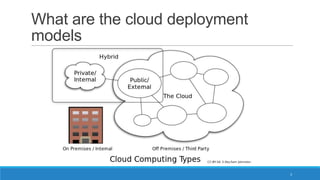
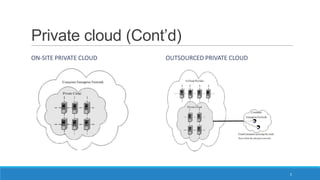
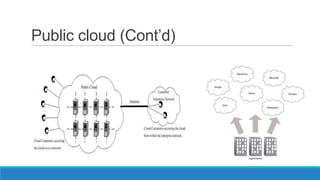
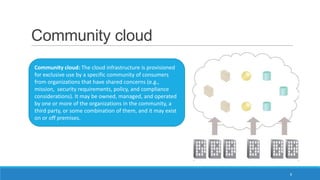
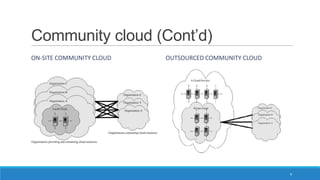
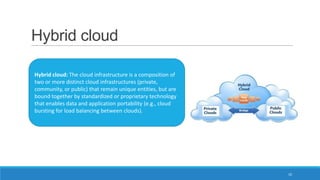
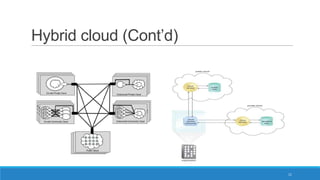
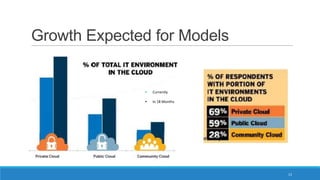
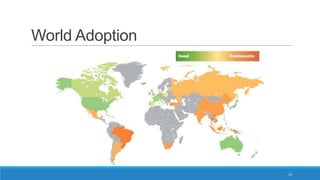
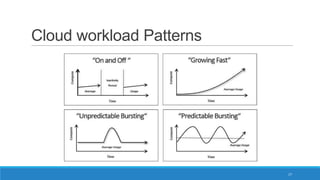
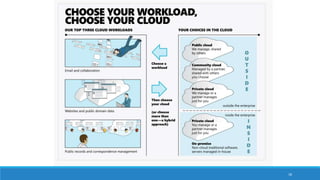
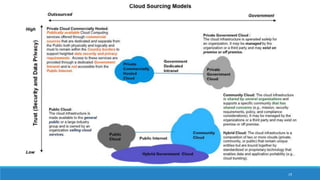
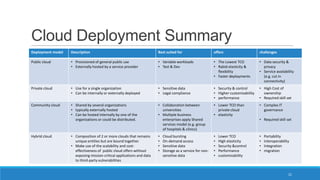
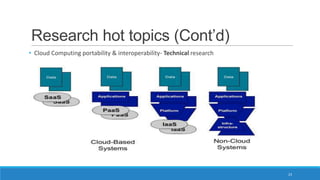
The document discusses various cloud deployment models including private, public, community, and hybrid clouds, outlining their characteristics, advantages, and challenges. It emphasizes factors to consider when selecting a model, such as security, compliance, and budget. Additionally, the document highlights research topics related to cloud computing, including data sovereignty and interoperability.