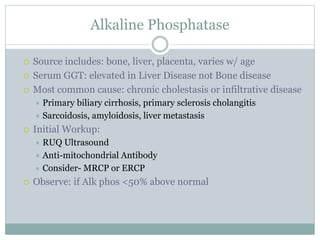
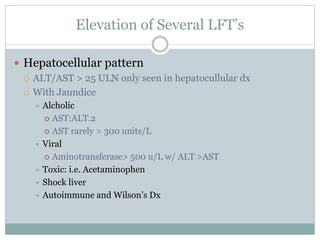
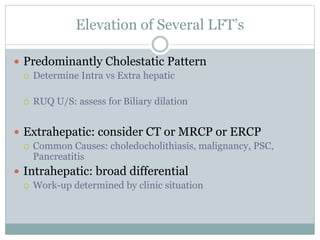
The document discusses liver function tests and their significance. It describes the patterns that different disease states can produce in liver enzyme levels and bilirubin. For the case presented with elevated AST and ALT, the next step in management would be an RUQ ultrasound to identify any underlying liver abnormalities. The document provides guidance on evaluating common causes of liver enzyme and bilirubin elevations and determining appropriate further workup and testing.