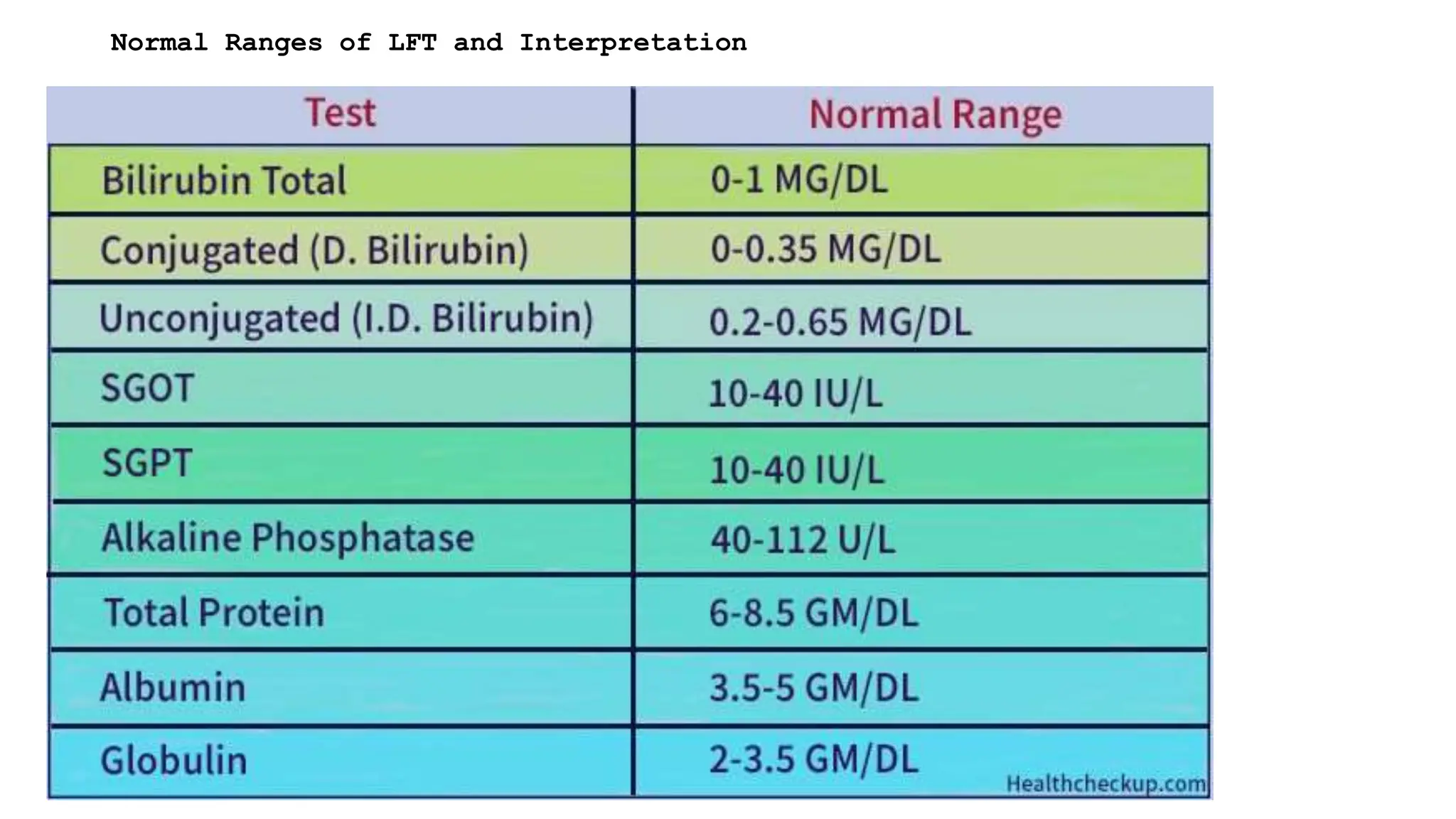
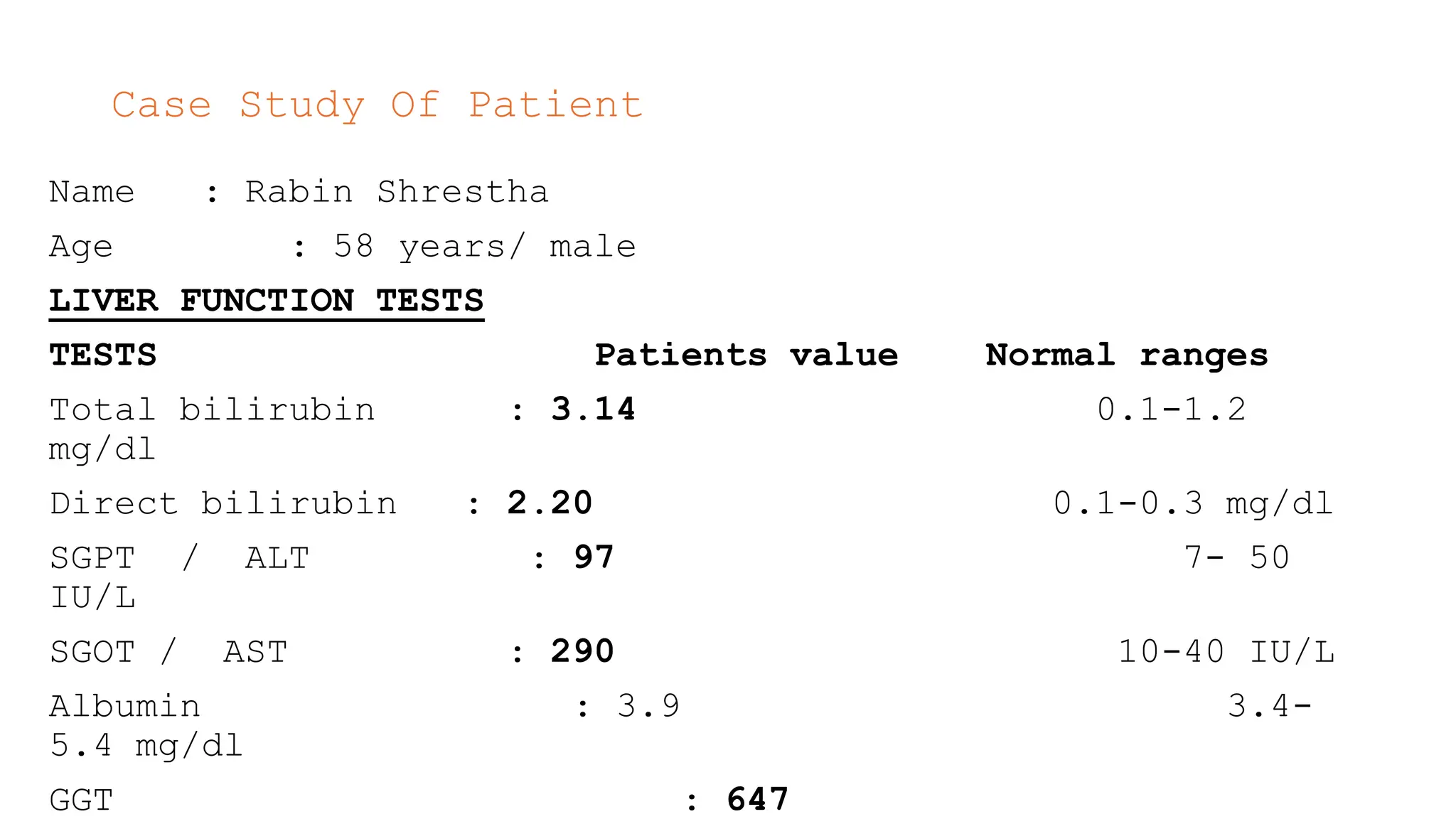
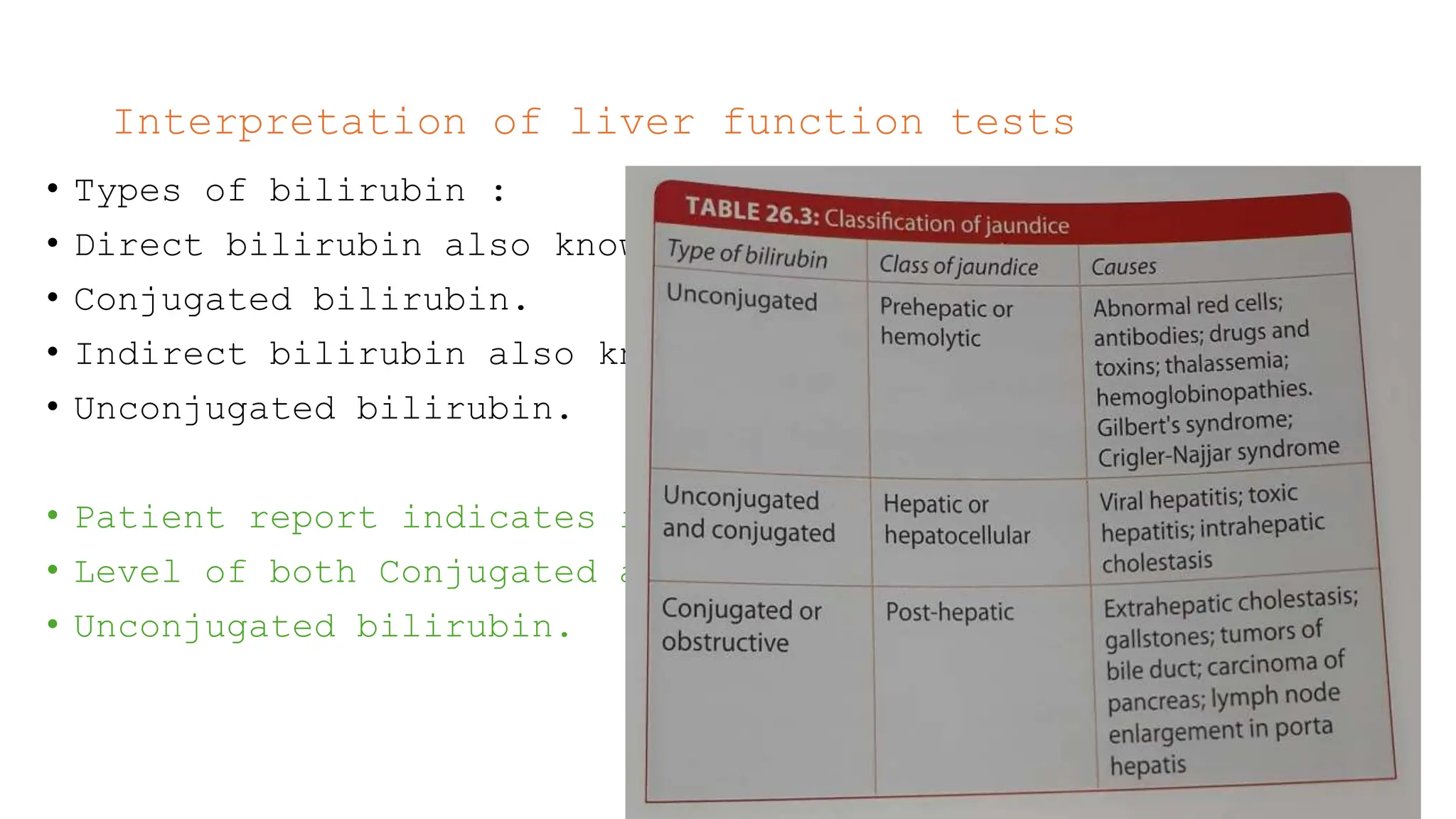
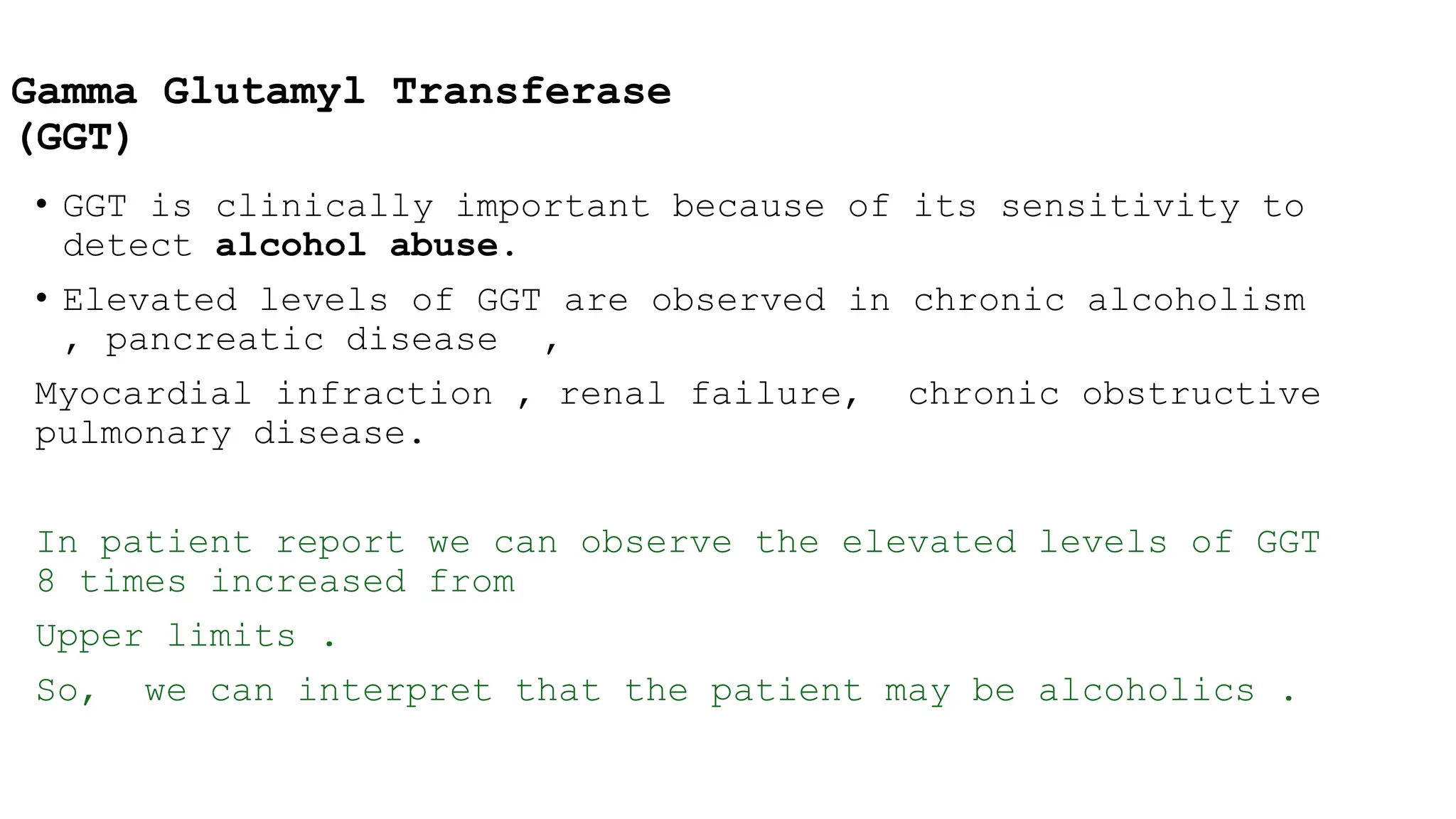
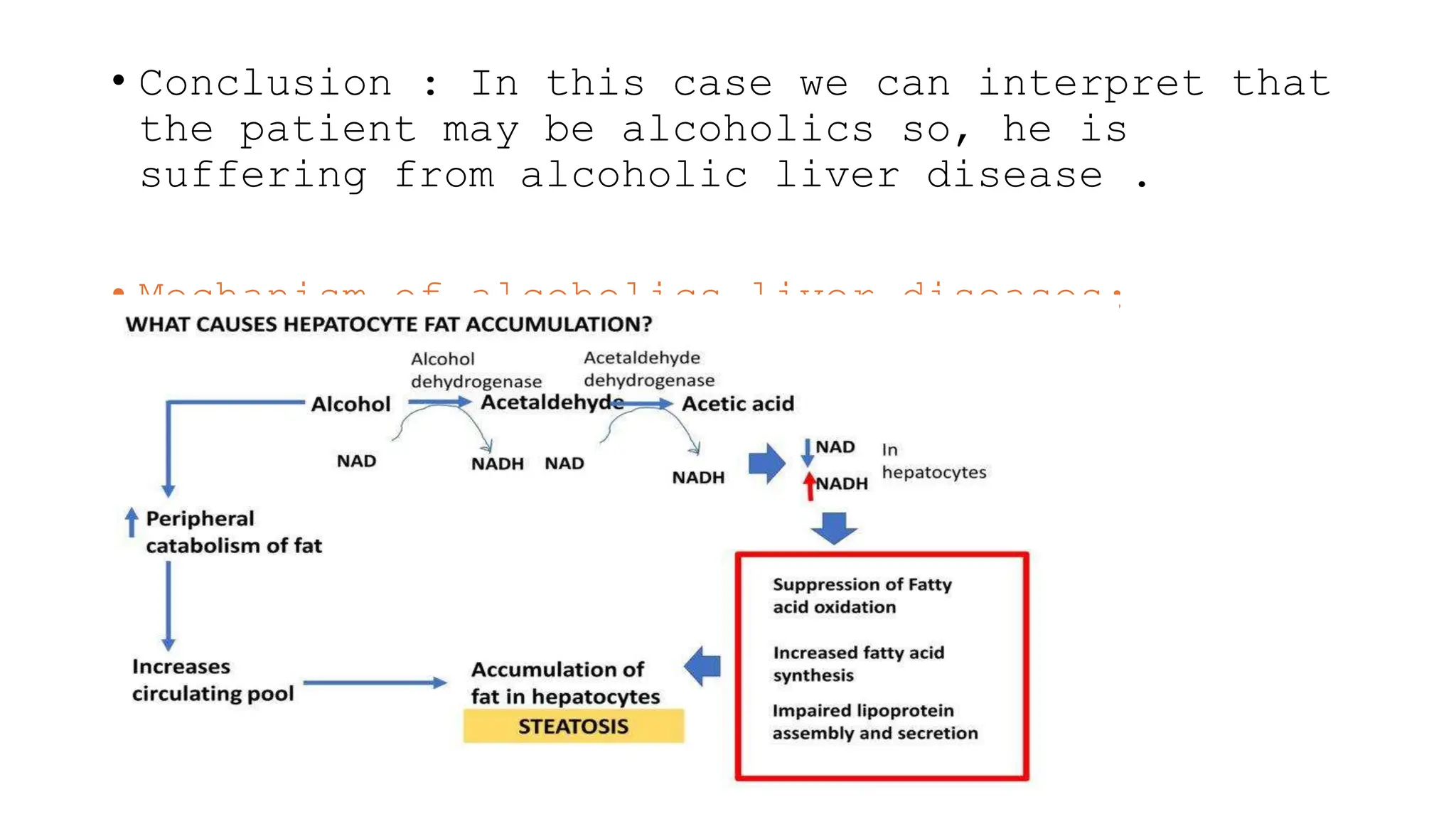
The document presents a case study on a 58-year-old male patient, Rabin Shrestha, with abnormal liver function tests indicating possible alcoholic liver disease. Key findings include elevated levels of total and direct bilirubin, AST, ALT, and GGT, suggesting hepatocellular damage and potential alcohol abuse. The patient’s alkaline phosphatase levels were normal, leading to the conclusion that his liver issues are likely related to chronic alcoholism.