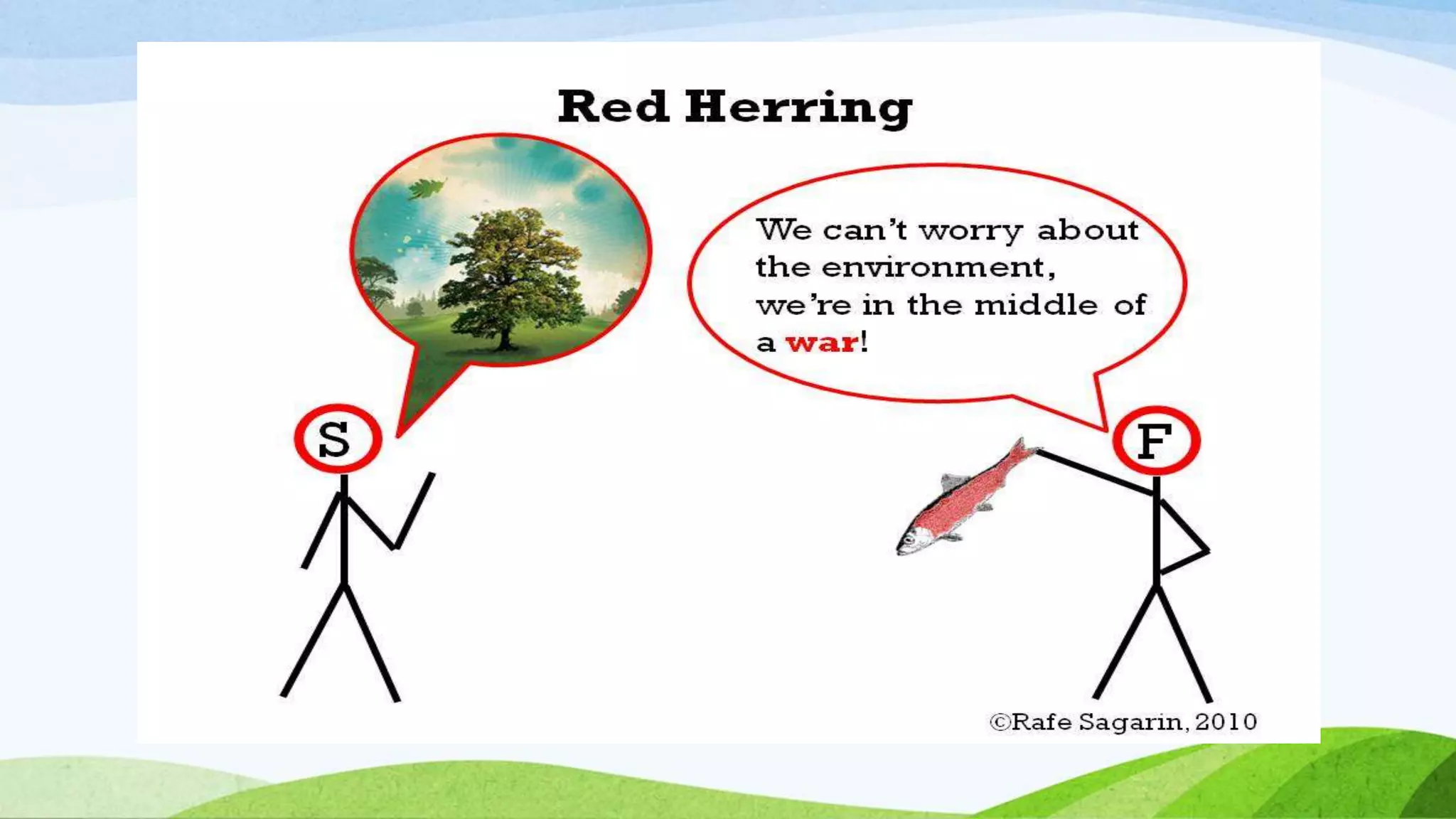
The document discusses common logical fallacies or tricks in reasoning. It identifies three main categories of fallacies: 1) providing erroneous assumptions, 2) distracting from the conclusion by making irrelevant information seem relevant, and 3) assuming a claim is true without proof. Specific fallacies defined include ad hominem, slippery slope, searching for the perfect solution, appeal to popularity, appeal to questionable authority, appeal to emotion, straw person, either-or, explaining by naming, glittering generality, red herring, begging the question, faulty analogy, and hasty generalization. Examples are provided for many of the fallacies.