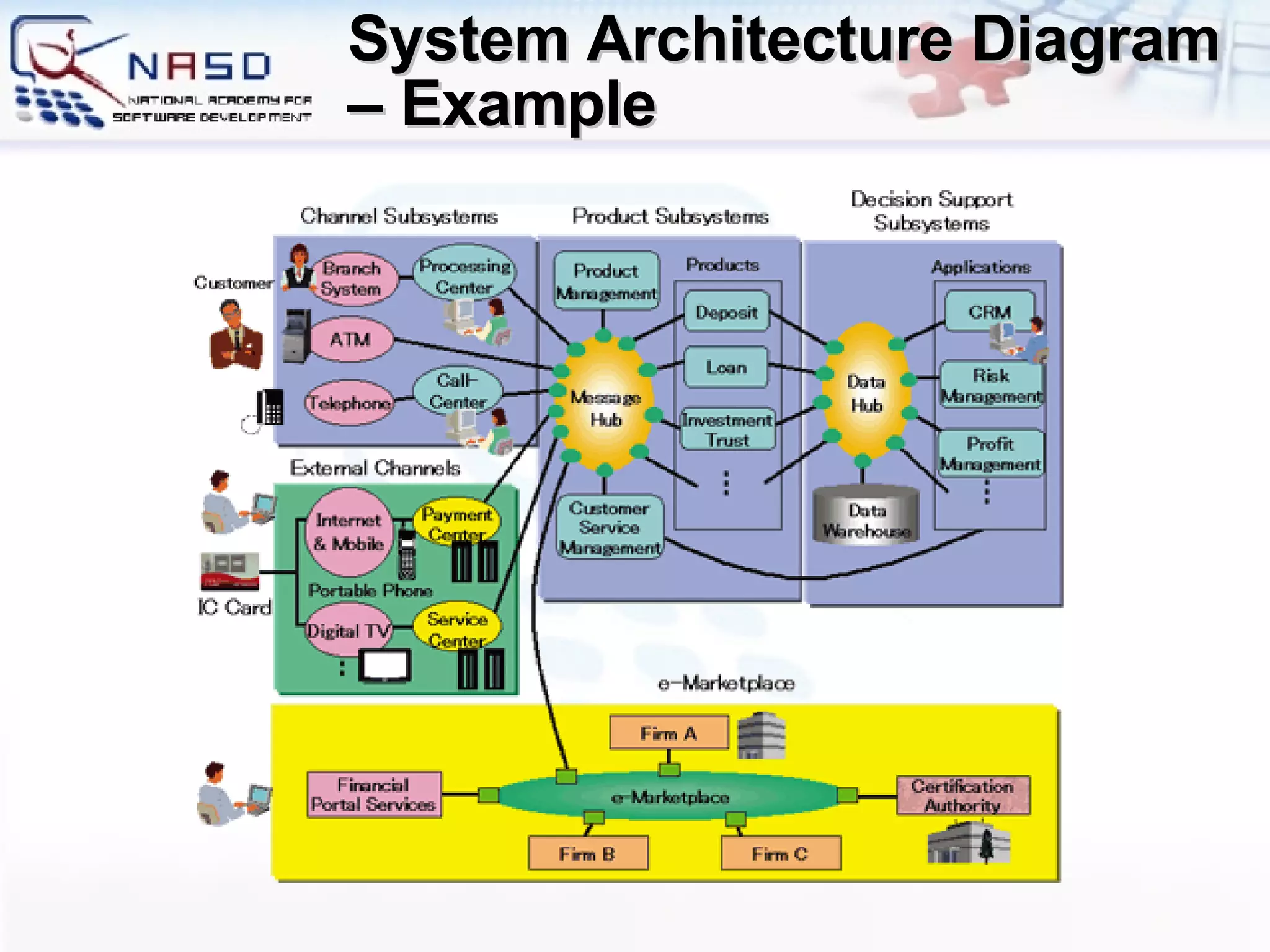
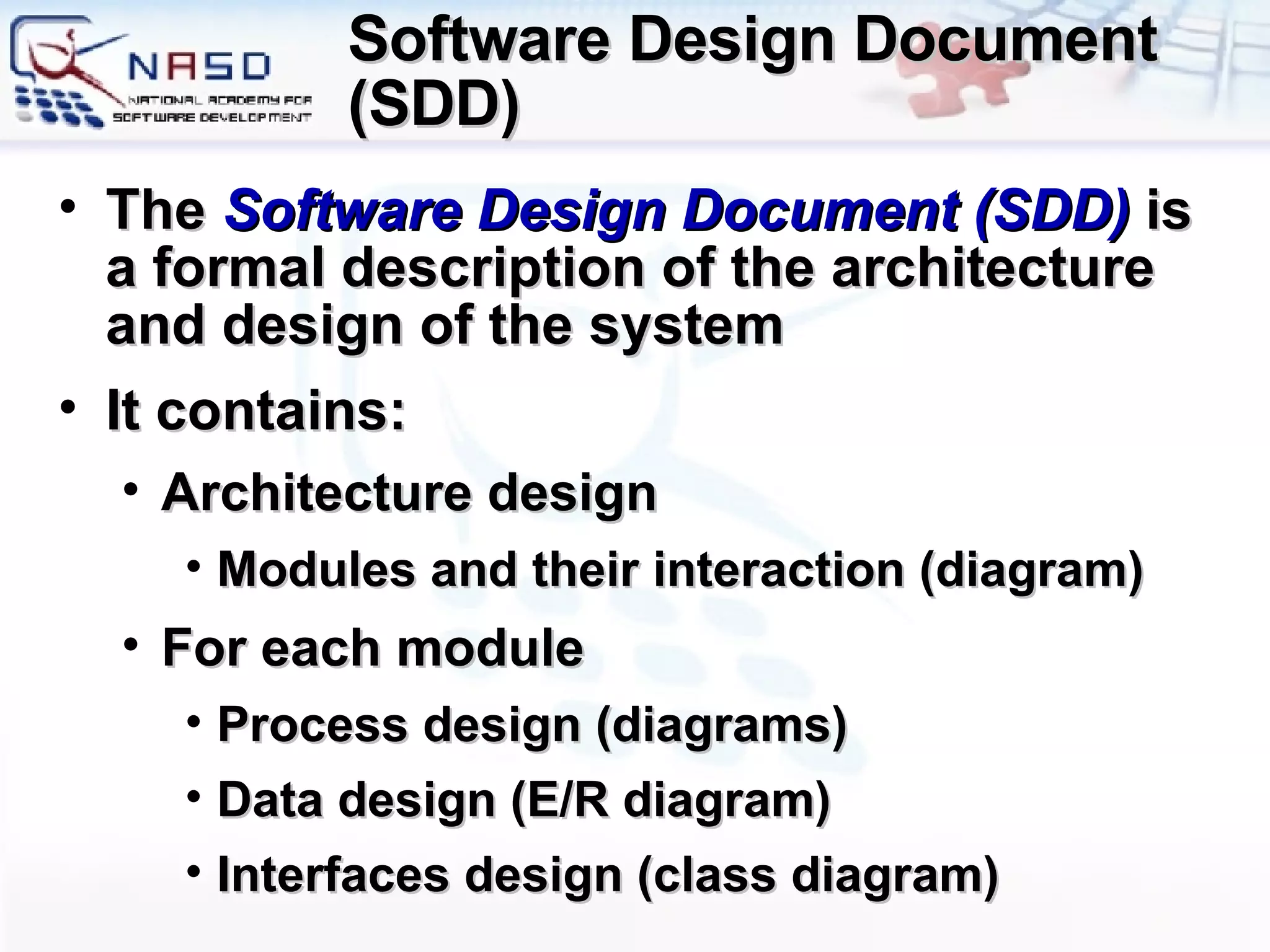
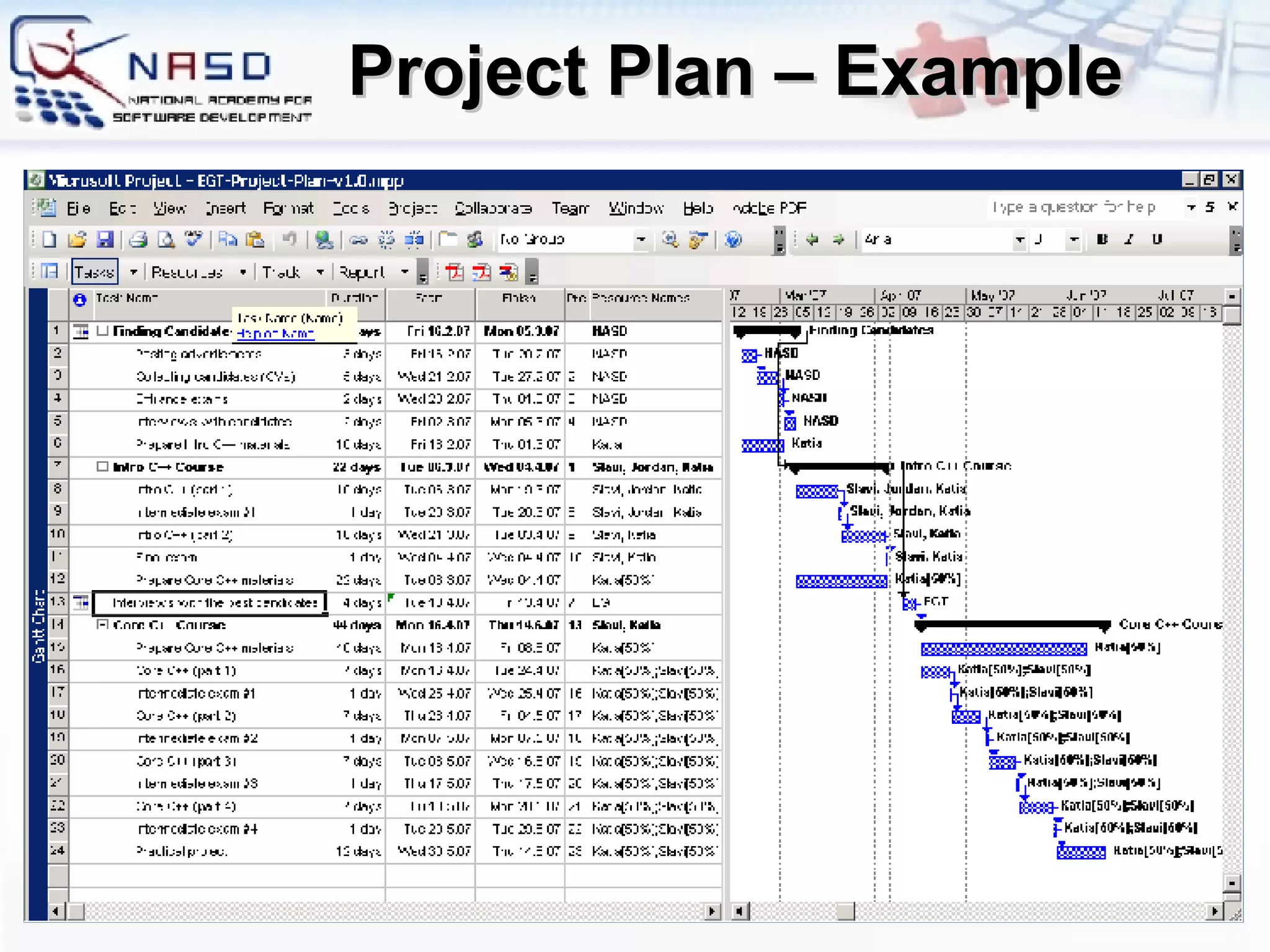
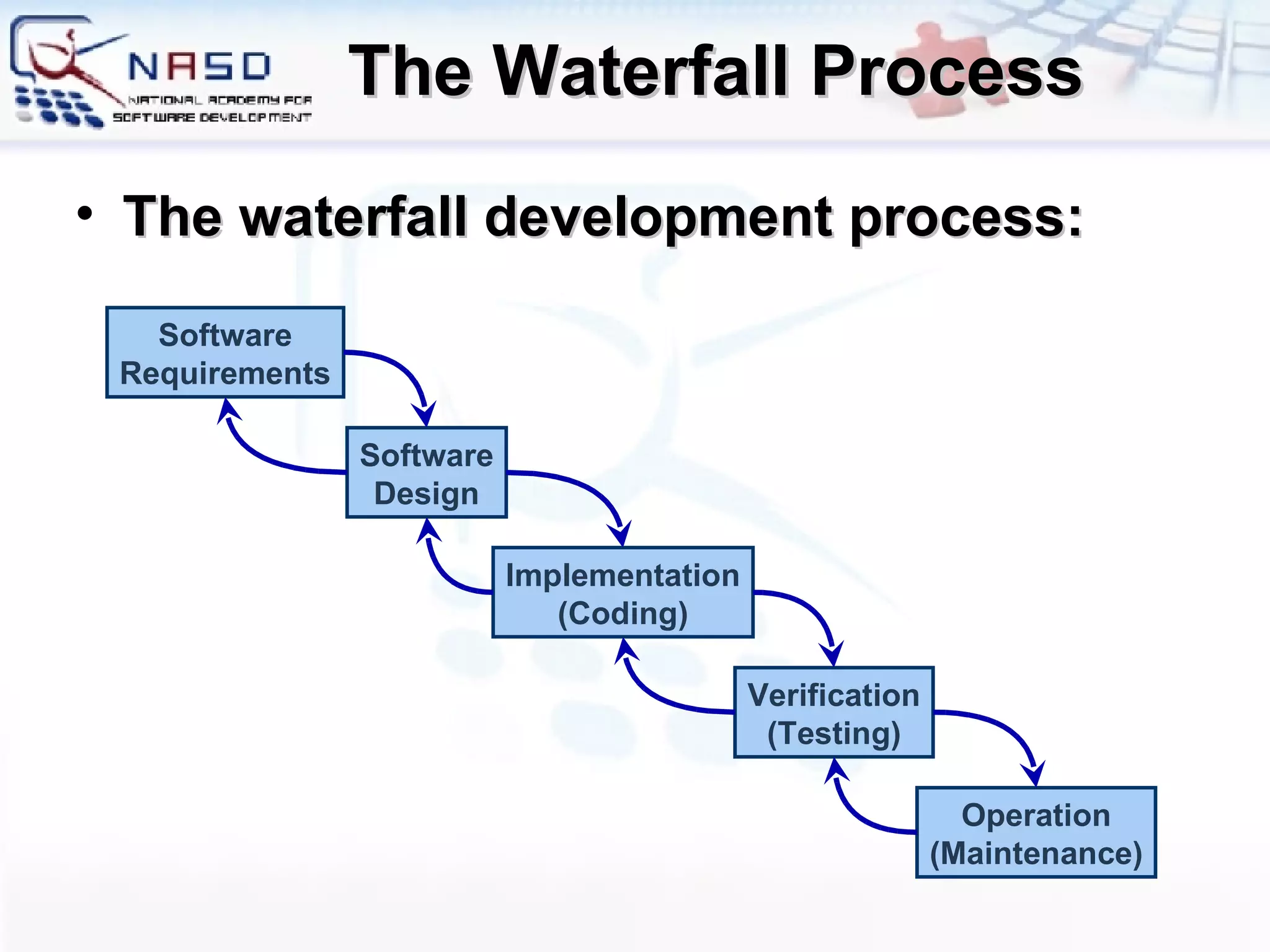
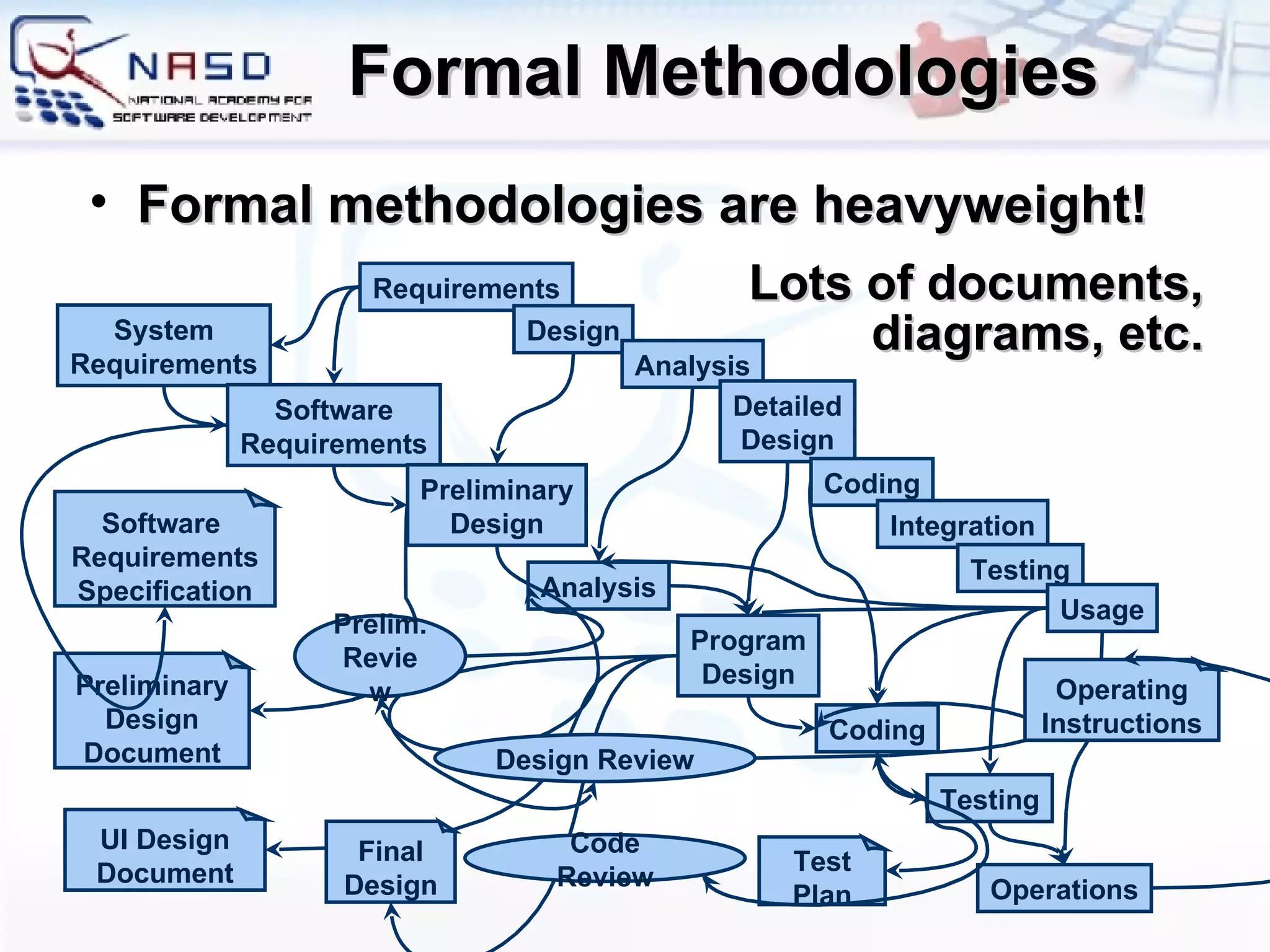
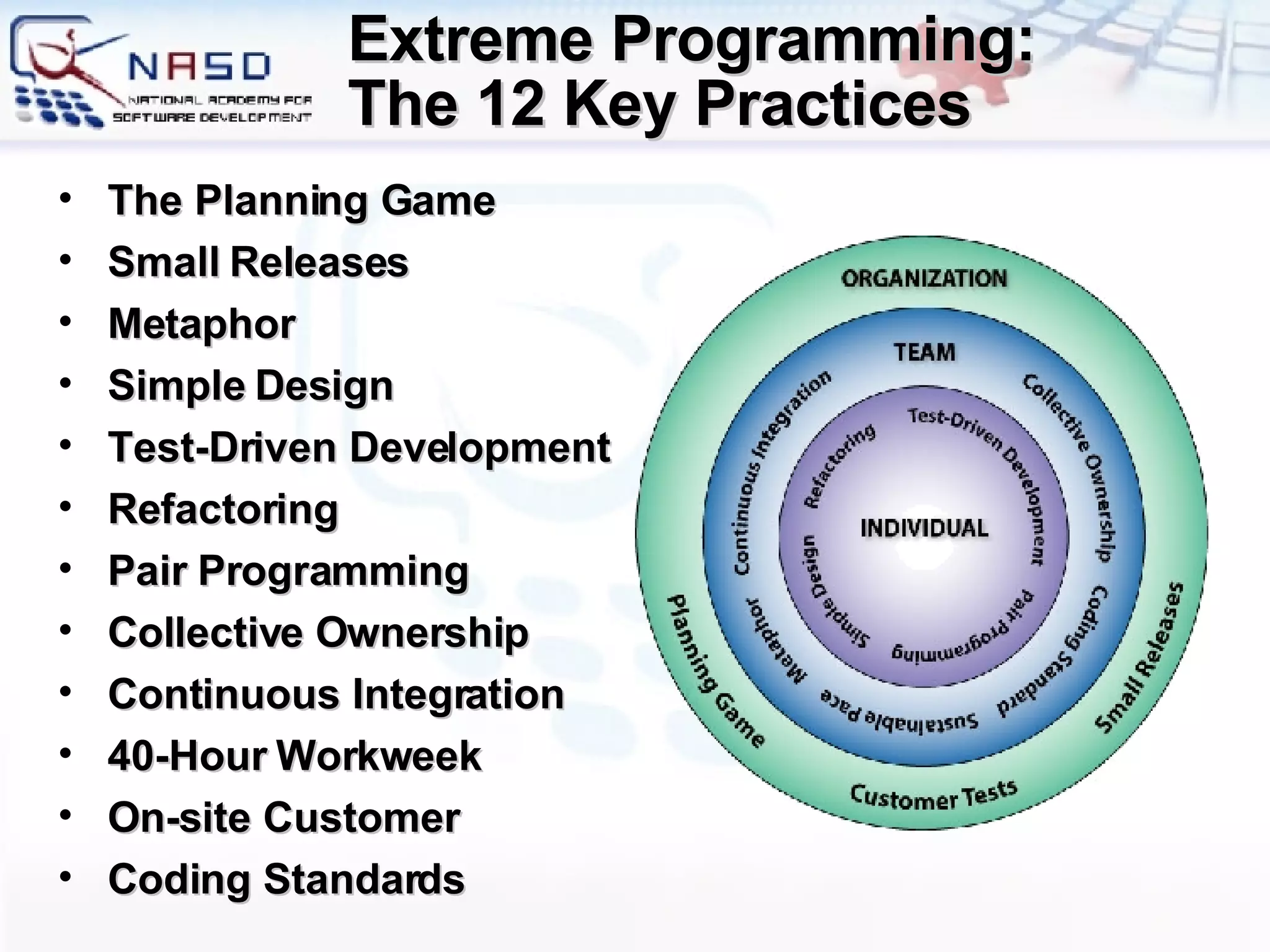
The document provides an overview of software engineering fundamentals including requirements, design, construction, testing, and project management. It discusses the waterfall development process and heavyweight methodologies as well as agile methodologies like eXtreme Programming. The speaker is introduced as having 15 years of developer experience and expertise in software engineering, training, and consulting.