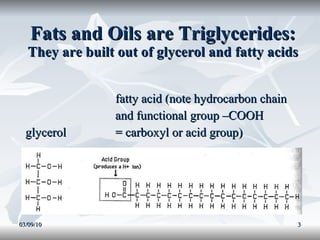
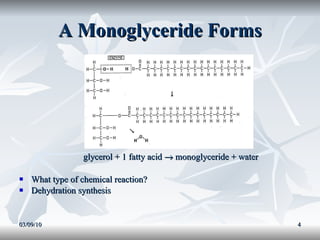
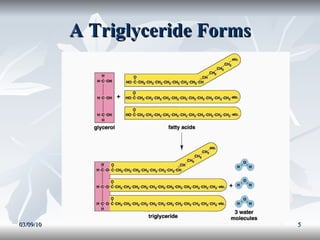
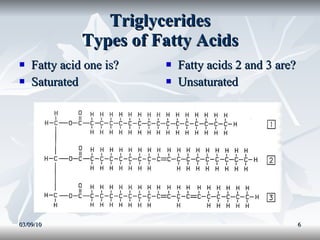
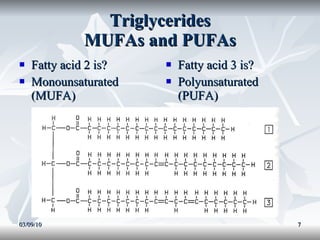
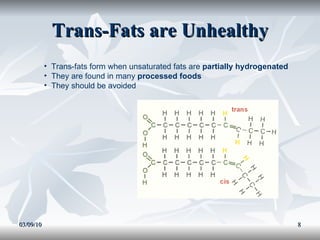
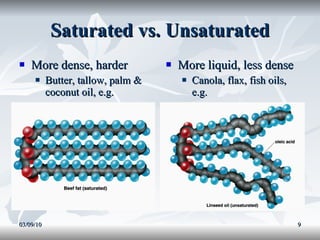
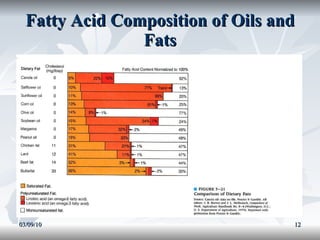
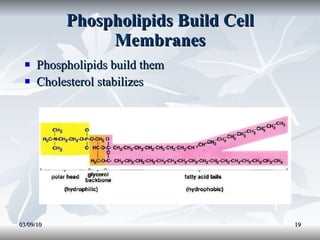
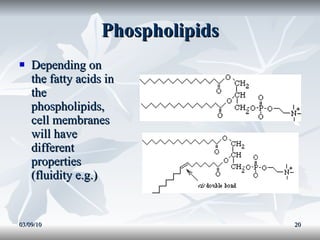
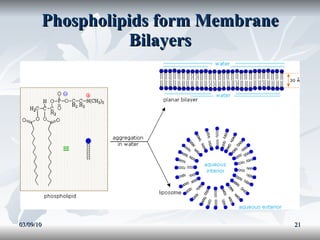
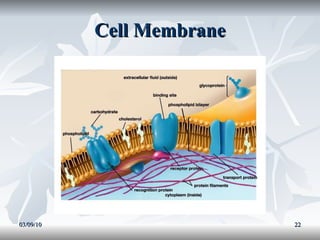
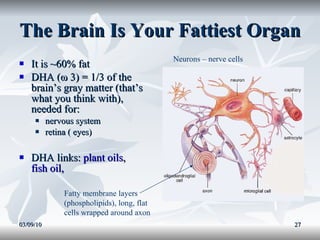
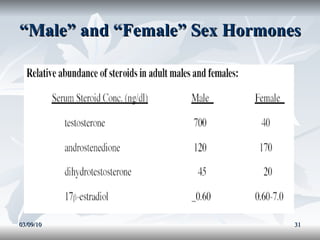
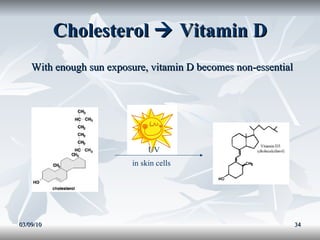
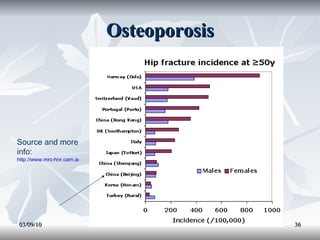
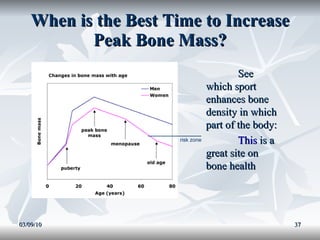
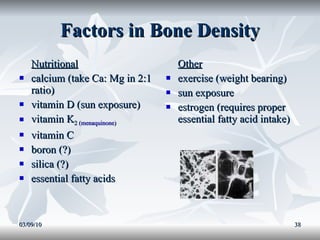
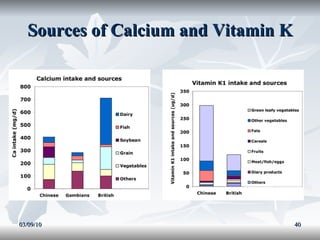
Lipids include fats, oils, and other compounds that do not dissolve in water. Fats and oils are made of triglycerides, which are composed of glycerol bonded to three fatty acid molecules. Fatty acids can be saturated, monounsaturated, or polyunsaturated. Lipids serve important functions in the body, including energy storage, insulation, hormone production, and as structural components of cell membranes.