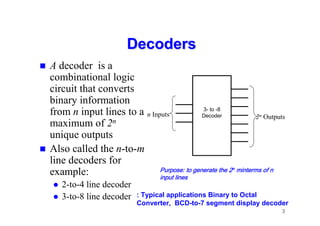
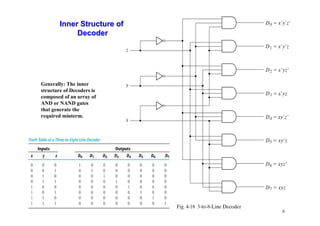
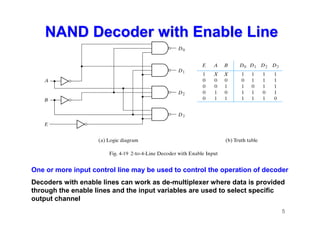
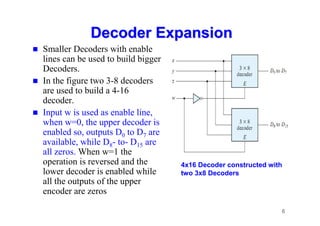
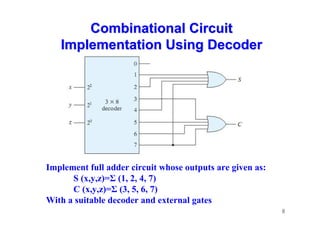
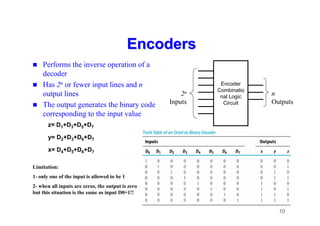
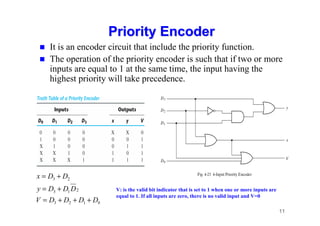
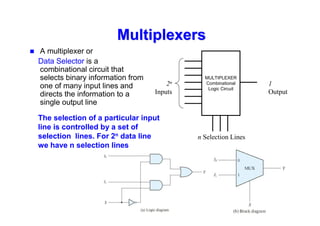
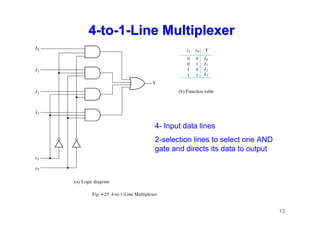
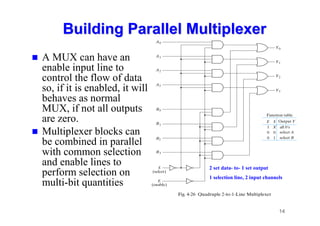
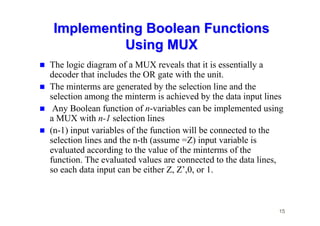
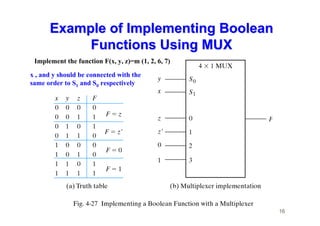
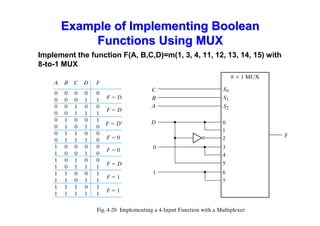
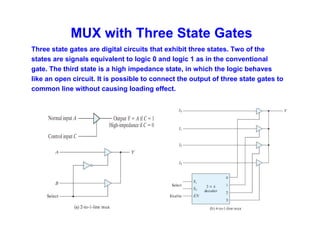
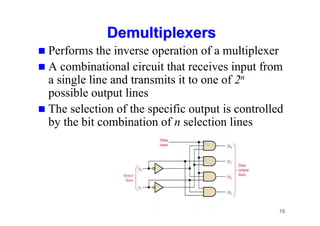
The document provides an in-depth overview of combinational logic circuits, focusing on components such as decoders, encoders, and multiplexers. It explains how these components function, their applications, and how to utilize them in digital logic implementations. Additionally, it discusses techniques for building larger decoders and combinational circuits with external gates.