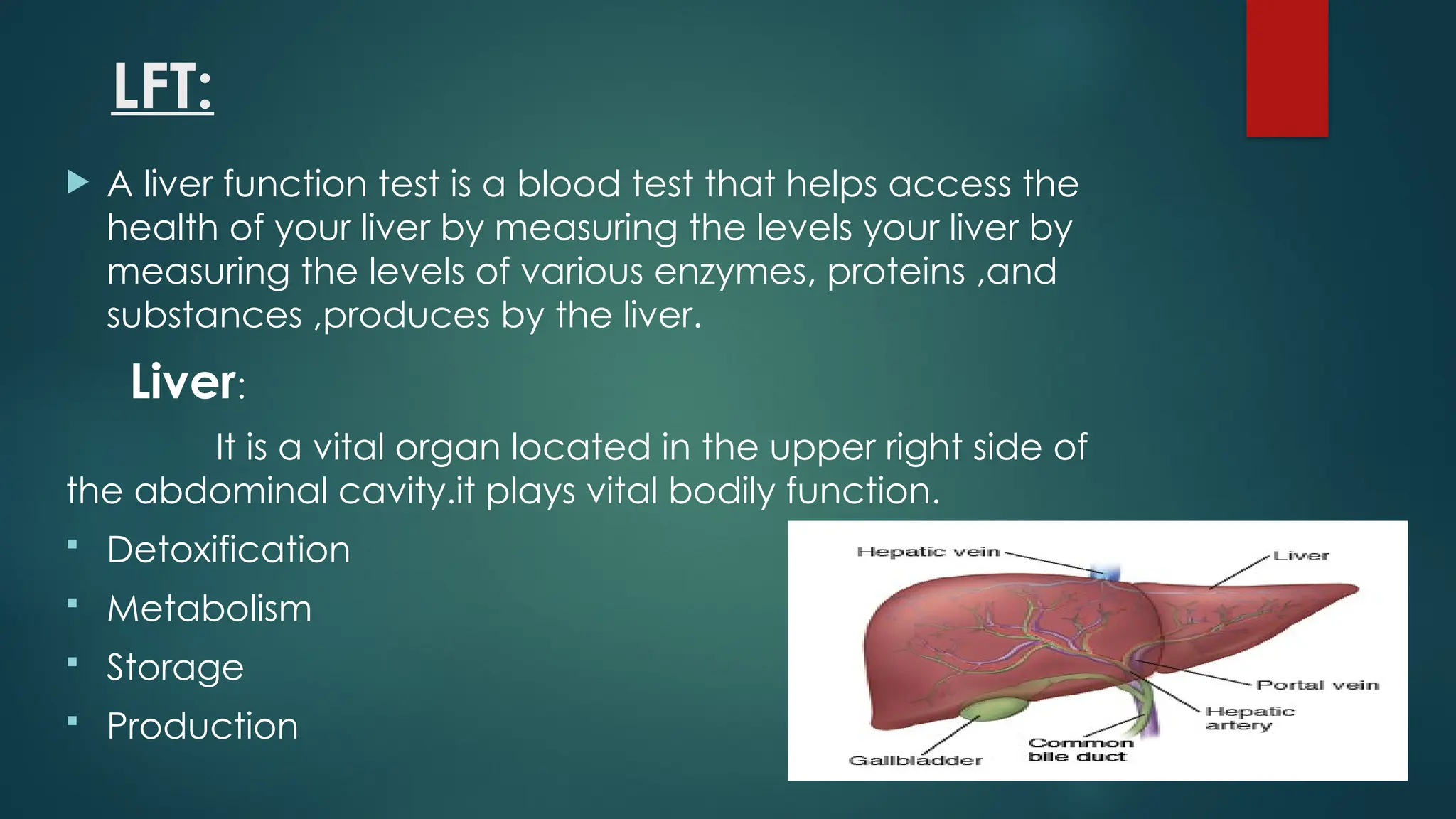
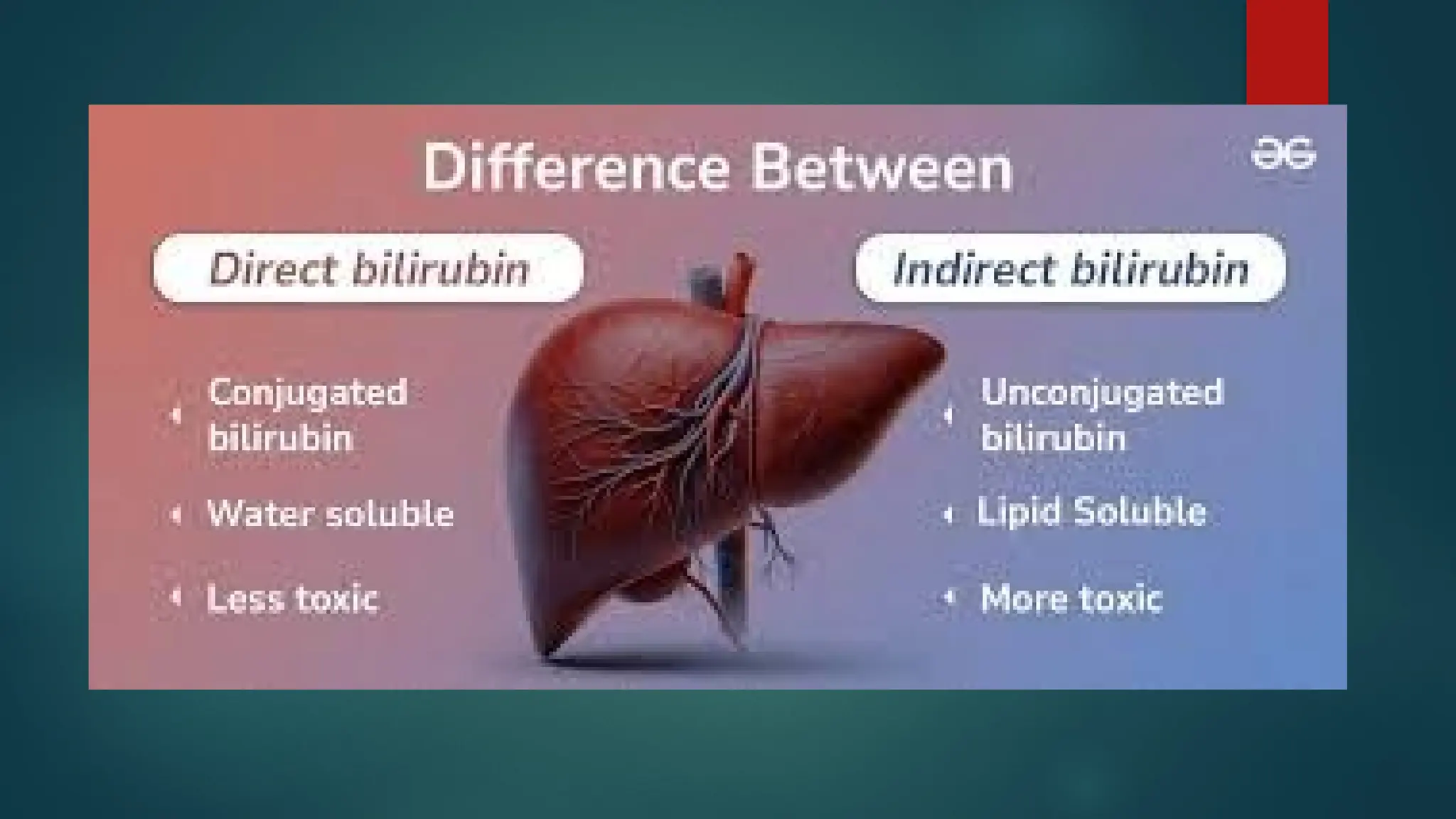
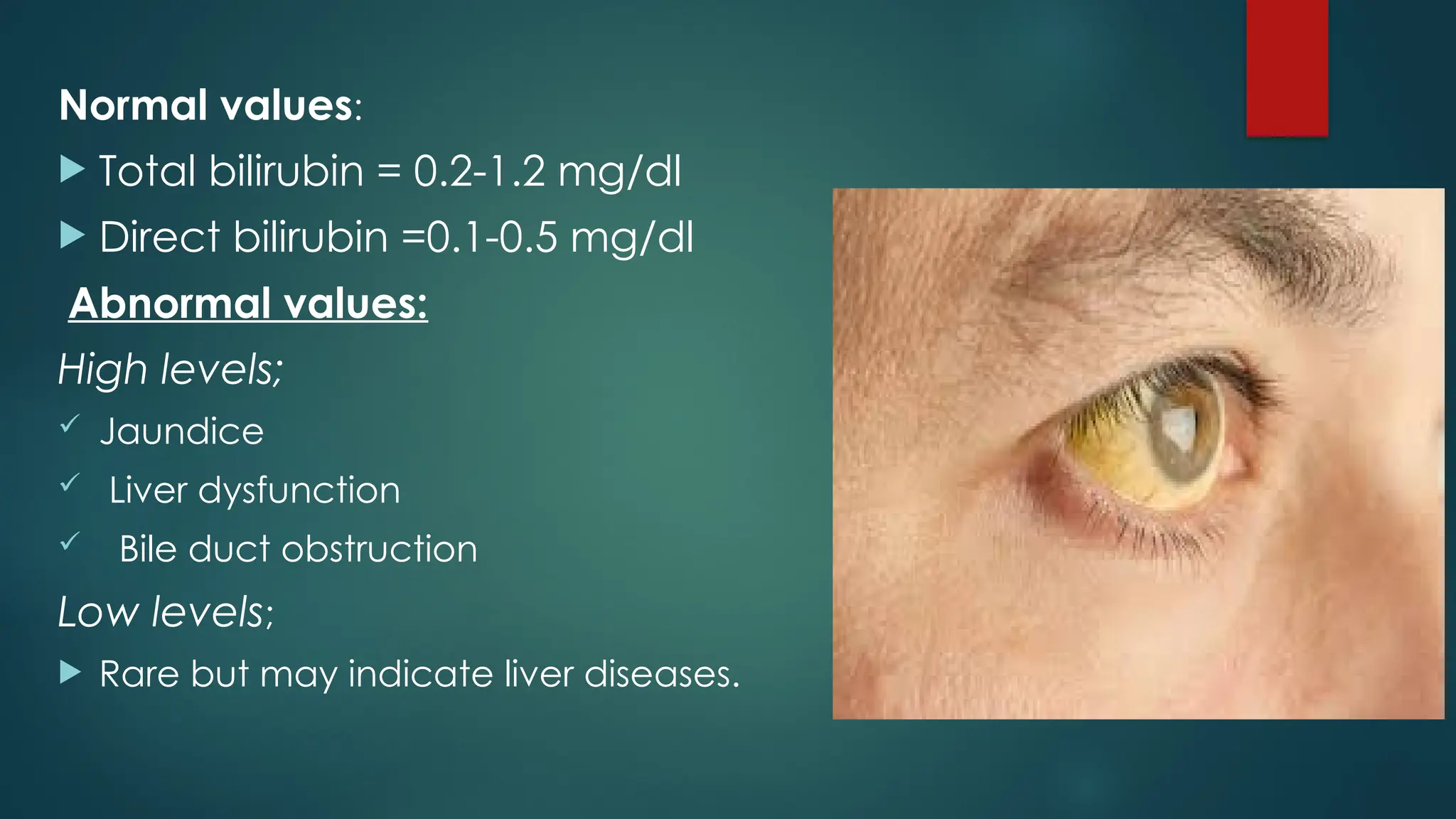
This document discusses liver function tests (LFTs), which assess liver health by measuring enzymes, proteins, and substances produced by the liver. It outlines liver anatomy, diseases, components of LFTs, and details various enzymes such as ALT, AST, ALP, and GGT, including their normal ranges and implications of elevated levels. The document also describes bilirubin types, functions, values, and clinical significance, emphasizing the importance of LFTs in diagnosing liver disorders.