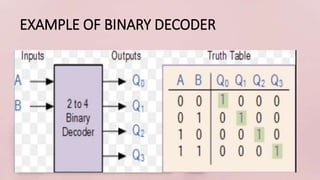
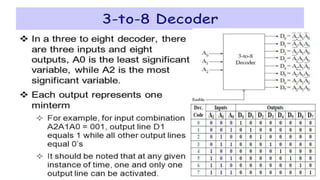
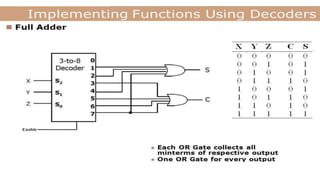
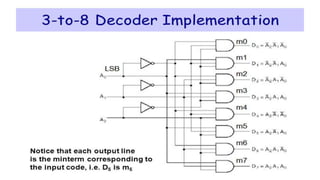
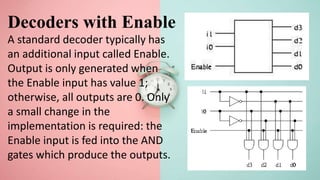
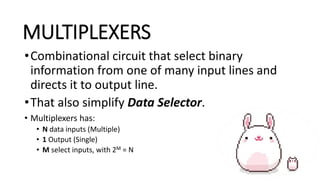
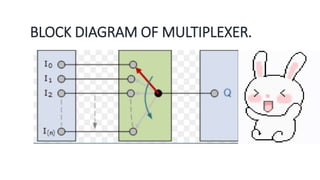
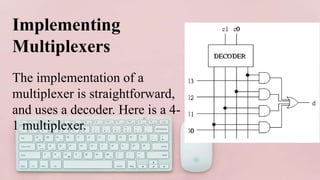
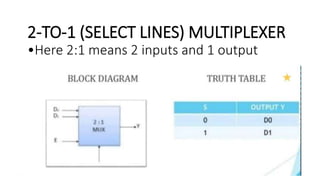
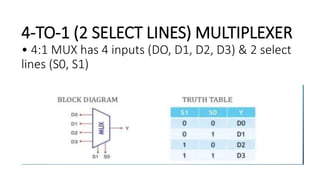
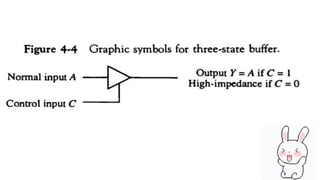
This document covers decoders, multiplexers, and three-state gates. It defines decoders as having multiple input lines and fewer output lines, with m=2^n outputs. Multiplexers are circuits that select one of several data inputs and direct it to a single output, with 2^M select lines for M inputs. Three-state gates can output high, low, or high impedance states.