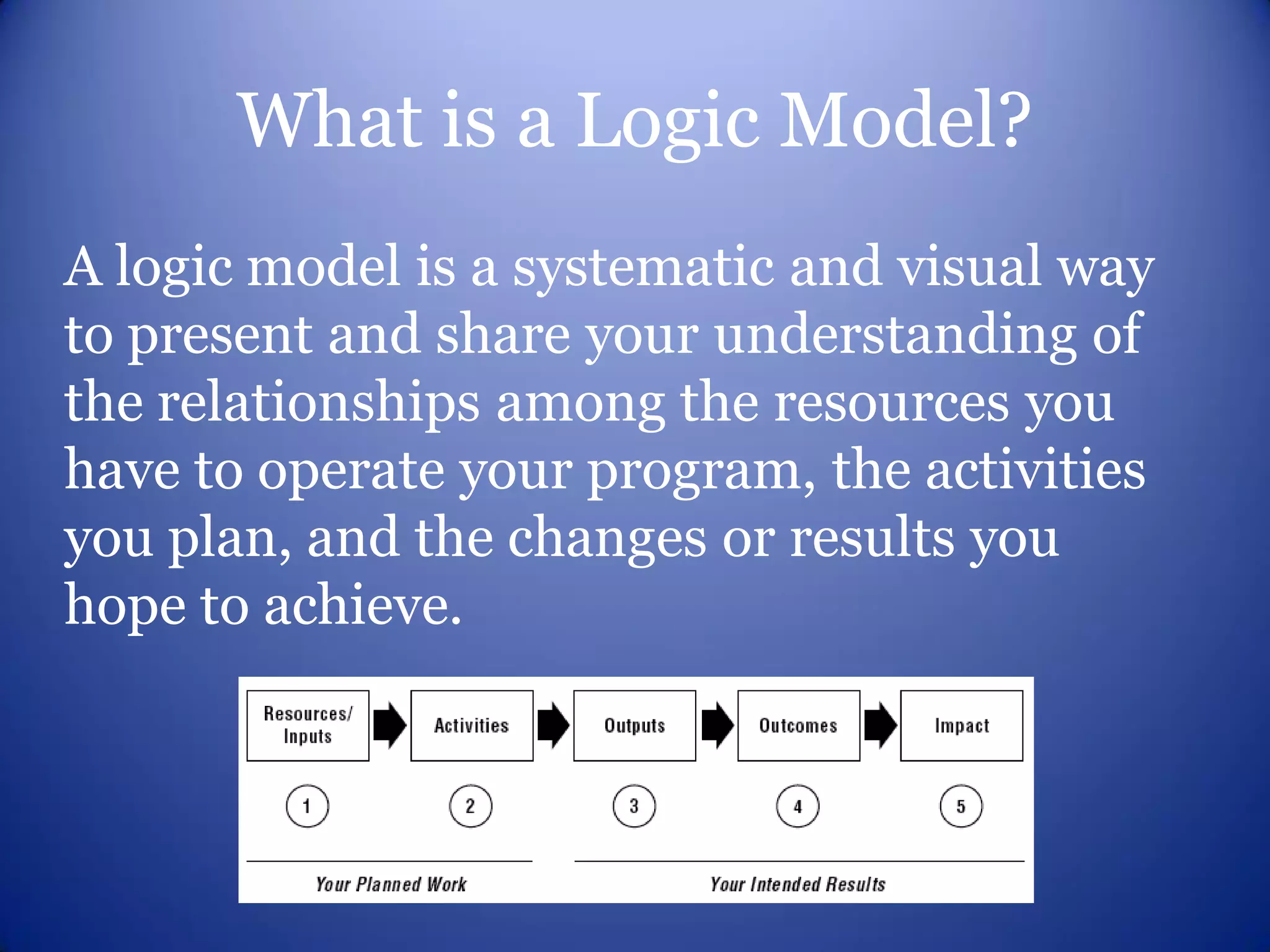
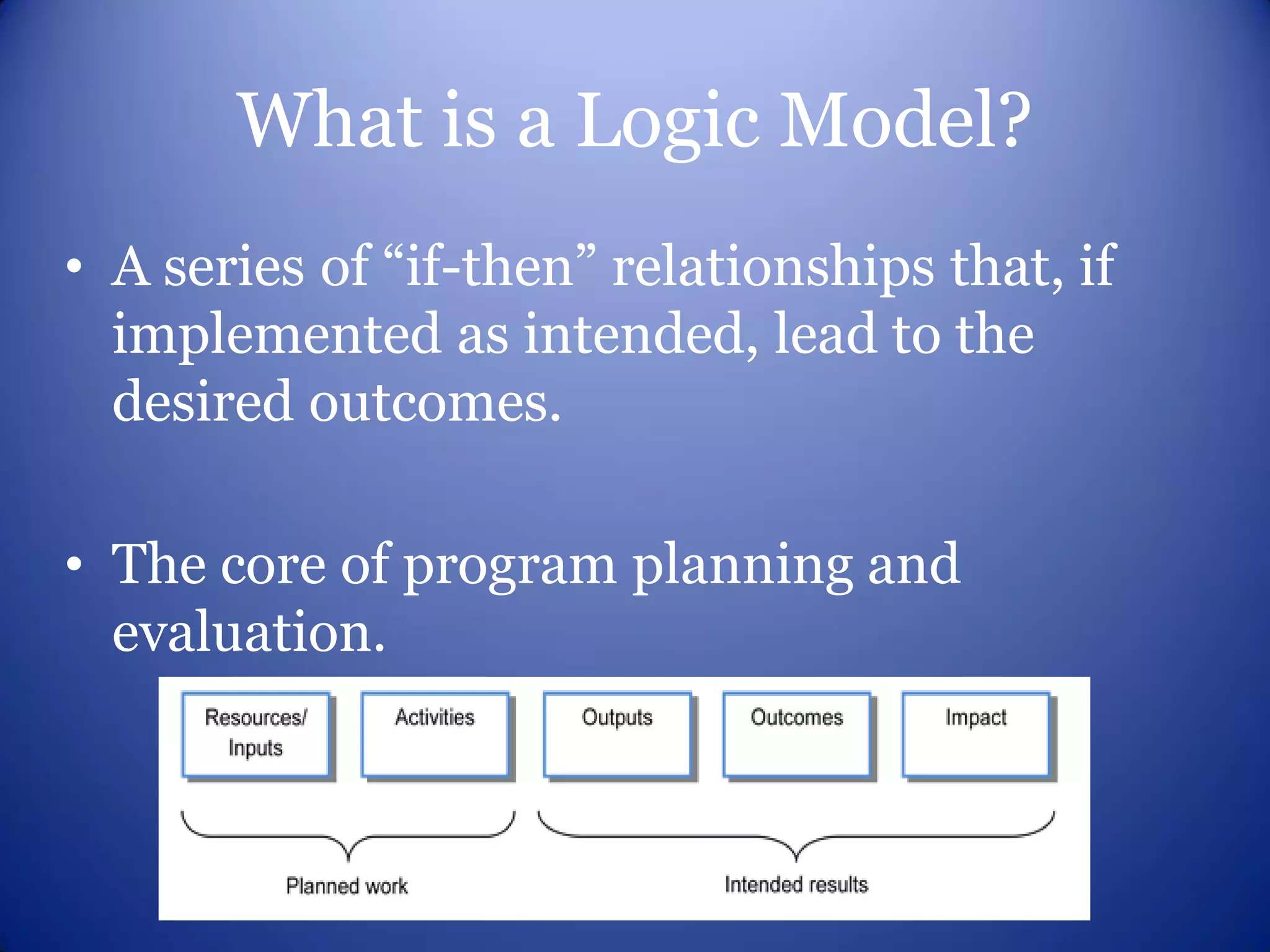
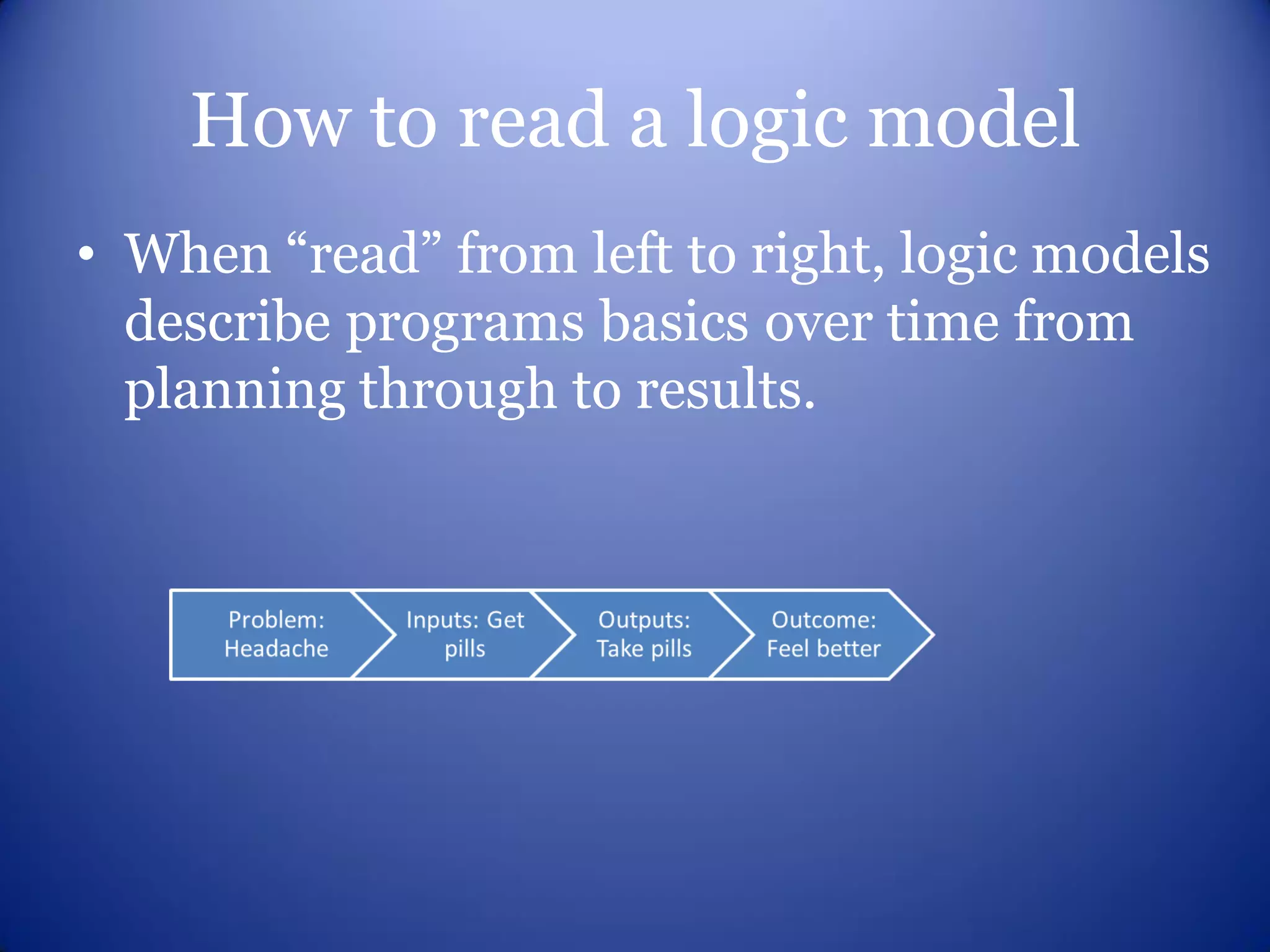
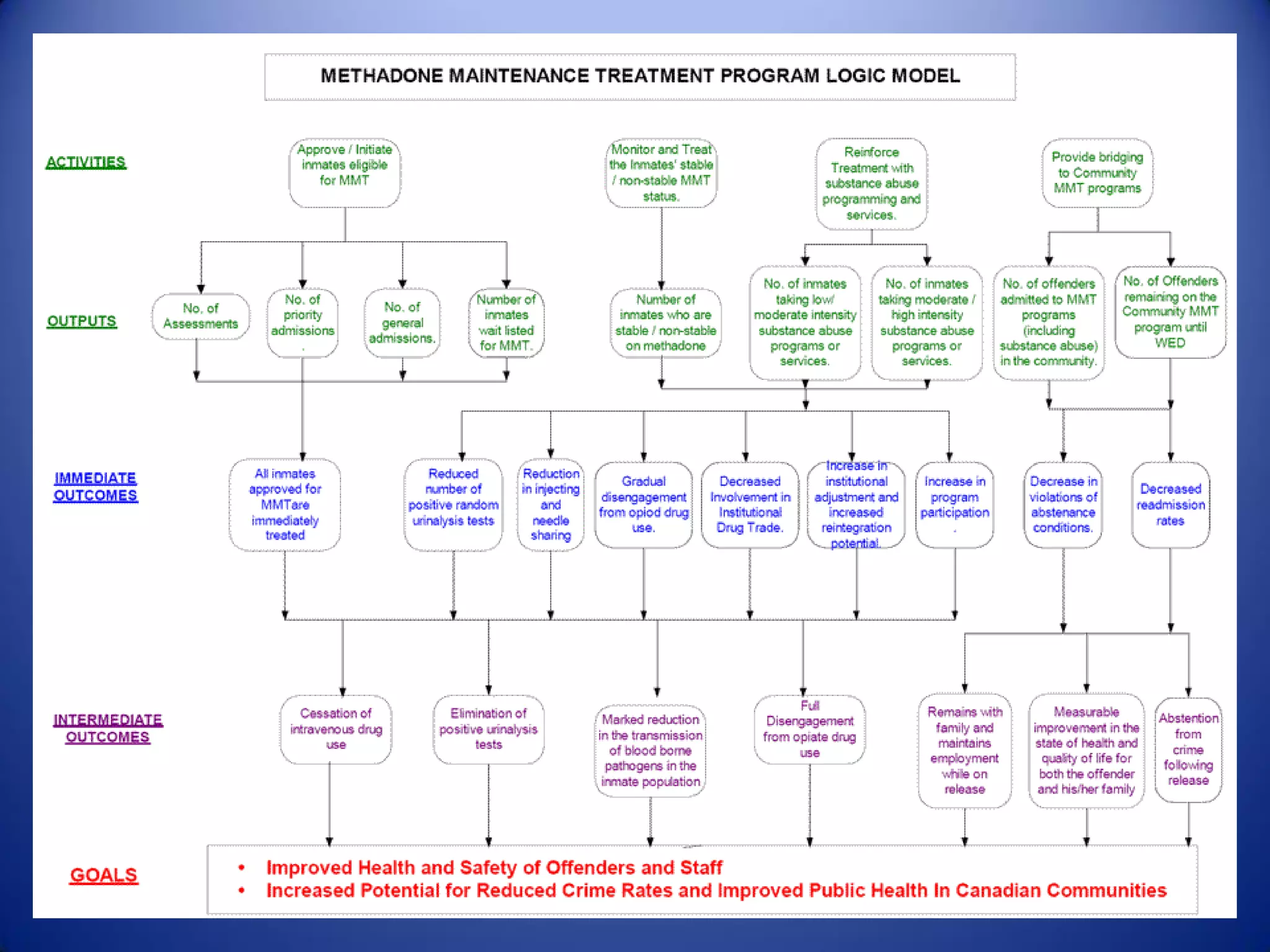
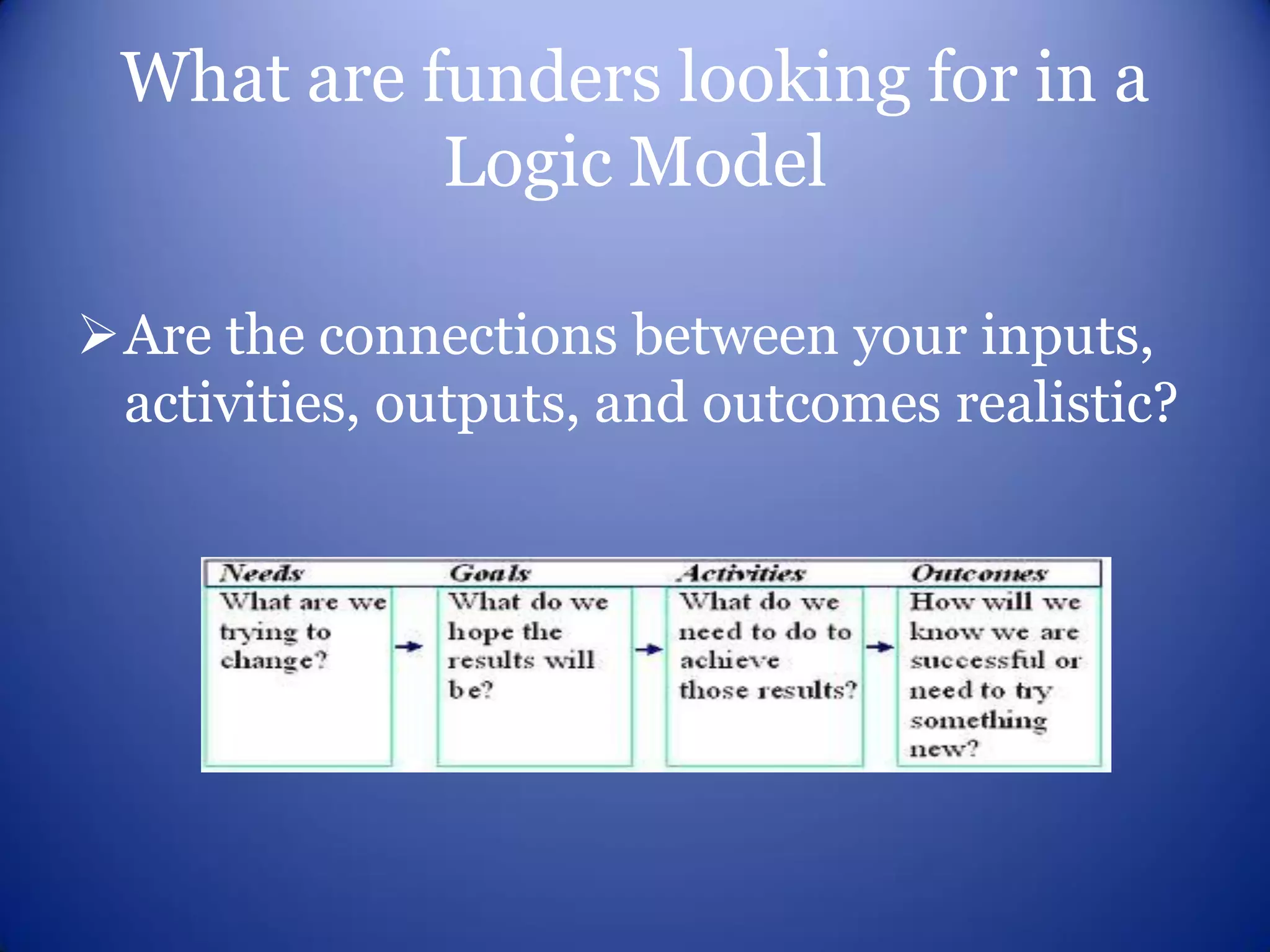
This document provides an overview of logic models for grant writing. It defines what a logic model is, explains why they are important for planning and evaluation, describes the core components of a logic model including resources, activities, outputs and outcomes, and discusses how to develop a logic model with stakeholder input. It also outlines benefits of logic models and what funders look for in a strong logic model.