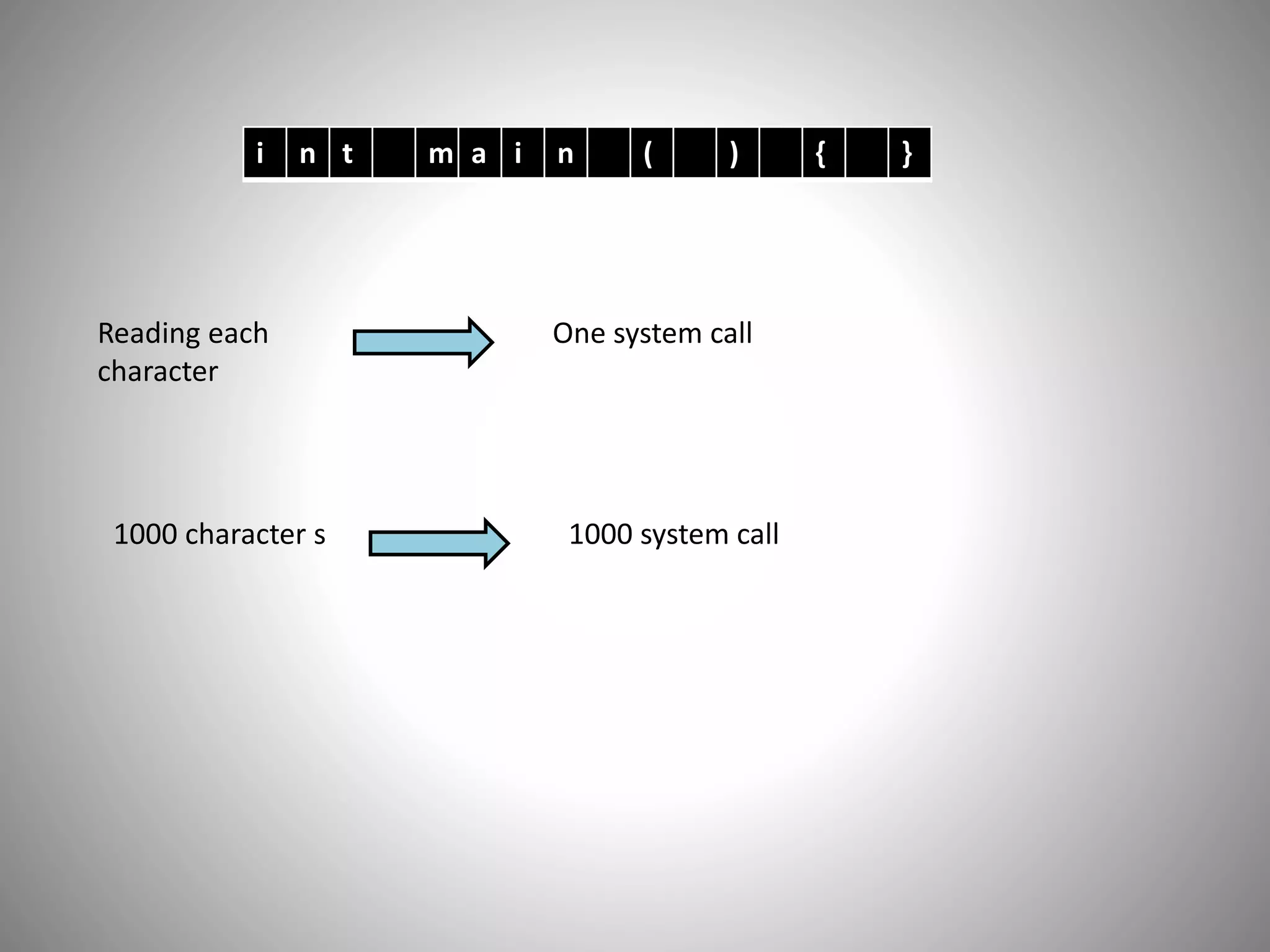
Details on reading each character with emphasis on system calls; mentions efficiency with 1000 characters per call.
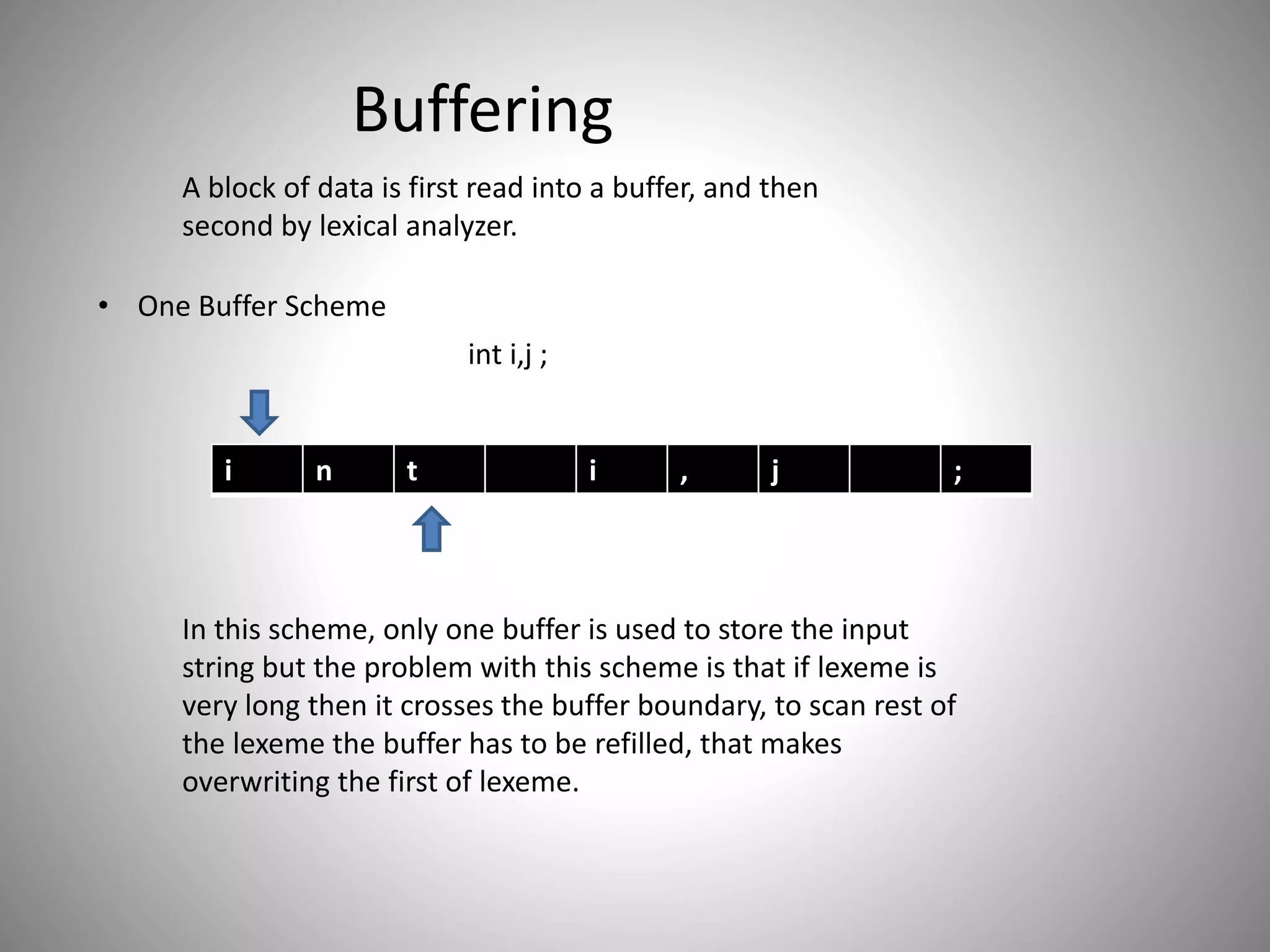
Introduction to buffering schemes: One Buffer Scheme (issues with long lexemes) and the need for efficient data handling.
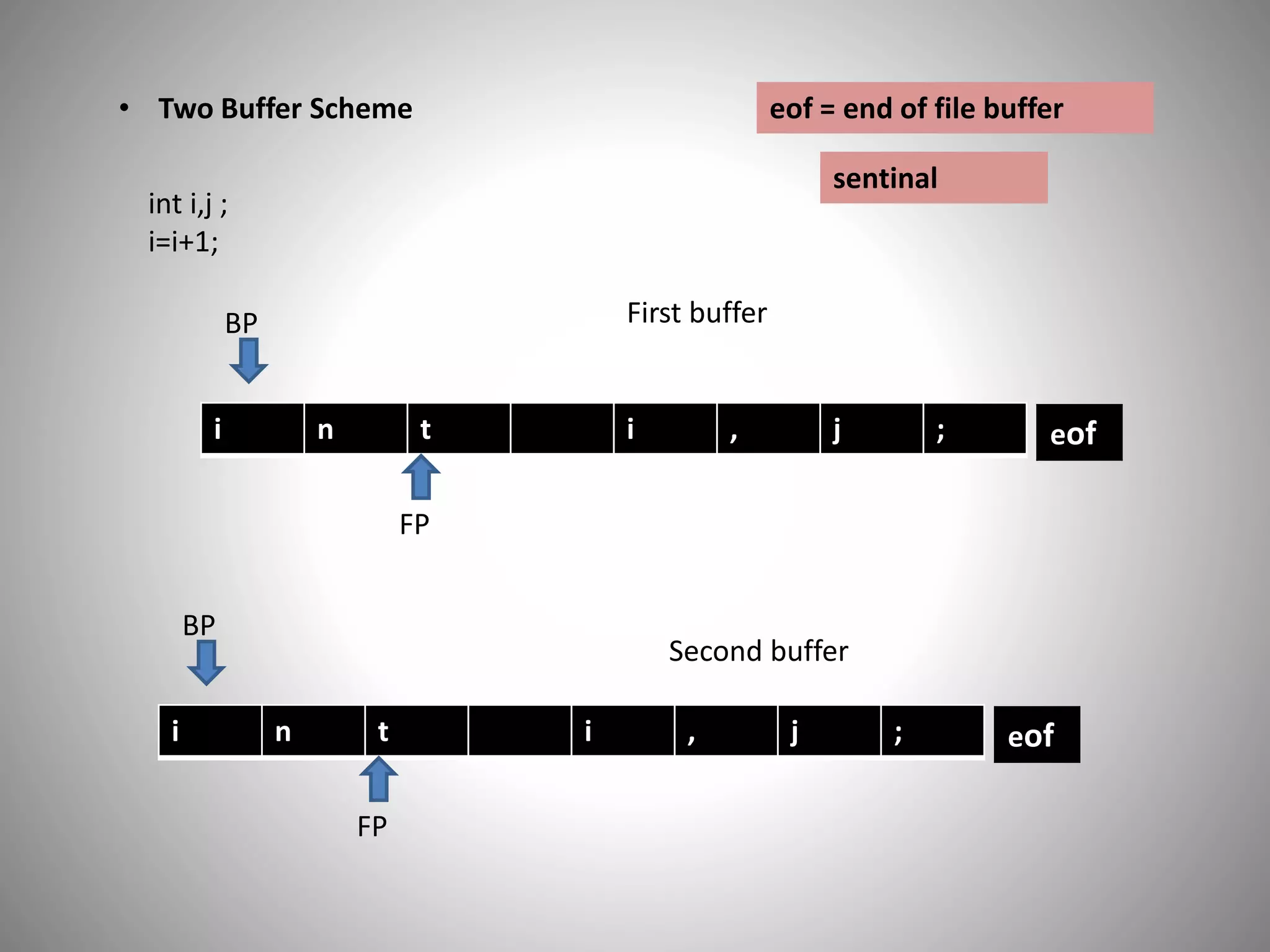
In-depth on the Two Buffer Scheme using 'int i,j;' demonstrating how two buffers facilitate lexeme processing.
Algorithm for handling input with buffer refilling logic for end of file and character processing using switches.
Concluding slide expressing gratitude and closing the presentation.










