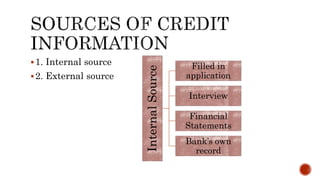
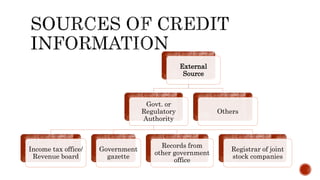
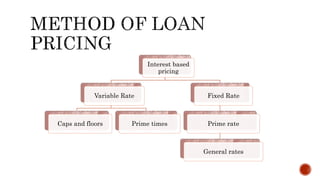
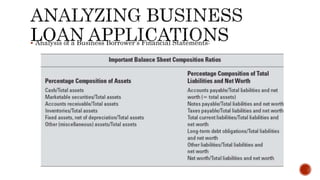
The document discusses various types of business loans provided by banks, including:
- Short-term loans like working capital and inventory loans that last 1 year or less.
- Long-term loans for purchasing equipment, property, or to support acquisitions that last over 1 year.
- Asset-based loans where the bank lends against a percentage of the value of the business's accounts receivable or inventory.
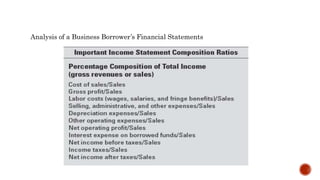
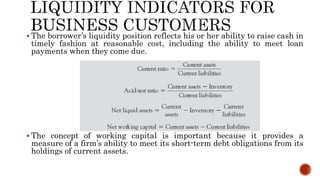
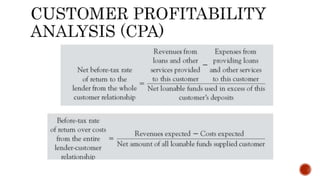
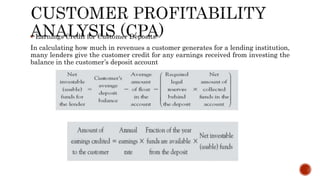
It also covers how banks evaluate business loan applications by analyzing financial ratios and statements to assess the business's profitability, expenses, liquidity, leverage, and ability to repay the loan. Pricing models for loans including cost-plus and relationship pricing are also summarized.