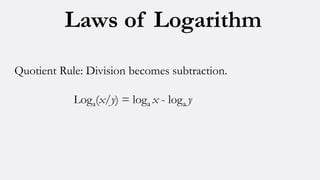
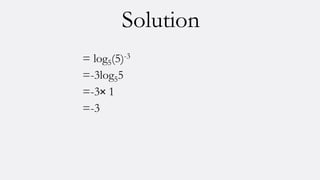Logarithms are exponents that represent the power to which a number must be raised to get another number. There are three laws of logarithms: the product rule states that multiplication becomes addition, the quotient rule states that division becomes subtraction, and the power rule states that exponents become multipliers. Matrices are rectangular arrangements of numbers that can be added, subtracted, multiplied, and have other operations performed on them. There are different types of matrices including identity, inverse, and triangular matrices. Sets are collections of objects that are used to define concepts like relations and functions. Basic set operations include union, intersection, and complement.