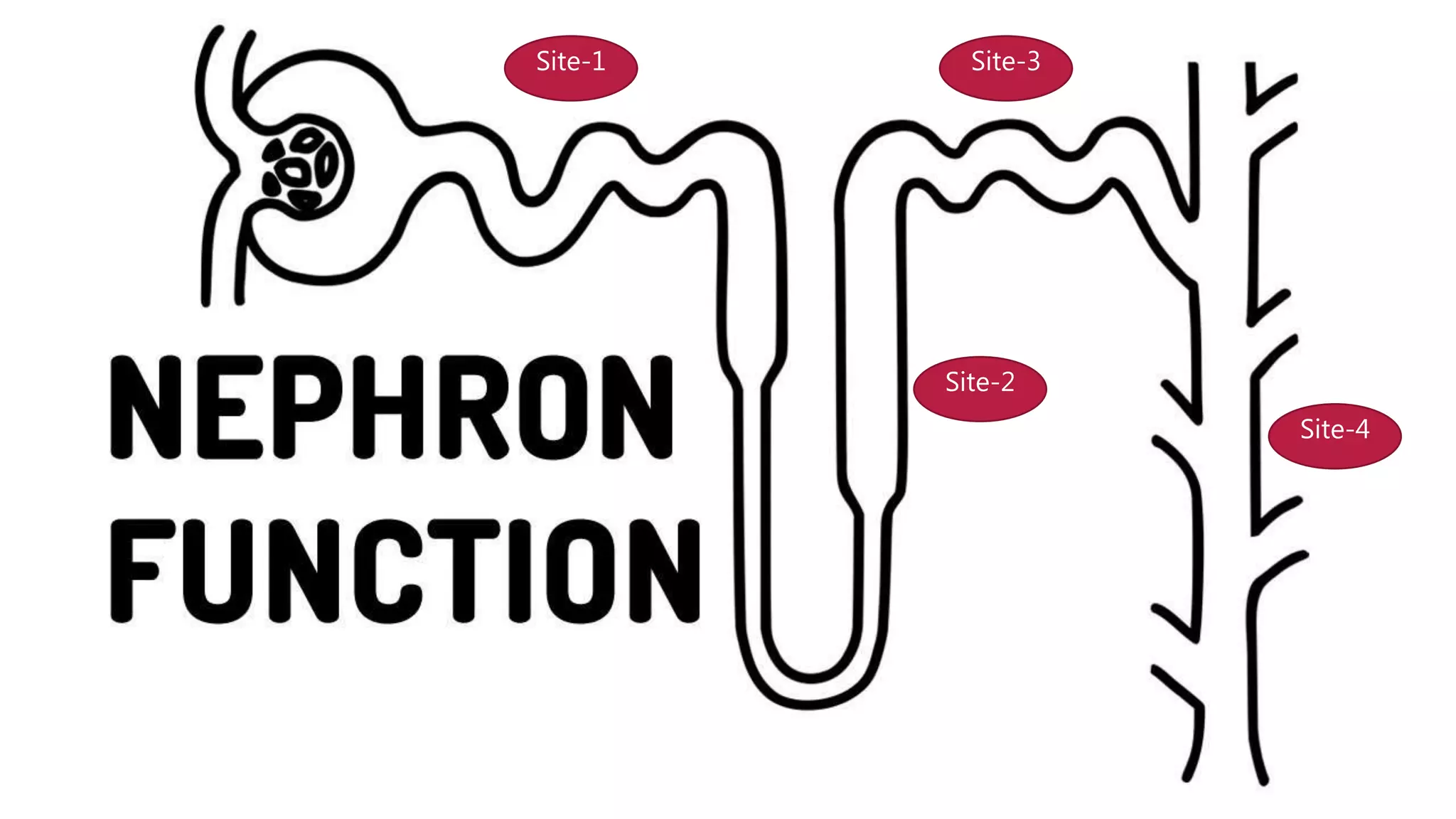
Loop diuretics act on the thick ascending loop of Henle by blocking the Na-K-2Cl symporter. They are used to treat conditions like acute cardiac failure, pulmonary edema, peripheral edema, hypertension, and hypercalcemia. Common side effects include hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and hypocalcemia. They can interact with aminoglycosides to cause ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Examples include furosemide, torsemide, and bumetanide. Furosemide is most commonly used and causes venodilation as well as increased renal blood flow through prostaglandin synthesis.