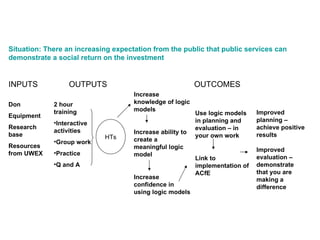
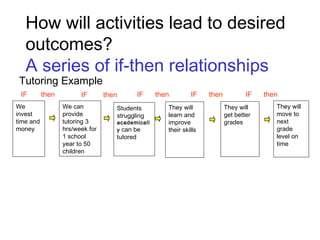
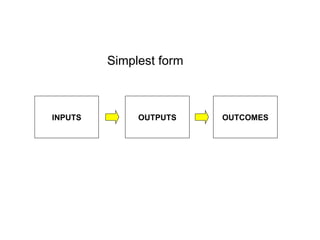
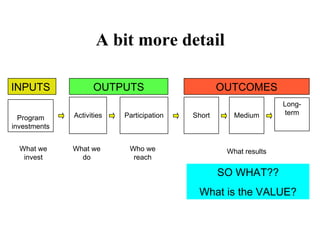
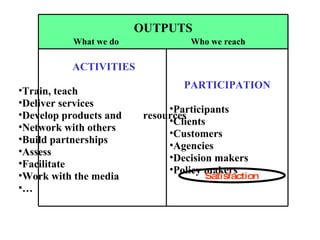
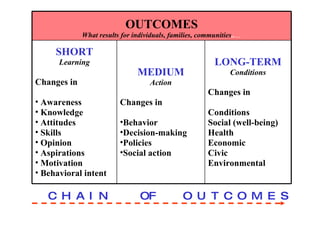
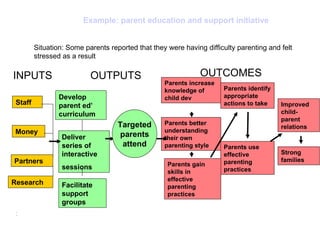
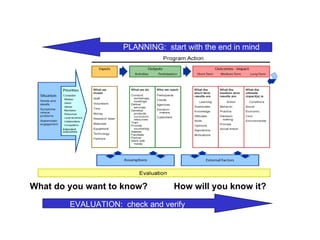
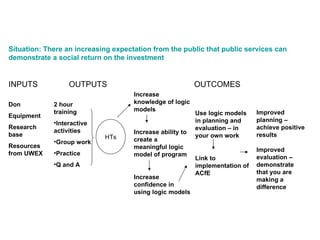
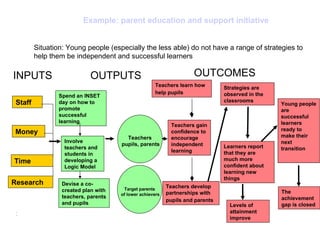
The document discusses the importance of logic models in evaluating and improving educational programs, emphasizing the need for clear inputs, outputs, and outcomes. It critiques the traditional top-down curriculum development approach and advocates for a collaborative process involving teachers as partners in curriculum creation. It also highlights the necessity of making assumptions explicit to enhance communication and facilitate continuous improvement in educational practice.