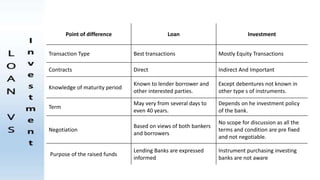
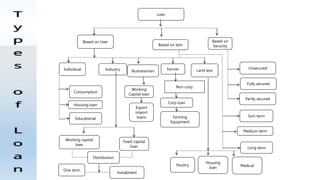
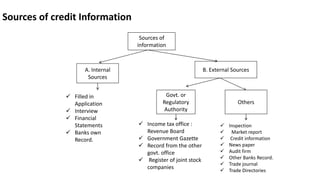
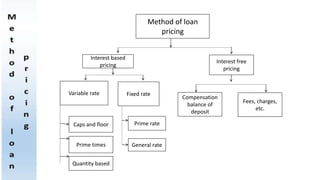
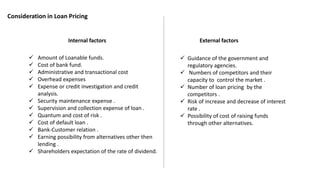
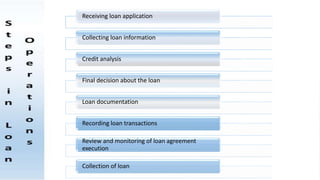
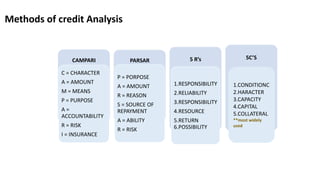
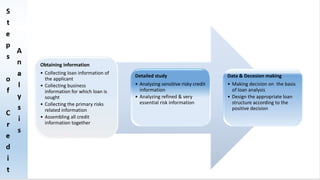
The document outlines the nature of loans as formal agreements between banks and borrowers, detailing conditions, maturity periods, and types of loans available. It further discusses the credit analysis process, including factors that influence eligibility and loan pricing, emphasizing the importance of borrower characteristics and external economic conditions. Finally, it explains methods of credit evaluation and considerations taken by banks when assessing loan applications.