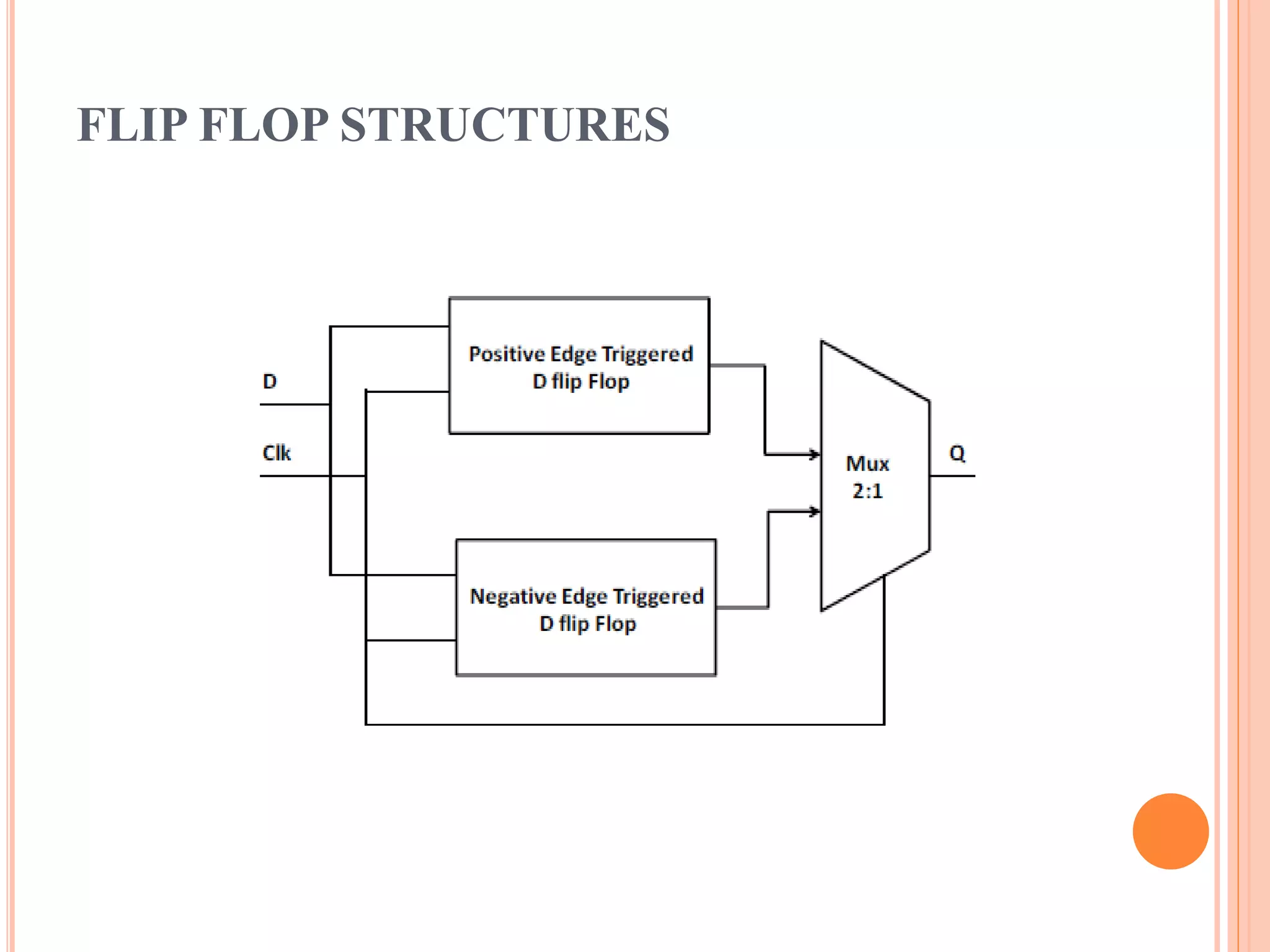
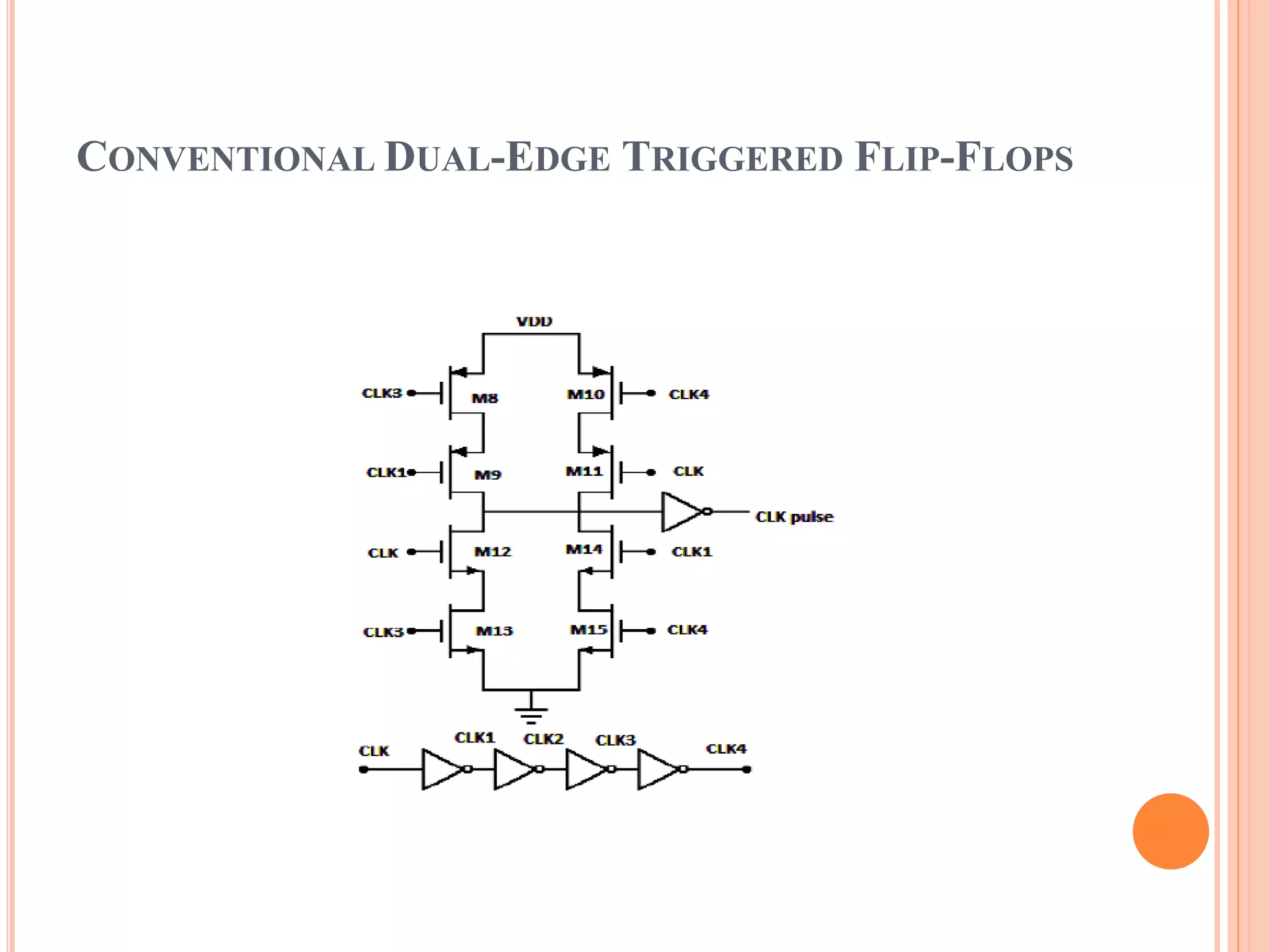
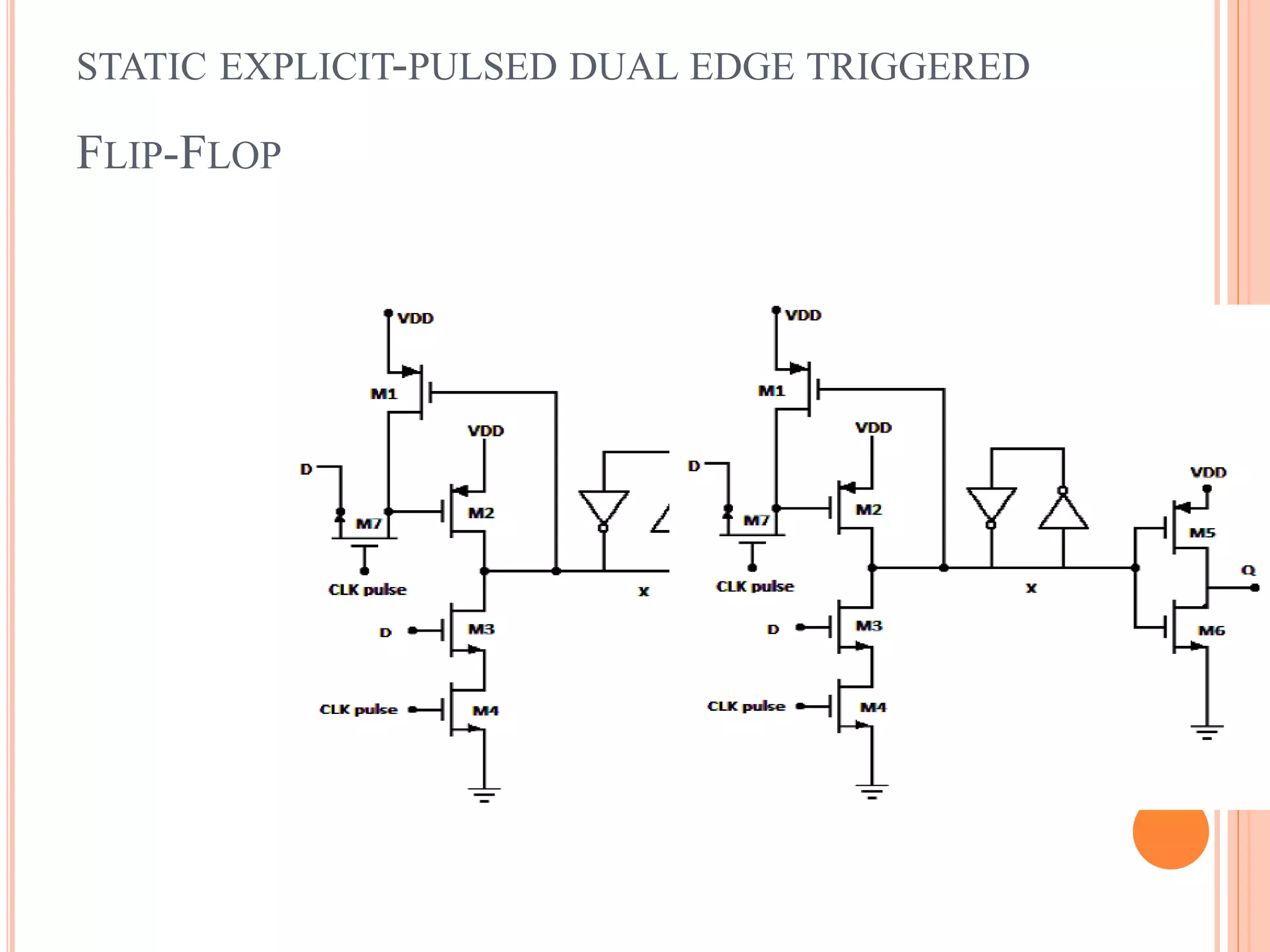
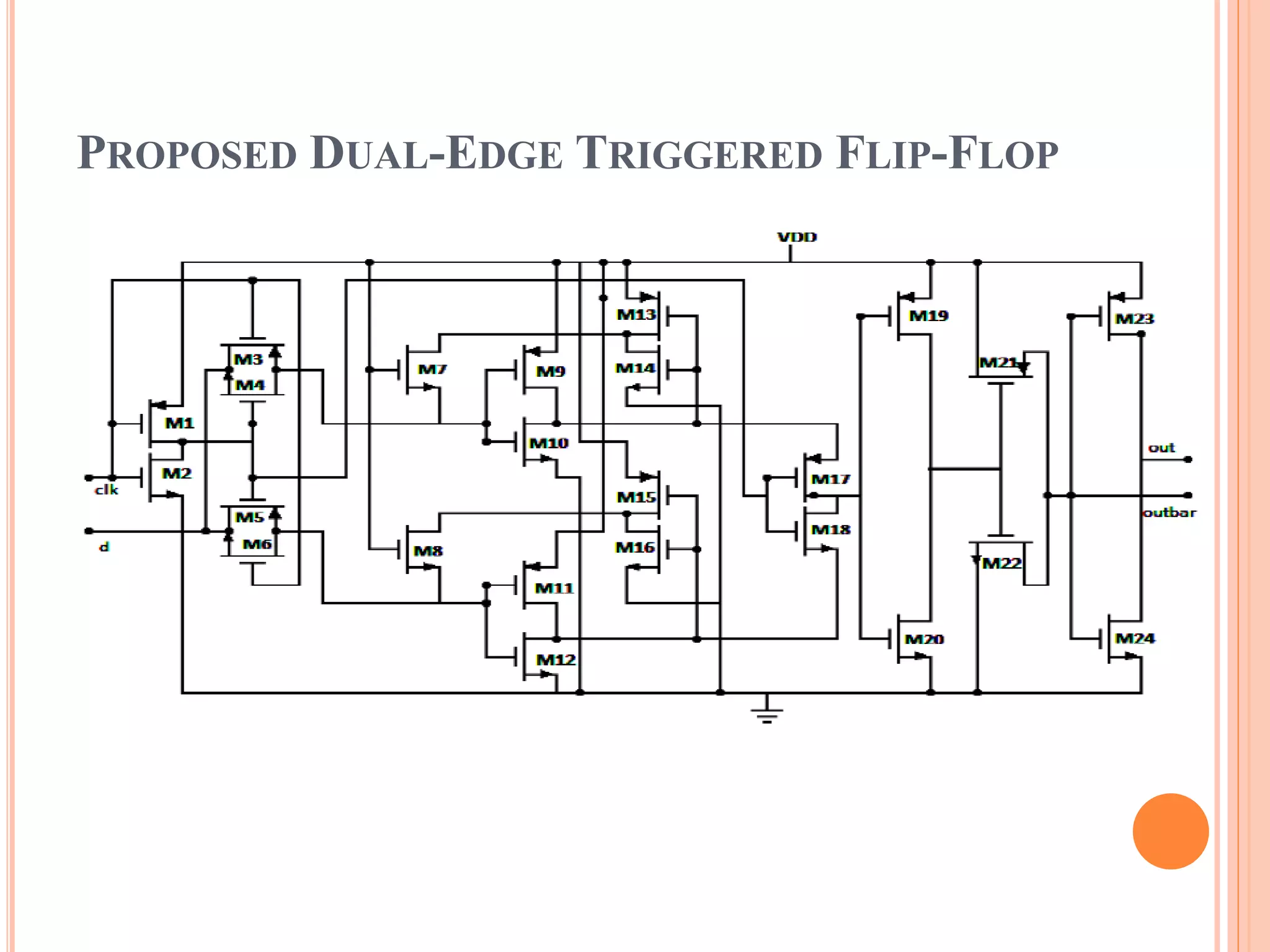
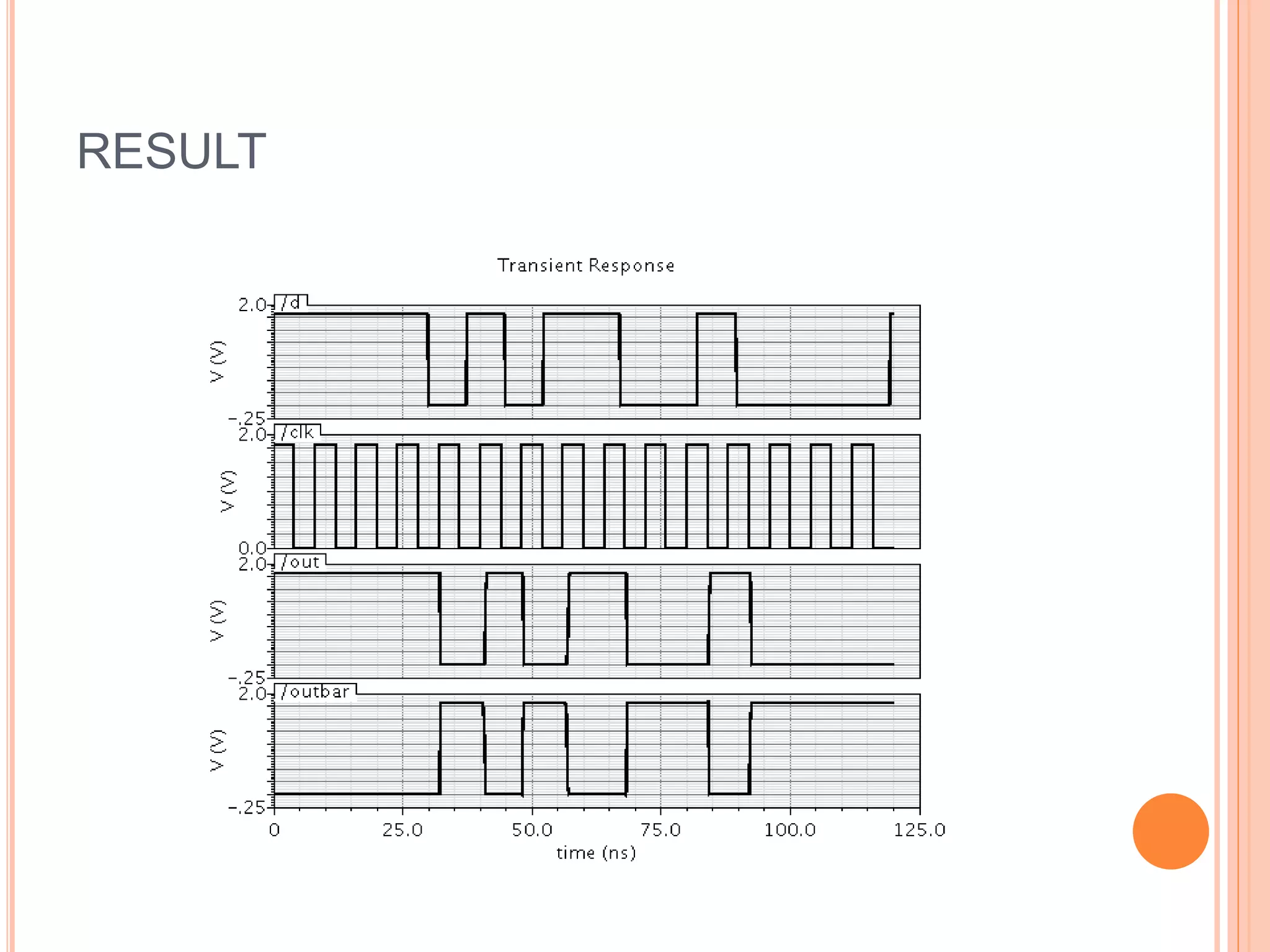
This document discusses low power dual edge triggered static flip-flops. It begins by explaining how increasing clock frequency increases power consumption. It then introduces dual edge triggered flip-flops (DETFFs) which can capture data on both the rising and falling clock edges, allowing the clock frequency to be doubled without increasing power. The document presents the structure of conventional DETFFs and a proposed new static DETFF design using parallel positive and negative latches with a multiplexer to select the appropriate sampled data value. Simulation results show the new design achieves lower power and higher speed compared to previous DETFF approaches.