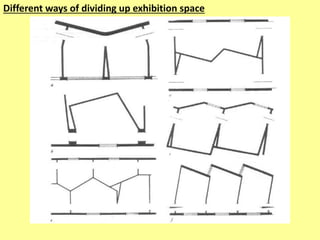
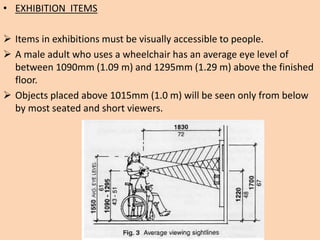
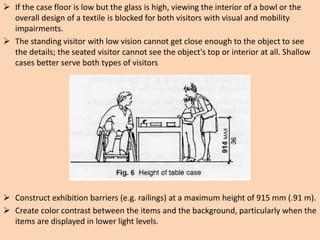
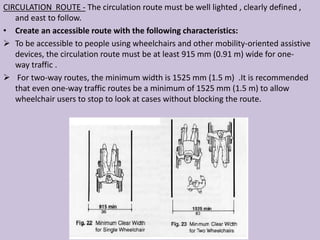
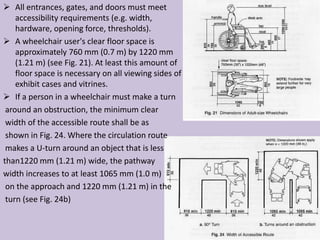
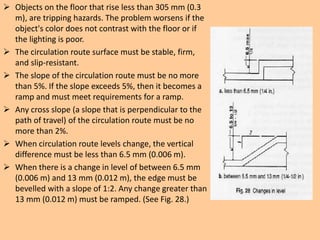
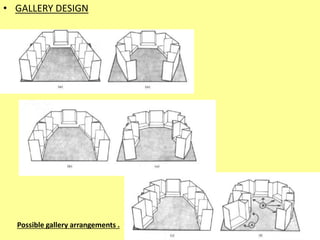
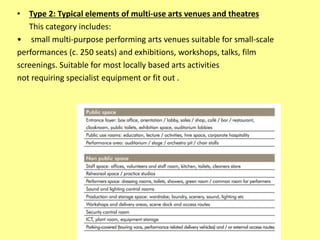
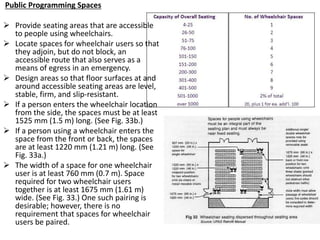
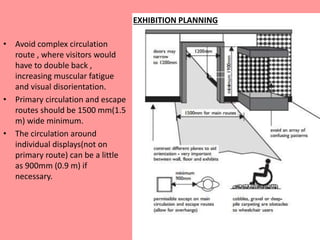
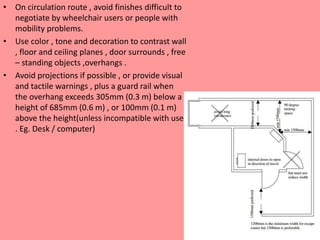
The document outlines the characteristics, design considerations, and types of art galleries, which are spaces for exhibiting various forms of art managed by curators. It details the requirements for gallery designs, including space allocation, lighting, accessibility features, and circulation routes to ensure visitor engagement and safety. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of accessible design for individuals with mobility impairments and the need for proper emergency egress and facility layouts.