This document discusses key concepts in transportation and logistics including:
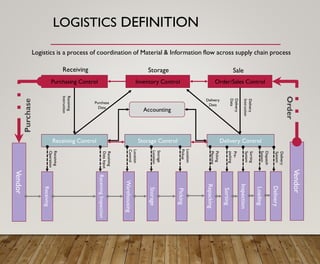
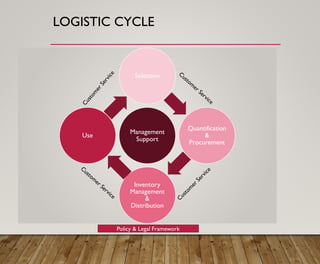
1. It defines logistics as the planning, implementation, and control of efficient material and information flow across a supply chain to meet customer requirements.
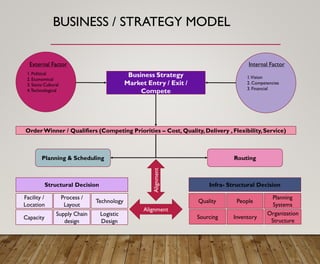
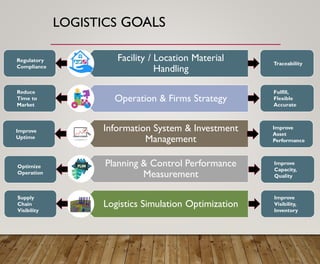
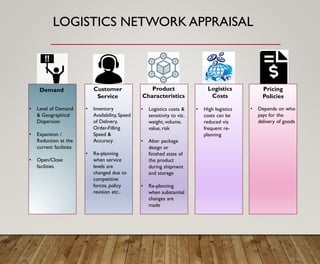
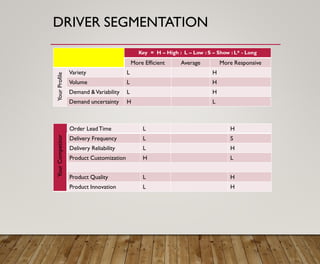
2. It discusses the importance of aligning a firm's logistics strategy with its overall business strategy by considering factors like costs, quality, delivery, flexibility and service.
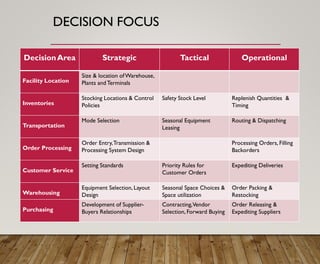
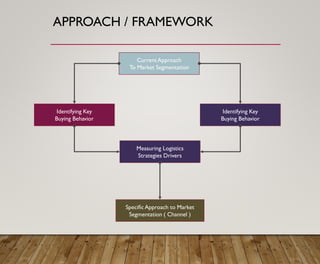
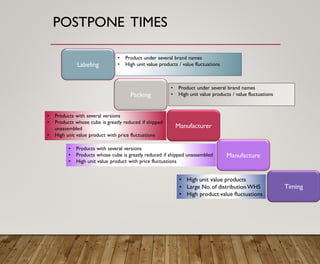
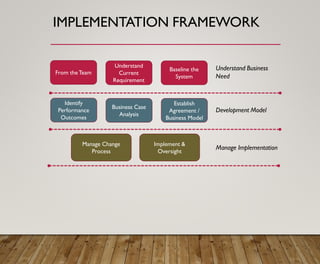
3. It provides an overview of logistics goals, decisions, networks and strategies around areas like inventory management, transportation, customer service and facility location planning.