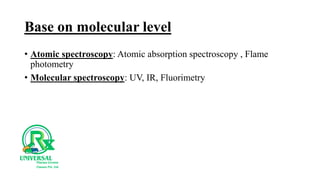
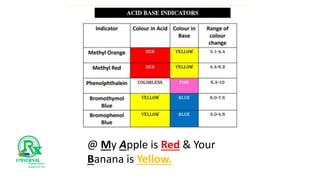
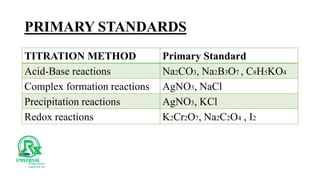
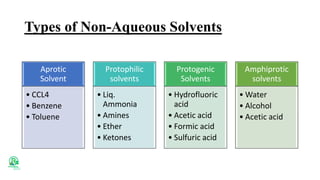
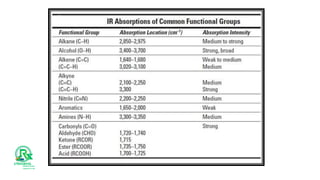
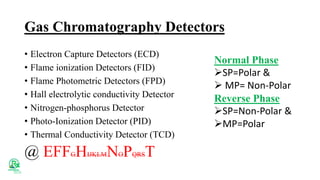
The document outlines various analytical methods used in pharmaceutical analysis, including atomic absorption and spectroscopy techniques, and discusses key concepts such as acid-base theories and titration methods. It also covers different types of detectors in gas chromatography and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), detailing their functions and applications. Additional topics include methods for determining nitrogen content and moisture in substances.