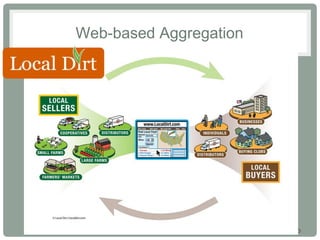
This document discusses regional food hubs and their role in aggregating, distributing, and marketing locally produced foods. It describes how food hubs help both farmers and buyers by expanding markets, providing distribution and marketing services, and reducing transaction costs. Food hubs have positive economic, social and environmental impacts by creating jobs, retaining agricultural jobs, and allowing farmers to receive a greater share of retail prices. However, food hubs also face challenges in balancing supply and demand, managing price sensitivity and growth, accessing capital, and other operational issues. The document provides examples of different food hub models and discusses strategies for achieving economic viability and overcoming common challenges.