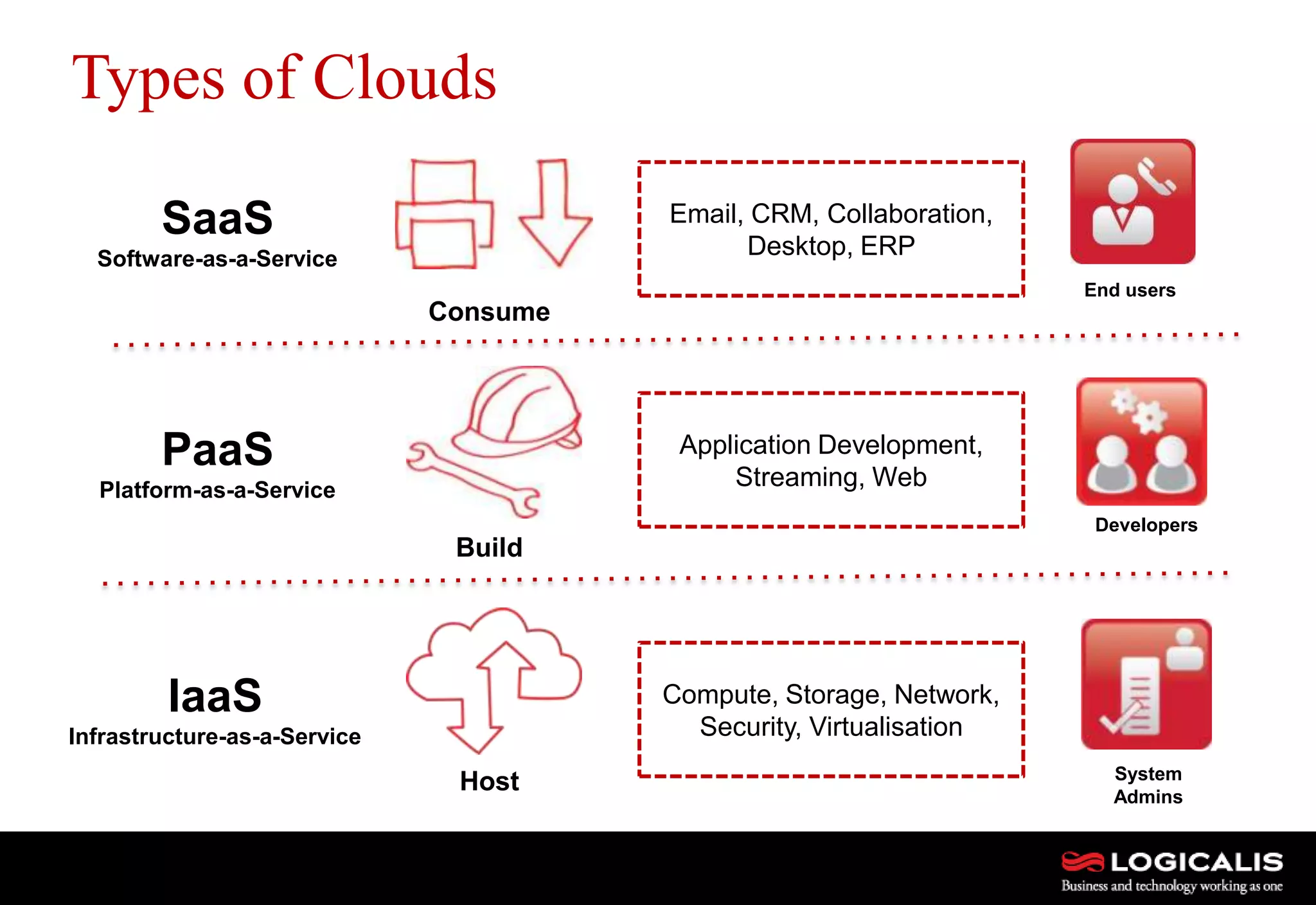
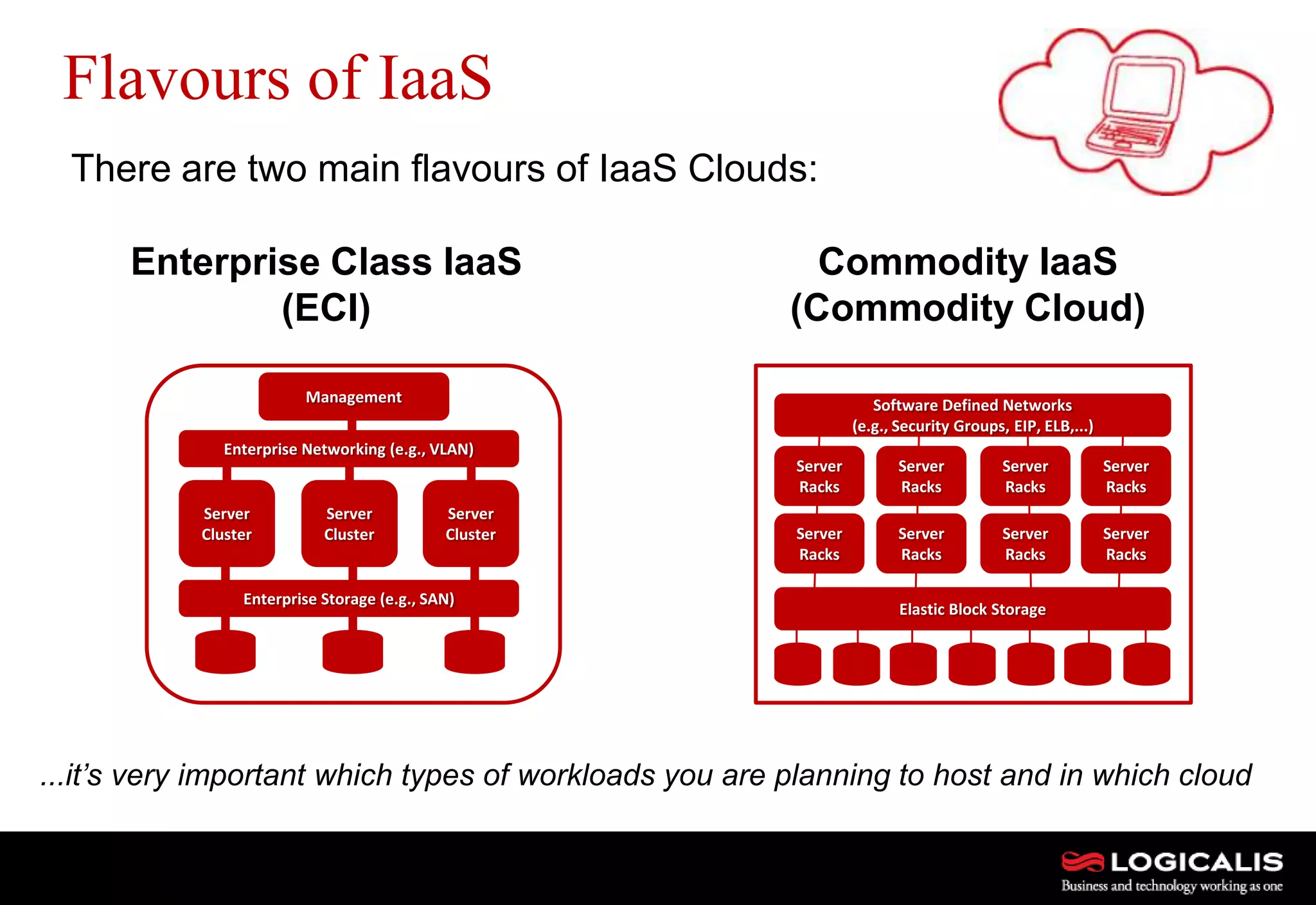
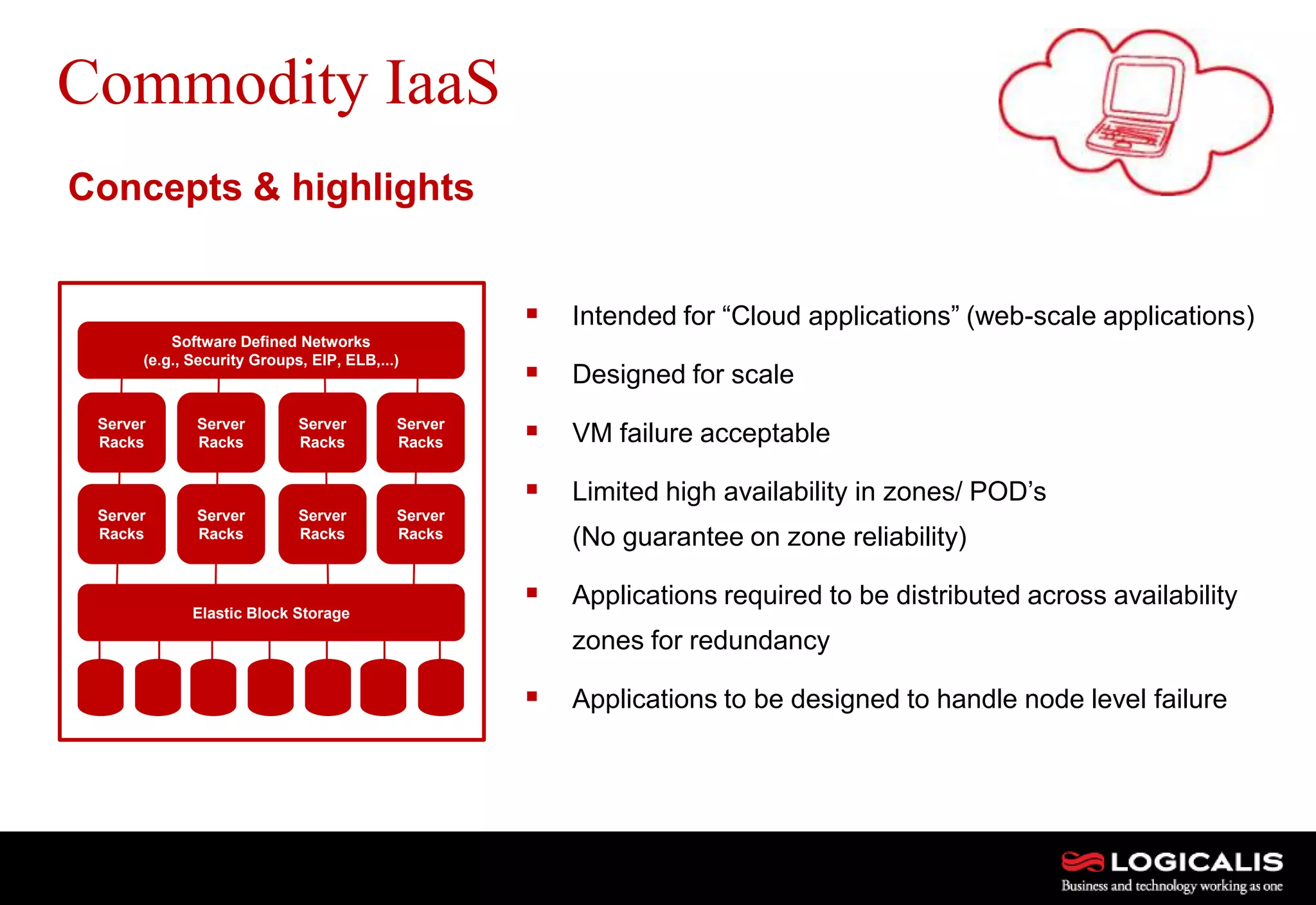
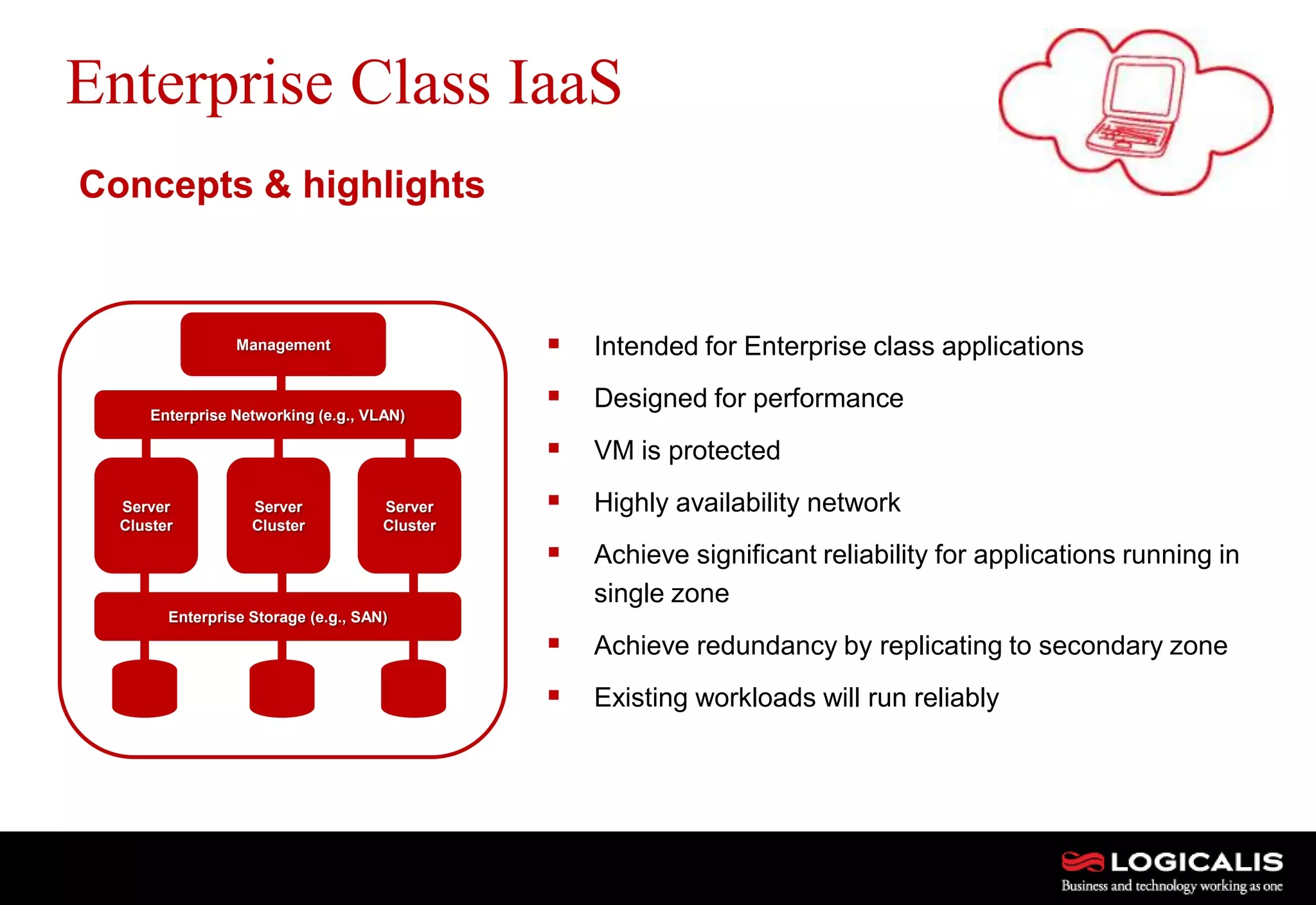
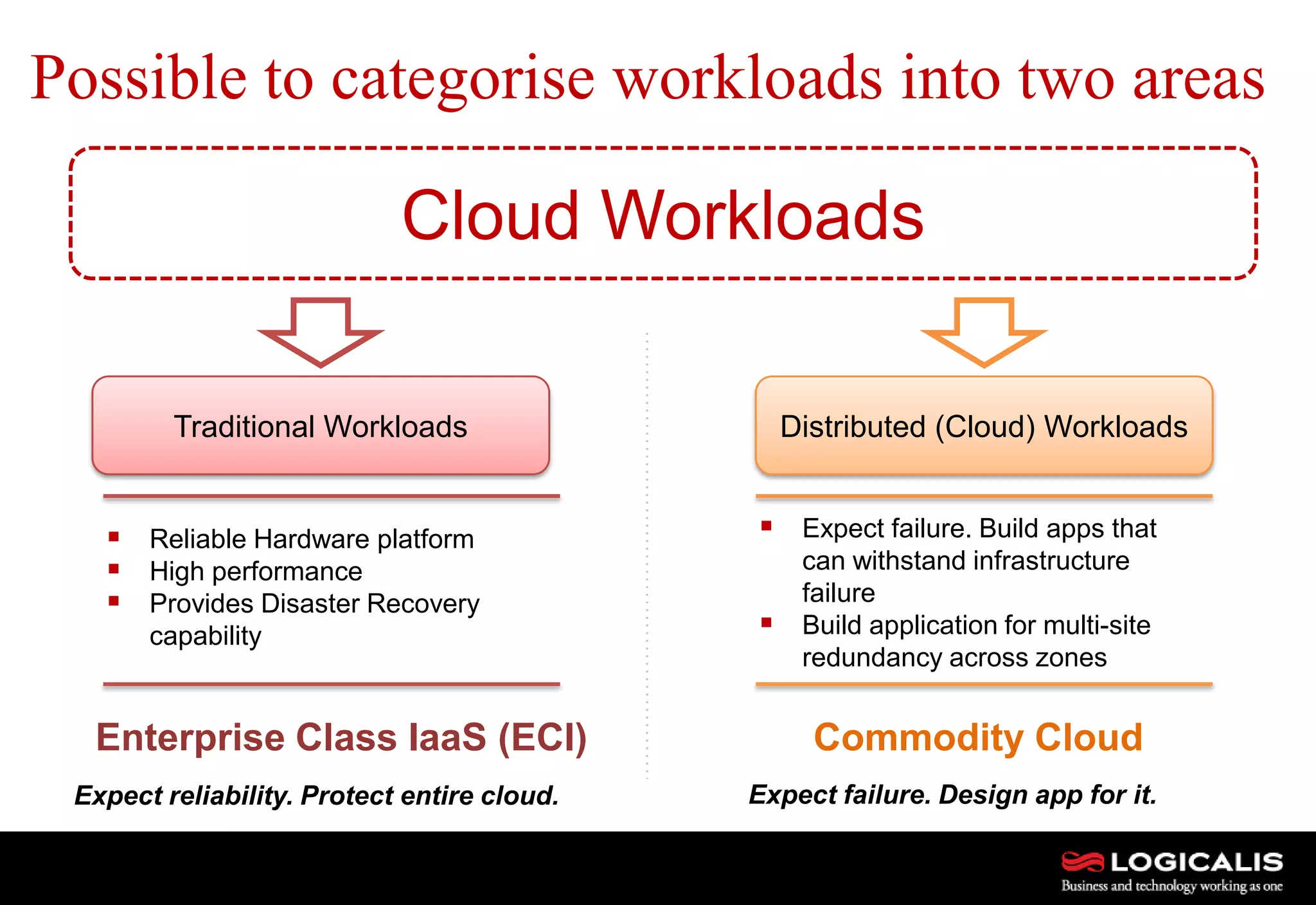
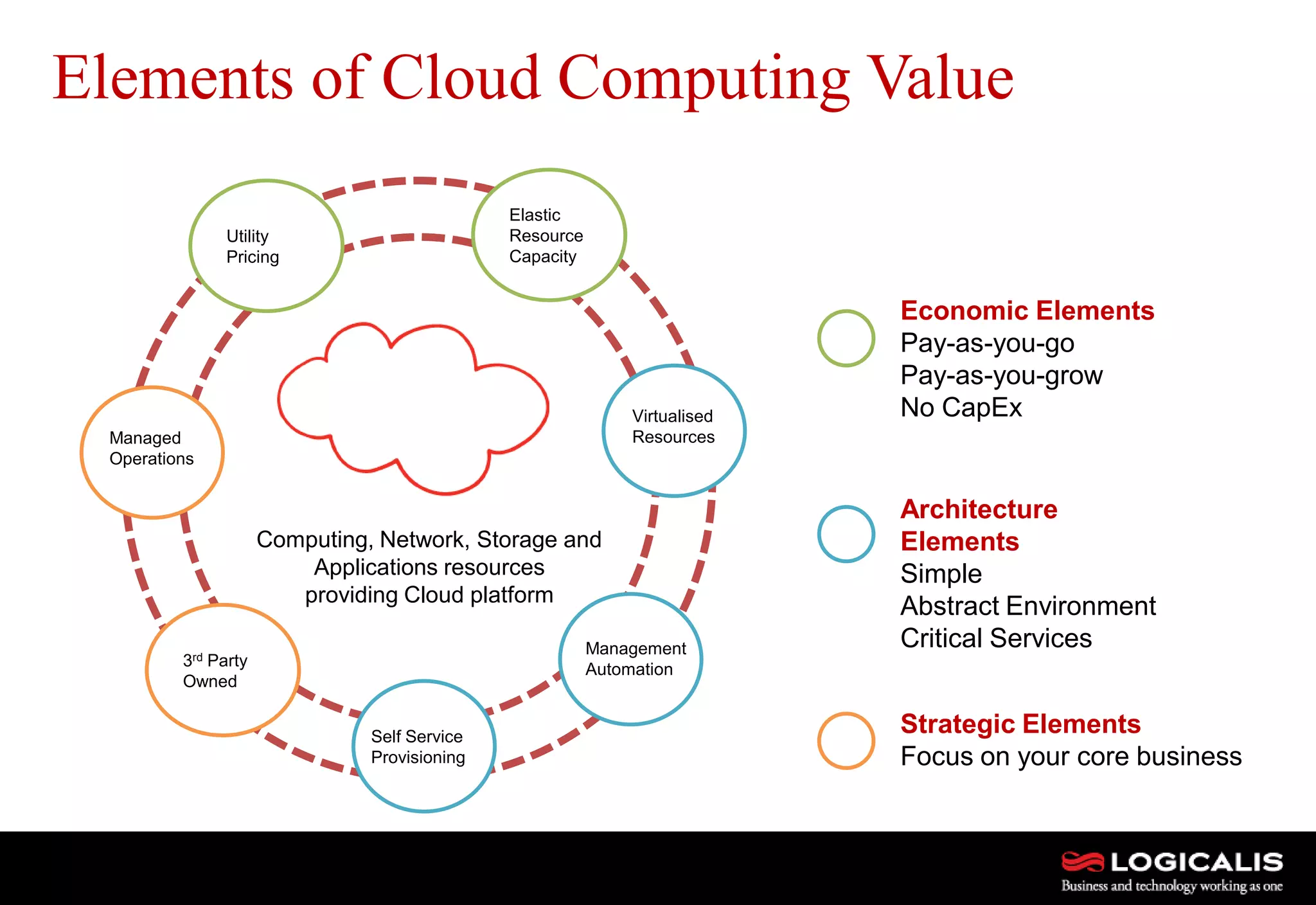
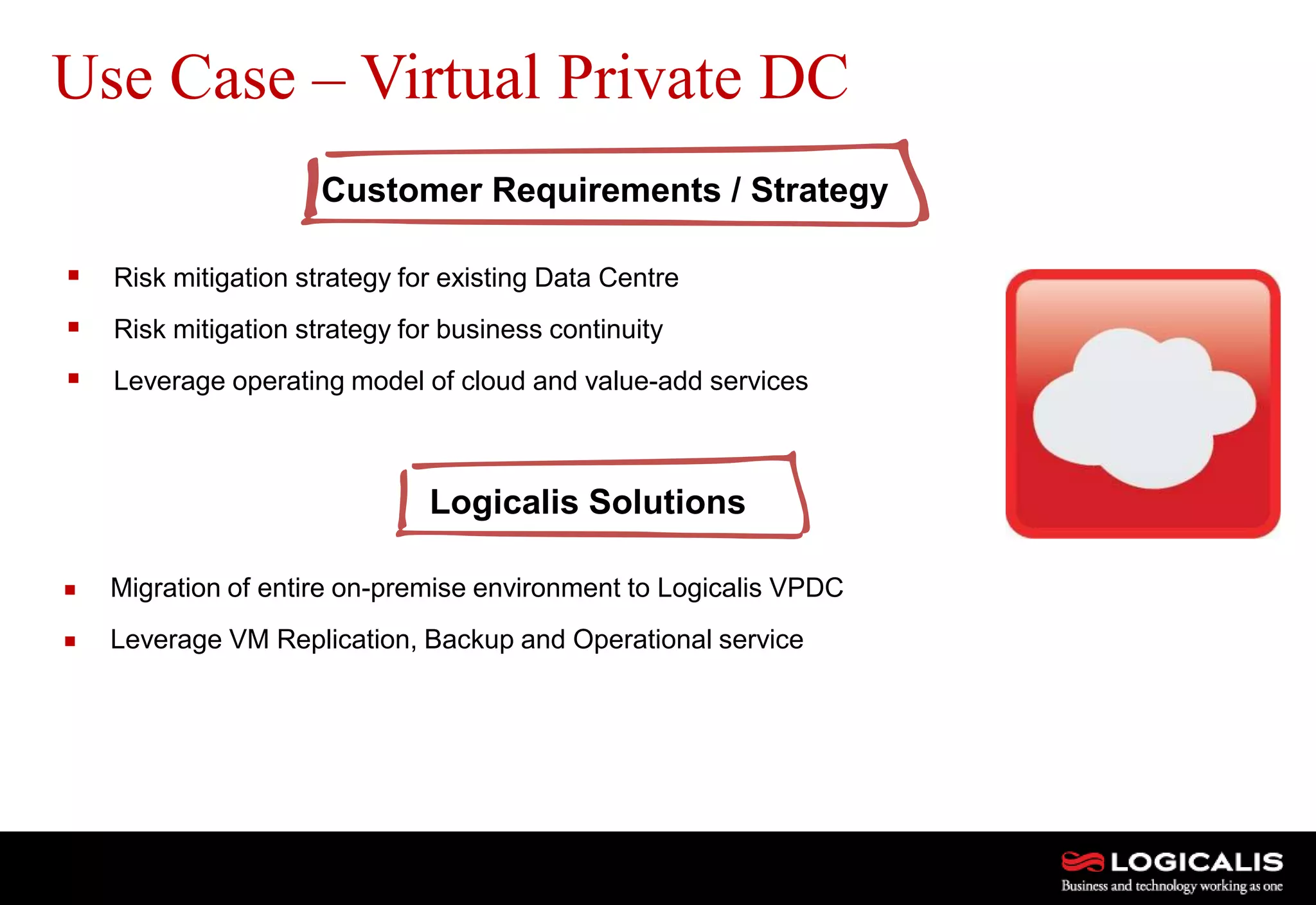
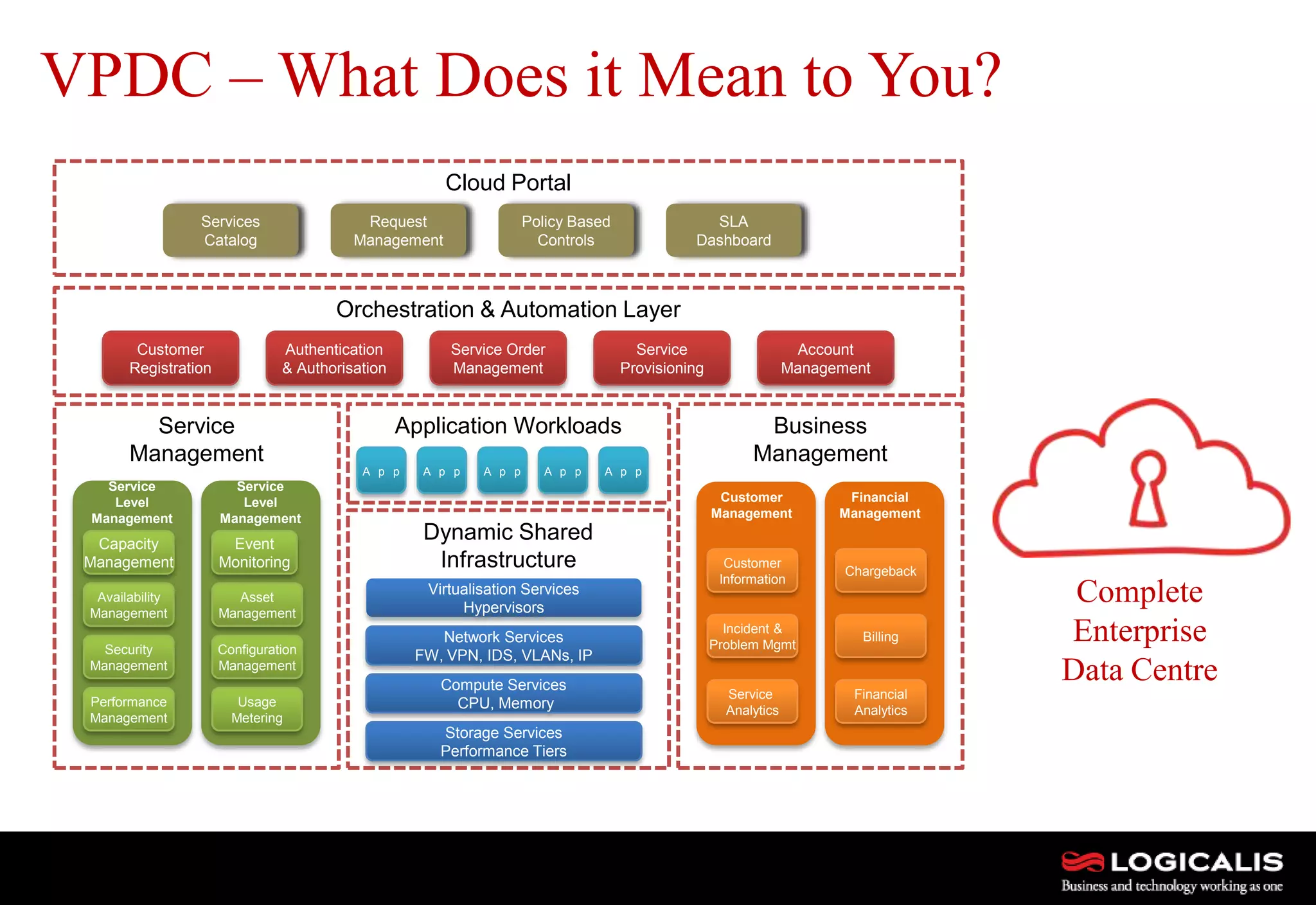
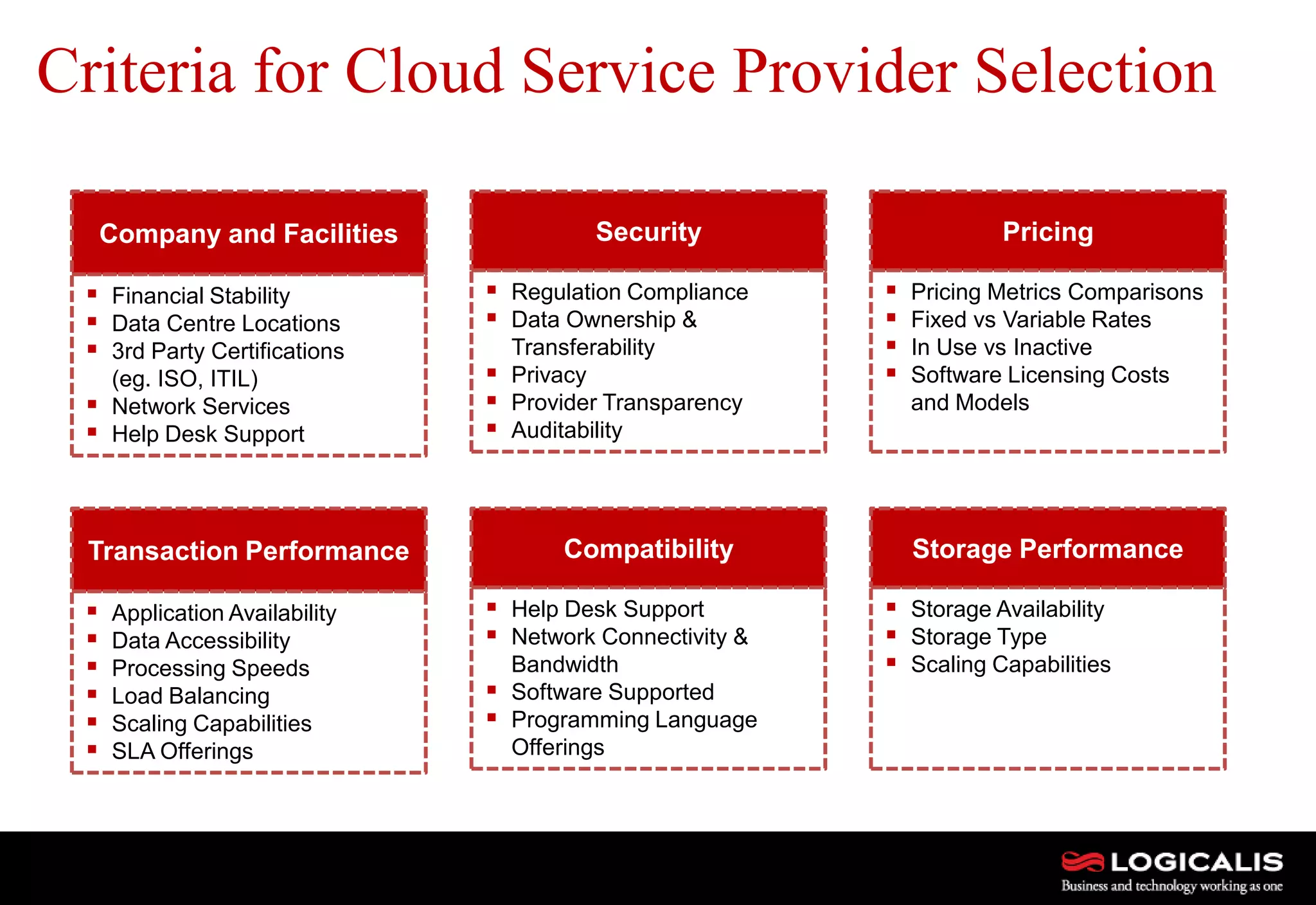
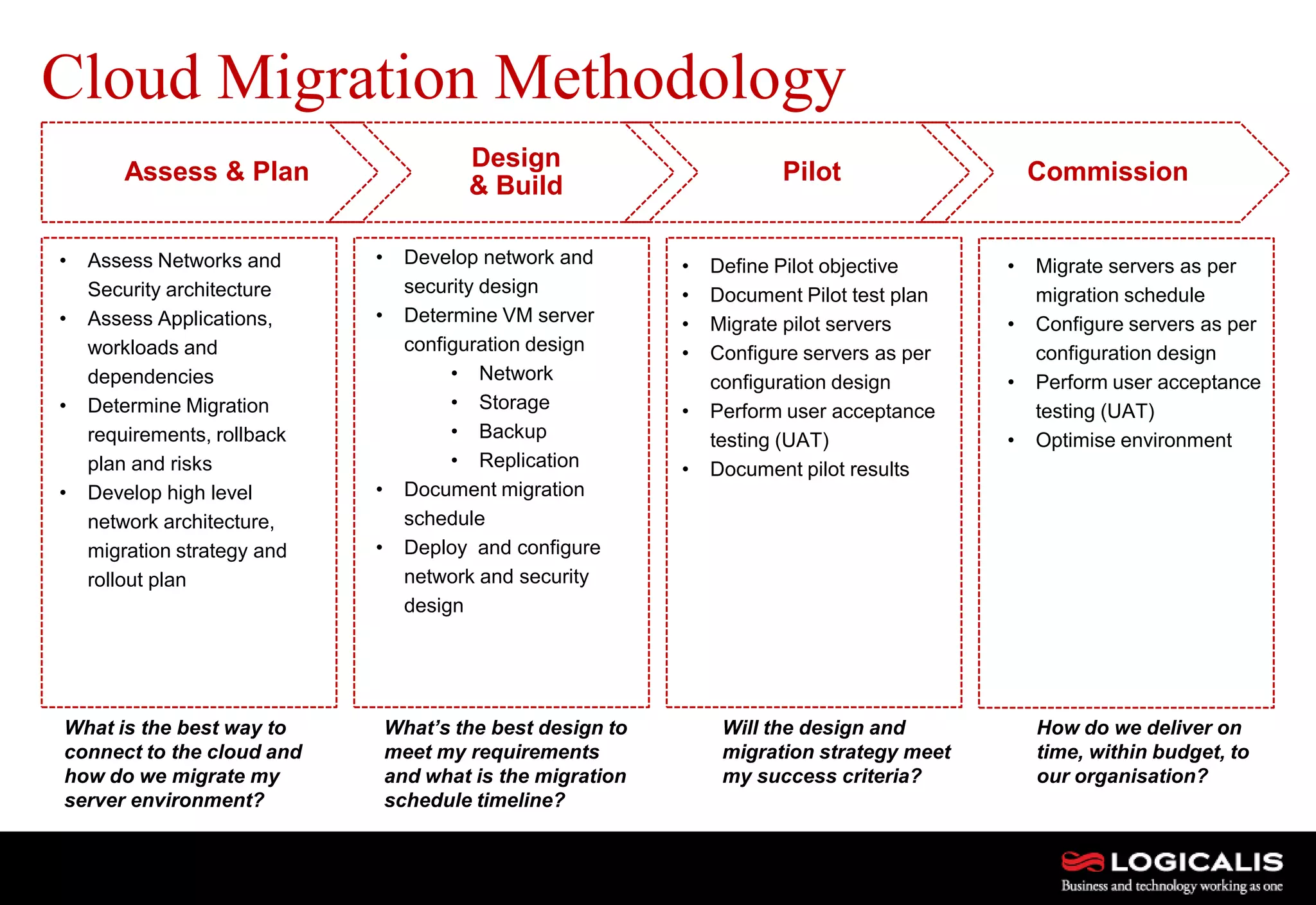
The document discusses various types and models of cloud computing including IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, highlighting their suitability for different workloads and applications. It outlines the differences between commodity and enterprise-class IaaS, emphasizing the importance of cloud value elements such as pricing, capacity, and management services. Additionally, the document addresses migration strategies and considerations for selecting a cloud service provider to meet specific business needs.