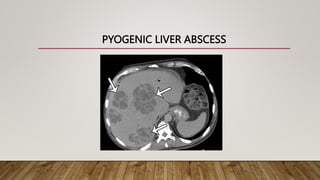
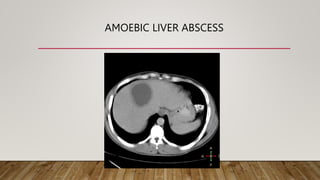
Pyogenic and amoebic liver abscesses are the two most common types of liver abscess. Pyogenic abscesses are usually caused by bacteria spreading from gastrointestinal or biliary infections, while amoebic abscesses are caused by the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Common symptoms include fever, right upper quadrant pain, and hepatomegaly. Investigations include blood tests, ultrasound, and CT scan. Treatment involves antibiotics for pyogenic abscesses and metronidazole for amoebic abscesses. Percutaneous drainage under imaging guidance is the primary treatment, while surgery is rarely needed.