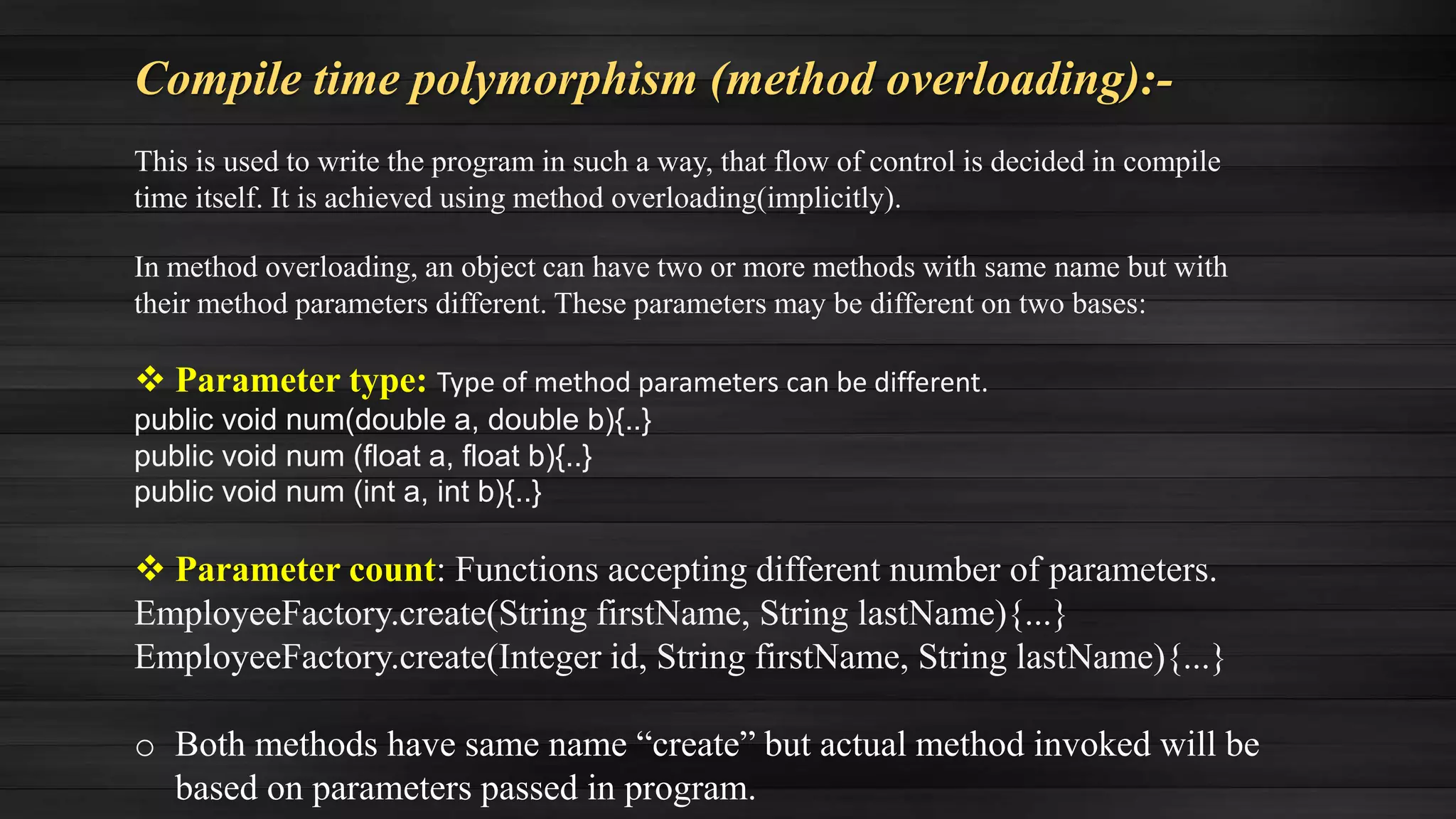
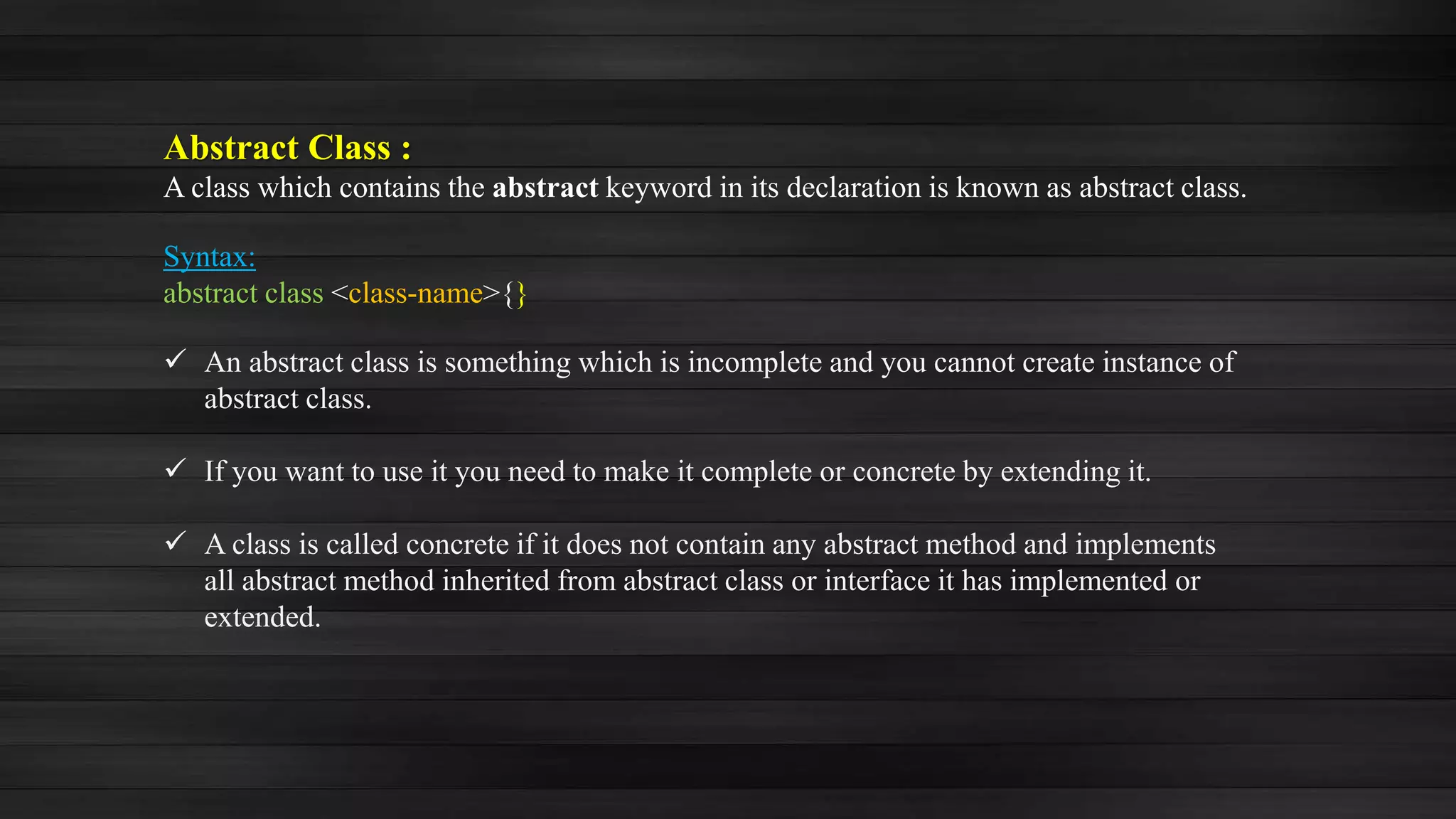
Polymorphism in Java allows an object to take on multiple forms. There are two types of polymorphism: compile-time polymorphism (method overloading) and runtime polymorphism (method overriding). Method overloading involves methods with the same name but different parameters, while method overriding involves subclasses providing their own implementation of a superclass method. Abstract classes allow defining methods without implementation, requiring subclasses to implement them, while interfaces only define method signatures that implementing classes must then define.



![Depends on type of actual instance created on runtime.
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
students a1 = new Ghazanfar();
a1.study();
students a2 = new rafah();
a2.study();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymorphismpresentation-160825122725-230804120908-b4bb5bd3/75/polymorphismpresentation-160825122725-pdf-5-2048.jpg)


![package program;
//abstract class
abstract class Sum{
//abstract methods
public abstract int SumOfTwo(int n1, int n2);
public abstract int SumOfThree(int n1, int n2, int n3);
//Regular method
public void disp(){ System.out.println("Method of class Sum");
} }
class AbstractDemo extends Sum{
public int SumOfTwo(int num1, int num2){
return num1+num2;
}
public int SumOfThree(int num1, int num2, int num3){
return num1+num2+num3;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
AbstractDemo obj = new AbstractDemo();
System.out.println(obj.SumOfTwo(3, 7));
System.out.println(obj.SumOfThree(4, 3, 19));
obj.disp();
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymorphismpresentation-160825122725-230804120908-b4bb5bd3/75/polymorphismpresentation-160825122725-pdf-9-2048.jpg)
![package presentation;
//Interface
interface Multiply{
//abstract methods
public abstract int multiplyTwo(int n1, int n2);
int multiplyThree(int n1, int n2, int n3);
}
class AbstractDemo2 implements Multiply{
public int multiplyTwo(int num1, int num2){
return num1*num2; }
public int multiplyThree(int num1, int num2, int num3){
return num1*num2*num3; }
public static void main(String args[]){
AbstractDemo2 obj = new AbstractDemo2();
System.out.println(obj.multiplyTwo(3, 7));
System.out.println(obj.multiplyThree(1, 9, 0)); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymorphismpresentation-160825122725-230804120908-b4bb5bd3/75/polymorphismpresentation-160825122725-pdf-10-2048.jpg)
